Do you want BuboFlash to help you learning these things? Or do you want to add or correct something? Click here to log in or create user.
Subject 2. Cost of Debt and Preferred Stock
#cfa #cfa-level-1 #corporate-finance #cost-of-capital #has-images
Capital components are the types of capital used by firms to raise fund. They include the items on the right side of a firm's balance sheet (debt, preferred stock, and common equity). Any increase in the firm's total assets must be financed by one or more of these capital components.
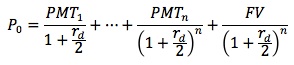
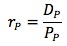
The cost of debt is defined as the cost to the firm in terms of the interest rate that it pays for ordinary debt (rd) less the tax savings that are achieved. Interest on debt is tax-deductible and therefore to calculate the cost of debt the tax benefit is deducted.
Two methods to estimate the before-tax cost of debt (rd) are discussed.
Yield-to-Maturity Approach
This approach uses the familiar bond valuation equation. Assuming semi-annual coupon payments, the equation is:
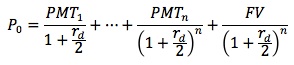
The six-month yield (rd/2) is derived and then annualized to arrive at the before-tax cost of debt, rd.
See Reading 54 for details of the yield-to-maturity approach.
Debt-Rating Approach
This approach can be used if there isn't a reliable market price for a firm's debt. Based on the company's debt rating, the before-tax cost of debt is estimated by using the yield on comparably rated bonds for maturities that are a close match to those of the firm's existing debt.
For example, assume that:
- A firm's debt has an average maturity of 5 years.
- Its credit rating is AAA.
- The yield on debt with the same debt rating and similar maturity is 6%.
- The marginal tax rate is 30%.
Then the company's after-tax cost of debt is 6% x (1 - 30%) = 4.2%.
Other factors, such as debt seniority and security, may complicate the calculation, so analysts must take care when determining the comparable debt rating and yield.
Issues in Estimating the Cost of Debt
- Fixed-rate debt versus floating-rate debt
Estimating the cost of floating-rate debt is difficult because the cost depends not only on the current yield but also on the future yields. The term structure of interest rates may be used to calculate an average rate. - Debt with option-like features
Be aware that some debt can have call or put options. (Valuating such debts is a topic for Level II candidates.) - Non-rated debt
The yields of a firm's debt may not be available, or a firm may not have rated bonds. - Leases
If a company uses leasing as a source of capital, the cost of these leases should be included in the cost of capital (long-term debt).
Cost of Preferred Stock
The cost of preferred stock is calculated by dividing the dollar amount of the dividend (which is normally paid on an annual basis) by the preferred stock current price.
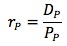
It is important to note that tax does not affect the calculation of the cost of preferred stock, since preferred dividends are not tax deductible.
If you want to change selection, open original toplevel document below and click on "Move attachment"
Summary
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Details
Discussion
Do you want to join discussion? Click here to log in or create user.