Do you want BuboFlash to help you learning these things? Or do you want to add or correct something? Click here to log in or create user.
Subject 4. Forward Calculations
#cfa #cfa-level-1 #economics #economics-in-a-global-context #has-images #reading-21-currency-exchange-rates
Spot and Forward Exchange Rates
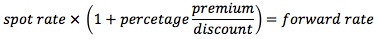
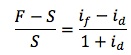
In the spot market, currencies are traded for immediate delivery. In the forward market, contracts are made to buy or sell currencies for future delivery.
In a typical forward transaction, a U.S. company buys textiles from England with payment of £1 million due in 90 days. The importer is thus short £ - that is, it owes £ for future delivery. Suppose the present price of £ is $1.71. Over the next 90 days, however, £ might rise against the U.S. dollar, raising the U.S. dollar cost of the textiles. The importer can guard against this exchange risk by immediately negotiating a 90-day forward contract with a bank at a price, say, £:$ = 1.72. In 90 days the bank will give the importer £1 million and the importer will give the bank 1.72 million U.S. dollars. By going long in the forward market, the importer is able to convert a short underlying position in £ to a zero net exposed position.
Three points are worth noting:
- The gain or loss on the forward contract is unrelated to the current spot rate of £:$ = 1.71.
- The forward contract gain or loss exactly offsets the change in the U.S. dollar cost of the textile order that is associated with movements in the GBP's value.
- The forward contract is not an option contract. Both parties must perform the agreed-on behavior.
Forward exchange rates are often quoted as a premium, or discount, to the spot exchange rate. A base currency is at a forward discount if the forward rate is below the spot rate, whereas a forward premium exists if the forward rate is above the spot rate.
For example, if the one-month forward exchange rate is $:€ = 0.8020 and the spot rate is $:€ = 0.8000, the $ quotes with a premium of 0.0020 €/$. In the language of currency traders, the $ is "strong" relative to the €.
Consequently, when a trader announces that a currency quotes at a premium (discount), the premium (discount) should be added to (subtracted from) the spot exchange rate to obtain the value of the forward exchange rate.
Occasionally, forward rates are presented in terms of percentages relative to the spot rate:
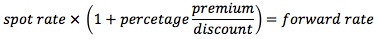
Interest Rate Parity
According the interest rate parity (IRP) theory, the currency of the country with a lower interest rate should be at a forward premium in terms of the currency of the country with the higher rate. In an efficient market with no transaction costs, the interest differential should be (approximately) equal to the forward differential.
The exact relationship between the forward rate and the spot rate of two currencies is as follows:
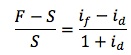
- The exchange rate is d:f = S for the spot rate and F for the forward rate.
- Both id and if are periodic interest rates, which should be computed as i = annual interest rate x number of days till the forward contract expires / 360.
- It is assumed that there are no transaction costs.
Example
Suppose that the annual interest rate in the U.S. is 5%. The spot exchange rate £:$ = 1.50 and the 180-day forward rate is £:$ = 1.45. The U.S. periodic interest rate (180) is: 0.05 x 180 / 360 = 0.025. If interest rate parity holds:
(1.45 - 1.5)/1.5 = (0.025 - iUK)/(1+iUK) => iUK = 6%
Therefore, the annual UK interest rate is approximately 12%.
Similarly, you can calculate the forward rate based on the two interest rates and the spot rate.
Interest parity ensures that the return on a hedged (or "covered") foreign investment will just equal the domestic interest rate in investments of identical risk, thereby eliminating the possibility of having a money machine. When this condition holds, the covered interest differential - the difference between the domestic interest rate and the hedged foreign rate - is zero.
If the difference is not zero, covered interest arbitrage will generate profits without any risk or investment.
For example, suppose the interest rate on GBP (£) is 12% in London and the interest rate on a comparable U.S. dollar investment in New York is 7%. The pound spot rate is £:$ = 1.75 and the one-year forward rate is £:$ = 1.68. These rates imply a forward discount on sterling of 4% [(1.68 - 1.75)/1.75] and a covered yield on sterling approximately equal to 8% (12% - 4%). Suppose the borrowing and lending rates are identical and the bid-ask spread in the spot and forward markets is zero. An arbitrageur will:
- Borrow $1,000,000 in New York at 7%;
- Convert the $1,000,000 to £571,428.57 at £1 = $1.75;
- Invest the £571,428.57 in London at 12% for one year, and sell £640,000 forward at a rate of £1 = $1.68 for delivery in one year.
- At the end of the year, collect £640,000 from his investment in London, deliver it to the bank's foreign exchange department in return for $1,075,200, and use $1,070,000 to repay the loan in New York. The arbitrageur will earn $5,200 on this set of transactions with no investment at all.
If you want to change selection, open original toplevel document below and click on "Move attachment"
Summary
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Details
Discussion
Do you want to join discussion? Click here to log in or create user.