Do you want BuboFlash to help you learning these things? Or do you want to add or correct something? Click here to log in or create user.
Subject 3. Unemployment
#cfa #cfa-level-1 #economics #has-images #macroeconomics #reading-18-understanding-business-cycles
The U.S. Census Bureau conducts monthly surveys to determine the status of the labor force in the U.S.
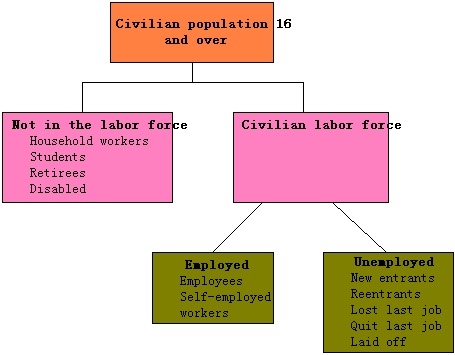

To be counted as unemployed, a person must be actively seeking employment but currently without work.
The unemployment rate is the percentage of persons in the labor force who are unemployed. This is a key parameter of conditions in the aggregate labor market.
There are special categories of unemployment, such as:
- Long-term unemployed: people who are unemployed because they do not have the skills required by the openings or reside far from the jobs.
- Frictionally unemployed: people who are not working because they are in between jobs.
Unemployment rate tends to be a lagging instead of a leading indicator of the economy, confirming but not foreshadowing long-term market trends. It tends to peak after the trough of the business cycle and bottom after the peak of the business cycle. This is because:
- The employment data is compiled afterwards.
- Employers are reluctant to lay people off when the economy turns bad. For large companies, it can take months to put together a layoff plan. Companies are even more reluctant to hire new workers until they are sure the economy is well into the expansion phase of the business cycle.
Underemployed is a measure of employment and labor utilization in the economy. It looks at how well the labor force is being utilized in terms of skills, experience, and availability to work.
Discouraged workers believe that continuing the job search is fruitless and thus give up looking for a job. They wish to work but because they are not actively searching for work they are excluded from the labor force and are not counted in the unemployment rate. The unemployment rate may fall during recessions as discouraged workers leave the labor force.
Voluntary unemployment refers to the number of persons in an economy without jobs because they choose to be unemployed.
Analysts also use other measures to get a better picture of the employment cycle. These measures include the size of payrolls, hours worked, and the use of temporary workers.
If you want to change selection, open original toplevel document below and click on "Move attachment"
Summary
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Details
Discussion
Do you want to join discussion? Click here to log in or create user.