Dizziness/Vertigo
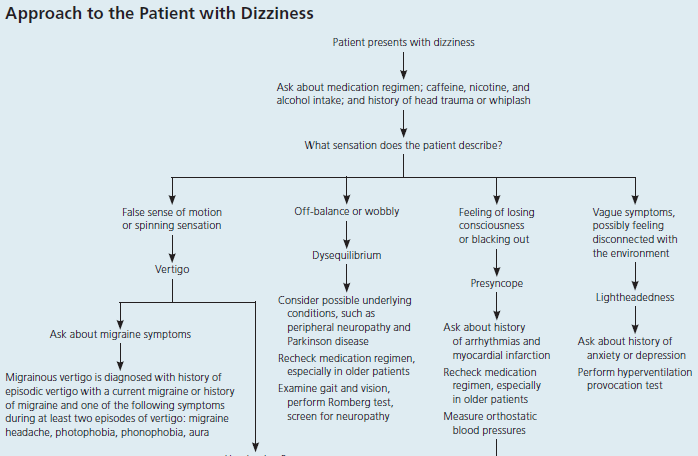
Approach to patient with Dizziness
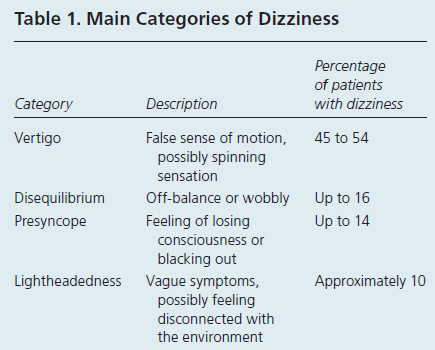
Subjective
-
“Does it feel like either the room is spinning or that you are spinning?” and/or “Is it triggered or worsened by turning your head or rolling over in bed?”
-
Yes = vertigo
-
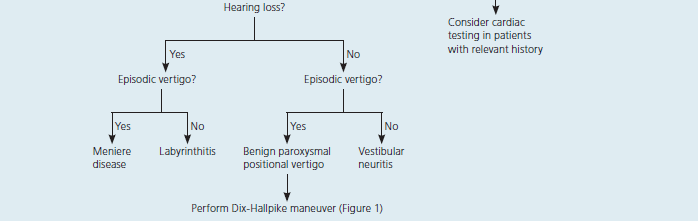
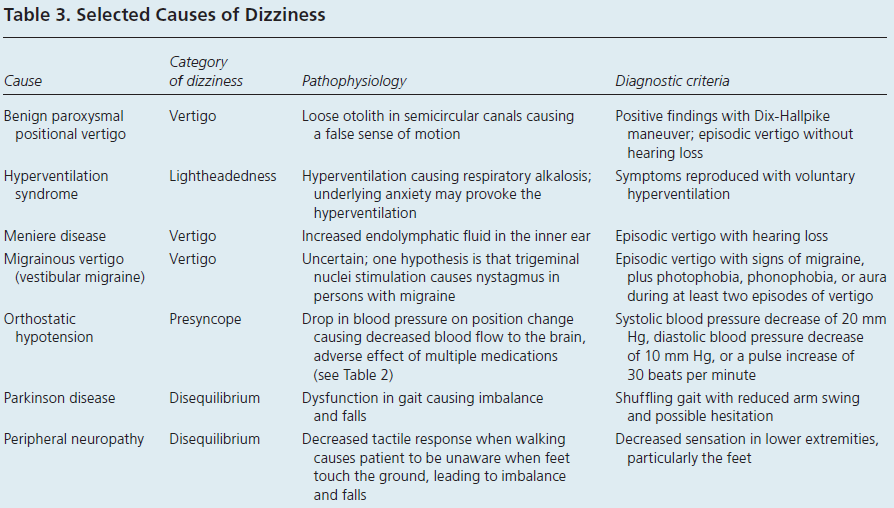
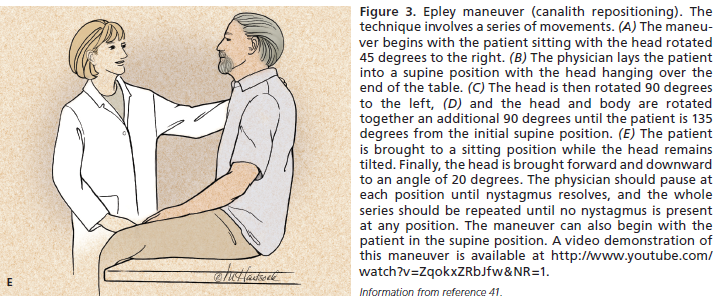
BENIGN PAROXYSMAL POSITIONAL VERTIGO (most common)
-
brief, recurrent episodes (seconds to minutes), +/- nausea and vomiting
-
-
Vestibular Neuritis
-
rapid onset, severe, persistent (days), N/V, imbalance
-
-
Ménière’s Disease
-
recurrent episodes (minutes to hours), fluctuating hearing loss, tinnitus, and sensation of aural fullness
-
-
Vestibular Toxicity
-
aminoglycosides (eg. gentamycin), loop diuretics, ASA, NSAIDs, amiodarone, quinine, cisplatin
-
-
-
No = other forms of dizziness
-
Presyncopal Dizziness – “feels like nearly fainting or blacking out”
-
ECG
-
Triggered by exertion? Chest pain/palpitations? Known structural heart dz? FmHx of sudden death? Abnormal ECG? (if pt stable, fax ECG for urgent advice)
-
If yes to any, suspect cardiac etiology. Refer to Emergency
-
If no, orthostatic hypotension?
-
Yes = investigate underlying cause. meds/alcohol? Consider CBC/lytes
-
No = likely vasovagal/situational etiology. If recurrent episodes or pt is at risk of injury, consider referral for tilt test (+/- carotid sinus massage if >40 yo)
-
-
-
-
Disequilibrium Dizziness – “unsteadiness while walking”
-
Often multifactorial, common in elderly, risk of falls. Complete neuro and MSK exams to rule out peripheral neuropathy, Parkinsonism, MSK d/o, CVA, etc
-
-
Nonspecific Dizziness – “woozy”, “giddy”, “light-headed”
-
DDx: hypoglycemic (glucose), thyroid disease (TSH), pregnancy (β-HCG), meds, psychiatric disorders, alcohol/drugs, menstruation, previous head trauma
-
-
-
-
Ask about: onset, duration, nausea, vomiting, hearing loss, tinnitus, headache, imbalance, aural fullness, ear pain, rash, facial paralysis, medications

Objective
Assessment
-
viral labyrinthitis
-
benign positional vertigo
-
Eustachian tube dysfunction (often with serous otitis media)
-
Meniere's disease
-
Vertebrobasilar insufficiency (in the elderly with vasculopathy)
-

Plan
Summary
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |