Edited, memorised or added to reading queue
on 06-Jun-2017 (Tue)
Do you want BuboFlash to help you learning these things? Click here to log in or create user.
Flashcard 1442157038860
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itThis type of financing provides direct loans to foreign buyers at a fixed interest rate or provides guarantees for term financing offered by commercial lenders.
Original toplevel document
Government-Assisted Foreign Buyer Financing (Eximbank USA)as their small business suppliers. Creditworthy foreign buyers can obtain loans needed for purchases of U.S. goods and services, especially high-value capital goods or services and exports to large-scale projects. <span>This type of financing provides direct loans to foreign buyers at a fixed interest rate or provides guarantees for term financing offered by commercial lenders. Financing is available for medium-term (up to 5 years) and long-term (generally up to 10 years) transactions. CHARACTERISTICS OF GOVERNMENT‑ASSISTED FORE
Flashcard 1442899954956
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itEn un sentido estrecho, la gramática sólo estudia las unidades significativas y su combinatoria. Comprende dos partes: la morfología y la sintaxis.
Original toplevel document
Open itEn un sentido estrecho, la gramática sólo estudia las unidades significativas y su combinatoria. Comprende dos partes: la morfología y la sintaxis. La [16] primera se ocupa de la estructura interna de las palabras. Su unidad de análisis es el morfema, la unidad significativa mínima. Una palabra como libro no es segmentable en par
Flashcard 1448749698316
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Open it
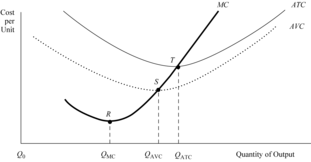
d MC in the short run. The marginal cost curve intersects both the ATC and AVC at their respective minimum points. This occurs at points S and T, which correspond to Q AVC and Q ATC , respectively. Mathematically, when <span>marginal cost is less than average variable cost, AVC will be decreasing . The opposite occurs when MC is greater than AVC. The same relationship holds true for MC and ATC . ATC declines when MC is less than ATC. ATC increases as MC exceeds ATC
Flashcard 1475135278348
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itA statement of retained earnings can be viewed as a component of the statement of stockholders’ equity, which shows all changes to owners’ equity, both changes resulting from retained earnings and changes resulting fro
Original toplevel document
3.2. Accounting Equationsements noted previously serve as the inputs for equations that underlie the financial statements. This section describes the equations for three of the financial statements: balance sheet, income statement, and statement of retained earnings. <span>A statement of retained earnings can be viewed as a component of the statement of stockholders’ equity, which shows all changes to owners’ equity, both changes resulting from retained earnings and changes resulting from share issuance or repurchase. The fourth basic financial statement, the statement of cash flows, will be discussed in a later section. The balance sheet presents a company’s financial position at a pa
Flashcard 1478168022284
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itAn important first step in analyzing financial statements is identifying the types of accruals and valuation entries in an entity’s financial statements. Most of these items will be noted in the critical accounting policies/estimates section of management’s discussion and analysi
Original toplevel document
7. USING FINANCIAL STATEMENTS IN SECURITY ANALYSISions of balance sheet accounts. Accruals and valuation entries require considerable judgment and thus create many of the limitations of the accounting model. Judgments could prove wrong or, worse, be used for deliberate earnings manipulation. <span>An important first step in analyzing financial statements is identifying the types of accruals and valuation entries in an entity’s financial statements. Most of these items will be noted in the critical accounting policies/estimates section of management’s discussion and analysis (MD&A) and in the significant accounting policies footnote, both found in the annual report. Analysts should use this disclosure to identify the key accruals and valuations for a company. The analyst needs to be aware, as Example 4 shows, that the manipulation of earnings and a
Flashcard 1598492380428
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itDisposal of a portion of a business component does not qualify as discontinued operations. Instead, this is recorded as an unusual or infrequent item.
