Do you want BuboFlash to help you learning these things? Or do you want to add or correct something? Click here to log in or create user.
Subject 1. Business Risk and Operating Leverage
#cfa #cfa-level-1 #corporate-finance #has-images #measures-of-leverage
Leverage
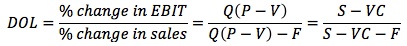
Leverage is the extent to which fixed costs are used in a company's cost structure.
- Operating leverage is the extent to which fixed operating costs (e.g., depreciation, rent) are used in a firm's operations.
- Financial leverage is the extent to which fixed-income securities (debt and preferred stock) are used in a firm's capital structure.
Leverage affects a firm's risk, as it can magnify earnings both up and down. The bigger the leverage, the more volatile the firm's future earnings and cash flows, and the greater the discount rate applied in the firm's valuation (by bondholders and stockholders).
Business Risk and its Components
Business risk is the uncertainty (variability) about projections of future operating earnings. It is the single most important determinant of capital structure. If other elements are the same, the lower a firm's business risk, the higher its optimal debt ratio.
Business risk is the combined risk of sales and operations risks.
- The sales risk is the uncertainty regarding the price and quantity of the firm's goods and services. If the demand for and the price of a firm's goods and services are stable, its sales risk is considered low.
- The operating risk is the uncertainty caused by a firm's operating cost structure. If a high percentage of operating costs are fixed costs, operating risk is considered to be high.
In general, management has more opportunity to manage and control operating risk than sales risk.
Operating Risk
A company that has high operating leverage is a company with a large proportion of fixed input costs, whereas a company with largely variable input costs is said to have low operating leverage (due to its small amount of fixed costs).
A company with a high degree of operating leverage that has a small change in sales will experience a large change in profits and rate of return. This is due to the fact that because the company has a large fixed cost component, any increase in sales will cause an even greater increase in net income, since the fixed costs have already been incurred.
In many respects operating leverage is determined by technology. High (low) operating leverage is usually associated with capital (labor) intensive industries.
The degree of operating leverage (DOL) is defined as the percentage change in EBIT (operating income) that results from a given percentage change in sales. It measures the impact of a change in sales on EBIT.
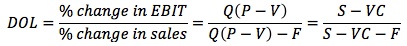
Here Q is the number of units, P is the average sales price per unit of output, V is the variable cost per unit, F is fixed operating cost, S is sales in dollars, and VC is total variable costs.
P - V is referred to as the per unit contribution margin, which is the amount that each unit contributes to covering fixed costs. S - VC is called the contribution margin.
For example, assume that a firm has sales of $100,000, variable costs of $50,000, and fixed costs of $20,000. Its DOL is (100,000 - 50,000) / (100,000 - 50,000 - 20,000) = 1.67.
If you want to change selection, open original toplevel document below and click on "Move attachment"
Summary
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Details
Discussion
Do you want to join discussion? Click here to log in or create user.