Do you want BuboFlash to help you learning these things? Or do you want to add or correct something? Click here to log in or create user.
Subject 4. Shutdown Analysis
#cfa #cfa-level #economics #has-images #microeconomics #reading-15-demand-and-supply-analysis-the-firm
For a price taker (a firm in a perfectly competitive market):
Profit = Total Revenue - Total Cost = (Price - Average Total Cost) x Quantity
However, maximum profit is not always a positive economic profit. In the short run, the firm might break even (making a zero economic profit), make an economic profit, or incur an economic loss.
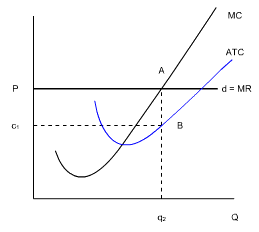
1. If the price equals minimum average total cost, the firm breaks even and makes a normal profit.
2. The ATC of producing each of q2 units is labeled as c1.

c1BAP indicates the economic profit being made by this firm. The firm is making a profit since the price per unit exceeds the ATC per unit and the total revenue exceeds the total costs.
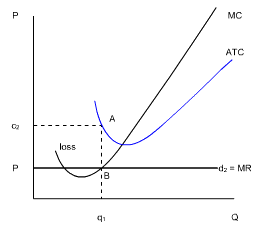
3. What would happen to profits if the price fell to below the ATC curve?

The firm therefore will produce q1 units of output, as shown where MC = MR. At q1, the firm can only charge P per unit, and yet the ATC per unit is higher, at c2. This means that the firm is making a total economic loss equal to the shaded area, PBAc2, or the distance of c2 to P per unit.
If the firm's current sales revenues can cover its variable cost, and the firm anticipates that the lower market price is temporary, it will continue to operate and will face short-run economic losses. It will produce the quantity at which MC = P. This option is better than "shut down" since the firm is able to cover its variable costs and pay some of its fixed costs. If it were to shut down, the firm would lose the entire amount of its fixed costs.

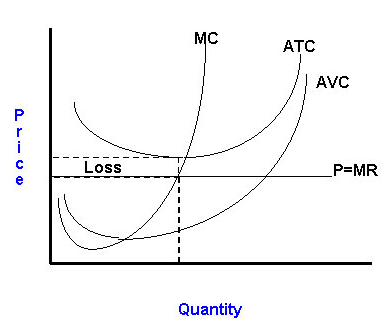
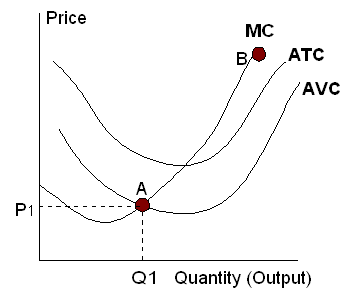
The shutdown point is the output and price at which the firm just covers its total variable cost.
- This point is where average variable cost is at its minimum.
- It is also the point at which the marginal cost curve crosses the average variable cost curve.
- At the shutdown point, the firm is indifferent between producing and shutting down temporarily. It incurs a loss equal to total fixed cost from either action.
If the market price is below the firm's average variable cost, a temporary shutdown is preferable to short-run operation. If the firm continues to operate, operating losses merely add to losses resulting from the firm's fixed costs. Shutdown will reduce losses.

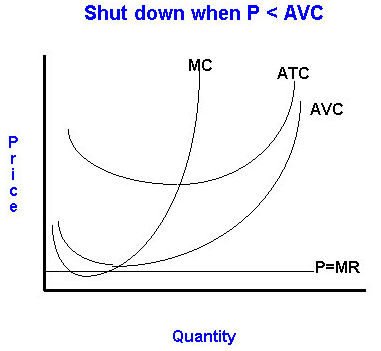
The Firm's Short-Run Supply Curve
The price taker that intends to stay in business will maximize profits (or minimize losses) when it produces the output level at which P = MC AND variable costs are covered. At this output level, the price taker can maximize its profits or minimizes its losses. Therefore, the portion of the firm's short-run marginal cost curve that lies above its average variable cost is the short-run curve of the firm.

In the above graph, if price is below P1, the firm should be shut down.
If you want to change selection, open original toplevel document below and click on "Move attachment"
Summary
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Details
Discussion
Do you want to join discussion? Click here to log in or create user.