Original toplevel document
Subject 6. Non-Recurring Items and Non-Operating Itemsf analysis, an important issue is to assess whether non-recurring items are really "non-recurring," regardless of their accounting labels. There are four types of non-recurring items in an income statement. <span>1. Discontinued operations Discontinued operations are not a component of persistent or recurring net income from continuing operations. To qualify, the assets, results of operations, and investing and financing activities of a business segment must be separable from those of the company. The separation must be possible physically and operationally, and for financial reporting purposes. Any gains or disposal will not contribute to future income and cash flows, and therefore can be reported only after disposal, that is - when realized. Subsidiaries and investees also qualify as separate components. Disposal of a portion of a business component does not qualify as discontinued operations. Instead, this is recorded as an unusual or infrequent item. 2. Extraordinary items Extraordinary items are BOTH unusual in nature AND infrequent in occurrence, and material in amount. They must be reported separately (b
Flashcard 1602809367820
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itulation plus the additional shares of common stock that would be issued upon conversion of the preferred. Thus, the formula to calculate diluted EPS using the if-converted method for preferred stock is: Equation (2) <span>Diluted EPS Net income ___________________________________ (Weighted average number of shares outstanding + New common shares that would have been issued at conversion) A diluted EPS calculation using the if-converted method for preferred stock is provided in Example 15. <span><body><html>
Original toplevel document
Earnings Per Shareincome) from continuing operations.46 Similar presentation is required under US GAAP.47 This section outlines the calculations for EPS and explains how the calculation differs for a simple versus complex capital structure. <span>Simple versus Complex Capital Structure A company’s capital is composed of its equity and debt. Some types of equity have preference over others, and some debt (and other instruments) may be converted into equity. Under IFRS, the type of equity for which EPS is presented is referred to as ordinary. Ordinary shares are those equity shares that are subordinate to all other types of equity. The ordinary shareholders are basically the owners of the company—the equity holders who are paid last in a liquidation of the company and who benefit the most when the company does well. Under US GAAP, this ordinary equity is referred to as common stock or common shares , reflecting US language usage. The terms “ordinary shares,” “common stock,” and “common shares” are used interchangeably in the following discussion. When a company has issued any financial instruments that are potentially convertible into common stock, it is said to have a complex capital structure. Examples of financial instruments that are potentially convertible into common stock include convertible bonds, convertible preferred stock, employee stock options, and warrants.48 If a company’s capital structure does not include such potentially convertible financial instruments, it is said to have a simple capital structure. The distinction between simple versus complex capital structure is relevant to the calculation of EPS because financial instruments that are potentially convertible into common stock could, as a result of conversion or exercise, potentially dilute (i.e., decrease) EPS. Information about such a potential dilution is valuable to a company’s current and potential shareholders; therefore, accounting standards require companies to disclose what their EPS would be if all dilutive financial instruments were converted into common stock. The EPS that would result if all dilutive financial instruments were converted is called diluted EPS . In contrast, basic EPS is calculated using the reported earnings available to common shareholders of the parent company and the weighted average number of shares outstanding. Companies are required to report both basic and diluted EPS. For example, Danone reported basic EPS (“before dilution”) and diluted EPS (“after dilution”) of €2.57 for 2009, somewhat lower than 2008. Kraft reported basic EPS of $2.04 and diluted EPS of $2.03 for 2009, much higher than basic and diluted EPS (from continuing operations) of $1.22 and $1.21 for 2008. (The EPS information appears at the bottom of Danone’s and Kraft’s income statements.) An analyst would try to determine the causes underlying the changes in EPS, a topic we will address following an explanation of the calculations of both basic and diluted EPS. <span><body><html>
