Do you want BuboFlash to help you learning these things? Or do you want to add or correct something? Click here to log in or create user.
Subject 3. Total Leverage and Breakeven Points
#cfa #cfa-level-1 #corporate-finance #has-images #measures-of-leverage
Operating leverage (first-stage leverage) affects EBIT, while financial leverage (second-stage leverage) affects earnings after interests and taxes (net income), which are the earnings available to shareholders. Financial leverage further magnifies the impact of operating leverage on earnings per share (EPS) due to changes in sales.
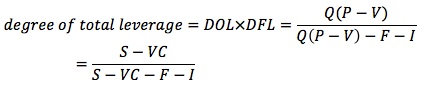
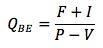
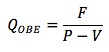
Both operating leverage and financial leverage contribute to the risk associated with a firm's future cash flows. The degree of total leverage (DTL) combines DOL and DFL, and measures the impact of a given percentage change in sales on EPS.
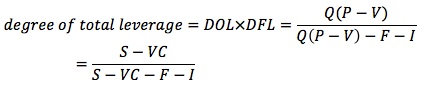
If both DOL and DFL are high, a small change in sales leads to wide fluctuations in EPS.
The breakeven point is the volume of sales at which total costs equal total revenues, causing net income to equal zero: PQ - VQ - F - I = 0. The breakeven number of units, QBE, is:
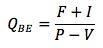
The operating breakeven point is the number of outputs at which revenues = operating costs: PQOBE = VQOBE + F. QOBE is:
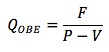
Consider a project where the fixed costs are $10,000, the variable costs are $2 per unit, the selling price per unit is $4, and the interest expense is $1,000. The breakeven sales quantity is 11,000 / (4 - 2) = 5,500 units and the operating breakeven sales quantity is 10,000 / (4 - 2) = 5,000 units.
In general, the farther unit sales are from the breakeven point for high-leverage companies, the greater the magnifying effect of this leverage.
If you want to change selection, open original toplevel document below and click on "Move attachment"
Summary
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Details
Discussion
Do you want to join discussion? Click here to log in or create user.