Do you want BuboFlash to help you learning these things? Or do you want to add or correct something? Click here to log in or create user.
Subject 1. Utility Theory
#cfa #cfa-level-1 #economics #has-images #microeconomics #reading-14-demand-and-supply-analysis-consumer-demand
Utility refers to the total satisfaction received by a person from consuming a good or service.
- Completeness. A person can compare any two bundles, A and B, in such a way that it leads to one of the three following results: (i) A is preferred to B, (ii) B is preferred to A, or (iii) A and B are the same (they are indifferent).
- Transitivity. Consider any three bundles A, B, and C. If a person prefers A to B and also prefers B to C, she or he must prefer A to C.
- Nonsatiation. Consider two bundles, A and B. A has more than B in every commodity and yet all these commodities are not economic "bads"; then a person will rank A higher than B.
Utility theory is a quantitative model of consumer preferences and is based on the above axioms. Consumer preferences can be represented by an ordinal utility function:
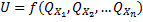
This is a mathematical expression that shows the relationship between utility values and every possible bundle of goods.
This ordinal - not cardinal - utility captures only ranking and not strength of preferences.
If you want to change selection, open original toplevel document below and click on "Move attachment"
Summary
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Details
Discussion
Do you want to join discussion? Click here to log in or create user.