Flashcard 1602910817548
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Comprehensive income
Comprehensive income includes both net income and other revenue and expense items that are excluded from the net income calculation. Comprehensive income is the sum of net income and other items that must bypass the income statement because they have not been realized, including items like an unrealized holding gain or loss from available-for-sale securities and foreign currency translation gains or losses. These items are not part of net income, yet are important enough to be included in comprehensive income, giving the user a bigger, more comprehensive picture of the organization as a wh
Comprehensive income includes both net income and other revenue and expense items that are excluded from the net income calculation. Comprehensive income is the sum of net income and other items that must bypass the income statement because they have not been realized, including items like an unrealized holding gain or loss from available-for-sale securities and foreign currency translation gains or losses. These items are not part of net income, yet are important enough to be included in comprehensive income, giving the user a bigger, more comprehensive picture of the organization as a wh
Flashcard 1603199438092
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 3. Financial Instruments: Financial Assets and Financial Liabilities
ts with fair value exposures hedged by derivatives. Financial liabilities: Derivatives. Financial liabilities held for trading. Non-derivative instruments with fair value exposures hedged by derivatives. <span>Measured at cost or amortized cost: Financial assets: Unlisted instruments (there is no reliable valuation measure). Held-to-maturity investments (bonds). Loans and receivables. Financial liabilities: All other liabilities (such as bonds payable or notes payable). Accounting for Gains and Losses on Marketable Securities Held-to-maturity securities. Debt securities that management intends to hold to their m
ts with fair value exposures hedged by derivatives. Financial liabilities: Derivatives. Financial liabilities held for trading. Non-derivative instruments with fair value exposures hedged by derivatives. <span>Measured at cost or amortized cost: Financial assets: Unlisted instruments (there is no reliable valuation measure). Held-to-maturity investments (bonds). Loans and receivables. Financial liabilities: All other liabilities (such as bonds payable or notes payable). Accounting for Gains and Losses on Marketable Securities Held-to-maturity securities. Debt securities that management intends to hold to their m
Flashcard 1612594941196
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itAn important first step in analyzing financial statements is identifying the types of accruals and valuation entries in an entity’s financial statements. Most of these items will be noted in the critical accounting policies/estimates section of management’s discussion and analysi
Original toplevel document
7. USING FINANCIAL STATEMENTS IN SECURITY ANALYSISions of balance sheet accounts. Accruals and valuation entries require considerable judgment and thus create many of the limitations of the accounting model. Judgments could prove wrong or, worse, be used for deliberate earnings manipulation. <span>An important first step in analyzing financial statements is identifying the types of accruals and valuation entries in an entity’s financial statements. Most of these items will be noted in the critical accounting policies/estimates section of management’s discussion and analysis (MD&A) and in the significant accounting policies footnote, both found in the annual report. Analysts should use this disclosure to identify the key accruals and valuations for a company. The analyst needs to be aware, as Example 4 shows, that the manipulation of earnings and a
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1612610145548
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1612621679884
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itBy definition, the opposite of the word comprehensive is incomplete, empty, limited or narrow. Some may say it is exclusive of something or unfinished in some way. So it is not surprising that when accountants speak of detail, they referen
Original toplevel document
Comprehensive Income Definition | Investopediart comprehensive income in a separate statement from income resulting from owner changes in equity but have the option of providing information in a single statement. BREAKING DOWN 'Comprehensive Income' <span>By definition, the opposite of the word comprehensive is incomplete, empty, limited or narrow. Some may say it is exclusive of something or unfinished in some way. So it is not surprising that when accountants speak of detail, they reference the word comprehensive. The more comprehensive a financial statement, the more detailed. Comprehensive Income One of the most important financial statements is the income statement. It provides an overview of sales and expenses, including taxes and interest. At the end
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Python (Programmiersprache) – Wikipedia
gen: CPython, Jython, IronPython, PyPy Beeinflusst von: ABC, Algol 68, Modula-3, Icon, C, C++, Perl, Java, Lisp, Haskell Beeinflusste: Ruby, Boo, Groovy, Cython, JavaScript, Swift Lizenz: Python-Software-Foundation-Lizenz [1] www.python.org <span>Python ([ˈpaɪθn̩], [ˈpaɪθɑn], auf Deutsch auch [ˈpyːtɔn]), ist eine universelle, üblicherweise interpretierte höhere Programmiersprache. [2] Sie will einen gut lesbaren, knappen Programmierstil fördern. [3] So werden beispielsweise Blöcke nicht durch geschweifte Klammern, sondern durch Einrückungen strukturiert. Python u
Flashcard 1612672797964
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itPython ([ ˈpaɪθn̩ ], [ ˈpaɪθɑn ], auf Deutsch auch [ ˈpyːtɔn ]), ist eine universelle, üblicherweise interpretierte höhere Programmiersprache. [2]
Original toplevel document
Python (Programmiersprache) – Wikipediagen: CPython, Jython, IronPython, PyPy Beeinflusst von: ABC, Algol 68, Modula-3, Icon, C, C++, Perl, Java, Lisp, Haskell Beeinflusste: Ruby, Boo, Groovy, Cython, JavaScript, Swift Lizenz: Python-Software-Foundation-Lizenz [1] www.python.org <span>Python ([ˈpaɪθn̩], [ˈpaɪθɑn], auf Deutsch auch [ˈpyːtɔn]), ist eine universelle, üblicherweise interpretierte höhere Programmiersprache. [2] Sie will einen gut lesbaren, knappen Programmierstil fördern. [3] So werden beispielsweise Blöcke nicht durch geschweifte Klammern, sondern durch Einrückungen strukturiert. Python u
Flashcard 1612674632972
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itPython ([ ˈpaɪθn̩ ], [ ˈpaɪθɑn ], auf Deutsch auch [ ˈpyːtɔn ]), ist eine universelle, üblicherweise interpretierte höhere Programmiersprache. [2]
Original toplevel document
Python (Programmiersprache) – Wikipediagen: CPython, Jython, IronPython, PyPy Beeinflusst von: ABC, Algol 68, Modula-3, Icon, C, C++, Perl, Java, Lisp, Haskell Beeinflusste: Ruby, Boo, Groovy, Cython, JavaScript, Swift Lizenz: Python-Software-Foundation-Lizenz [1] www.python.org <span>Python ([ˈpaɪθn̩], [ˈpaɪθɑn], auf Deutsch auch [ˈpyːtɔn]), ist eine universelle, üblicherweise interpretierte höhere Programmiersprache. [2] Sie will einen gut lesbaren, knappen Programmierstil fördern. [3] So werden beispielsweise Blöcke nicht durch geschweifte Klammern, sondern durch Einrückungen strukturiert. Python u
Flashcard 1612675681548
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itPython ([ ˈpaɪθn̩ ], [ ˈpaɪθɑn ], auf Deutsch auch [ ˈpyːtɔn ]), ist eine universelle, üblicherweise interpretierte höhere Programmiersprache. [2]
Original toplevel document
Python (Programmiersprache) – Wikipediagen: CPython, Jython, IronPython, PyPy Beeinflusst von: ABC, Algol 68, Modula-3, Icon, C, C++, Perl, Java, Lisp, Haskell Beeinflusste: Ruby, Boo, Groovy, Cython, JavaScript, Swift Lizenz: Python-Software-Foundation-Lizenz [1] www.python.org <span>Python ([ˈpaɪθn̩], [ˈpaɪθɑn], auf Deutsch auch [ˈpyːtɔn]), ist eine universelle, üblicherweise interpretierte höhere Programmiersprache. [2] Sie will einen gut lesbaren, knappen Programmierstil fördern. [3] So werden beispielsweise Blöcke nicht durch geschweifte Klammern, sondern durch Einrückungen strukturiert. Python u
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Python (Programmiersprache) – Wikipedia
des angegebenen Programmiercodes Weitere Grafiken[Bearbeiten | Quelltext bearbeiten] [imagelink] Bunter Kreis [imagelink] Stern [imagelink] Die Turtle zeichnet ein Quadrat <span>Beispiel[Bearbeiten | Quelltext bearbeiten] Als nicht triviales Beispiel sei hier der kompakte Sortieralgorithmus Quicksort angegeben: def quicksort(liste): if len(liste) <= 1: return liste pivotelement = liste.pop() links = [element for element in liste if element < pivotelement] rechts = [element for element in liste if element >= pivotelement] return quicksort(links) + [pivotelement] + quicksort(rechts) Hier ermöglicht insbesondere die Listennotation für die Variablen links und rechts eine kompakte Darstellung. Zum Vergleich eine iterative Formulierung dieser zwei Zeilen: ... links, rechts = [], [] # leere Listen für links und rechts anlegen pivotelement = liste.pop() # das letzte Element aus der Liste nehmen als Referenz for element in liste: # die restlichen Elemente der Liste durchlaufen ... if element < pivotelement: # ... und mit dem pivotelement vergleichen links .append(element) # wenn kleiner: dann an linke Liste anhängen else: rechts.append(element) # ansonsten wenn nicht kleiner: dann an rechte Liste anhängen ... Dies ist nur ein Beispiel für die gesparte Schreibarbeit durch die Listennotation. Tatsächlich ist in diesem Fall die iterative Formulierung die schnellere, da pro Durchgang nur
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itBeispiel [ Bearbeiten | Quelltext bearbeiten ] Als nicht triviales Beispiel sei hier der kompakte Sortieralgorithmus Quicksort angegeben: def quicksort ( liste ): if len ( liste ) <= 1 : return liste pivotelement = liste . pop () links = [ element for element in liste if element < pivotelement ] rechts = [ elemen
Original toplevel document
Python (Programmiersprache) – Wikipediades angegebenen Programmiercodes Weitere Grafiken[Bearbeiten | Quelltext bearbeiten] [imagelink] Bunter Kreis [imagelink] Stern [imagelink] Die Turtle zeichnet ein Quadrat <span>Beispiel[Bearbeiten | Quelltext bearbeiten] Als nicht triviales Beispiel sei hier der kompakte Sortieralgorithmus Quicksort angegeben: def quicksort(liste): if len(liste) <= 1: return liste pivotelement = liste.pop() links = [element for element in liste if element < pivotelement] rechts = [element for element in liste if element >= pivotelement] return quicksort(links) + [pivotelement] + quicksort(rechts) Hier ermöglicht insbesondere die Listennotation für die Variablen links und rechts eine kompakte Darstellung. Zum Vergleich eine iterative Formulierung dieser zwei Zeilen: ... links, rechts = [], [] # leere Listen für links und rechts anlegen pivotelement = liste.pop() # das letzte Element aus der Liste nehmen als Referenz for element in liste: # die restlichen Elemente der Liste durchlaufen ... if element < pivotelement: # ... und mit dem pivotelement vergleichen links .append(element) # wenn kleiner: dann an linke Liste anhängen else: rechts.append(element) # ansonsten wenn nicht kleiner: dann an rechte Liste anhängen ... Dies ist nur ein Beispiel für die gesparte Schreibarbeit durch die Listennotation. Tatsächlich ist in diesem Fall die iterative Formulierung die schnellere, da pro Durchgang nur
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Python (Programmiersprache) – Wikipedia
ython ab Version 2.4 im Standardsprachumfang enthalten. Diese Datenstruktur kann beliebige (paarweise unterschiedliche) Objekte aufnehmen und stellt Mengenoperationen wie beispielsweise Durchschnitt, Differenz und Vereinigung zur Verfügung. <span>Objektsystem[Bearbeiten | Quelltext bearbeiten] Das Typsystem von Python ist auf das Klassensystem abgestimmt. Obwohl die eingebauten Datentypen genau genommen keine Klassen sind, können Klassen von einem Typ erben. So kann man die Eigenschaften von Zeichenketten oder Wörterbüchern erweitern – auch von Ganzzahlen. Python unterstützt Mehrfachvererbung. Die Sprache unterstützt direkt den Umgang mit Typen und Klassen. Typen können ausgelesen (ermittelt) und verglichen werden und verhalten sich wie Objekte – in Wirklichkeit sind die Ty
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itObjektsystem [ Bearbeiten | Quelltext bearbeiten ] Das Typsystem von Python ist auf das Klassensystem abgestimmt. Obwohl die eingebauten Datentypen genau genommen keine Klassen sind, können Klass
Original toplevel document
Python (Programmiersprache) – Wikipediaython ab Version 2.4 im Standardsprachumfang enthalten. Diese Datenstruktur kann beliebige (paarweise unterschiedliche) Objekte aufnehmen und stellt Mengenoperationen wie beispielsweise Durchschnitt, Differenz und Vereinigung zur Verfügung. <span>Objektsystem[Bearbeiten | Quelltext bearbeiten] Das Typsystem von Python ist auf das Klassensystem abgestimmt. Obwohl die eingebauten Datentypen genau genommen keine Klassen sind, können Klassen von einem Typ erben. So kann man die Eigenschaften von Zeichenketten oder Wörterbüchern erweitern – auch von Ganzzahlen. Python unterstützt Mehrfachvererbung. Die Sprache unterstützt direkt den Umgang mit Typen und Klassen. Typen können ausgelesen (ermittelt) und verglichen werden und verhalten sich wie Objekte – in Wirklichkeit sind die Ty