Do you want BuboFlash to help you learning these things? Or do you want to add or correct something? Click here to log in or create user.
Subject 4. Evaluating Accounts Receivable, Inventory and Accounts Payable Management
#cfa #cfa-level-1 #corporate-finance #has-images #working-capital-management
Accounts Receivable
How much does the firm sell each year? 5,500 x $2,000 = $11,000,000
The average collection period: [0.80 x 10] + [(1 - 0.80) x 45] = 8 + 9 = 17 days.
The accounts receivable turnover: 365 / 17 = 21.470588.
The average receivables balance: $11,000,000 / 21.470588 = $512,328.77.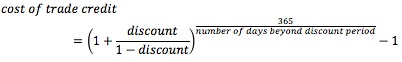
The most popular measures to evaluate receivables are receivable turnover and number of days of receivables.
Example
Build It Right, Inc. sells 5,500 curio cabinets a year at a price of $2,000 each. The credit terms of the sale are 2/10, net 45. Eighty percent of the firm's customers take the discount. What is the amount of the firm's accounts receivable?
If 80% of the customers pay in 10 days, then the other 20% must pay in 45 days.
How much does the firm sell each year? 5,500 x $2,000 = $11,000,000
The average collection period: [0.80 x 10] + [(1 - 0.80) x 45] = 8 + 9 = 17 days.
The accounts receivable turnover: 365 / 17 = 21.470588.
The average receivables balance: $11,000,000 / 21.470588 = $512,328.77.
Inventory
Managing inventory is a juggling act. Excessive stocks can place a heavy burden on the cash resources of a business. Insufficient stocks can result in lost sales, delays for customers, etc. The goal of inventory management is to identify the level of inventory which allows for uninterrupted production but reduces the investment in raw materials - and minimizes reordering costs - and hence increases cash flow.
Just-In-Time (JIT) is an inventory strategy implemented to improve a business's return on investment by reducing in-process inventory and its associated costs. Economic order quantity (also known as the EOQ Model) is a model that defines the optimal quantity to order that minimizes total variable costs required to order and hold inventory.
To evaluate inventory management analysts compute the inventory turnover ratio and the number of days of inventory. These measures are covered in Study Session 8.
Accounts Payable
Two countering forces should be considered when managing accounts payable:
- Paying too early is costly unless the company can take advantage of discounts.
- Postponing payment beyond the end of the net (credit) period is known as "stretching accounts payable" or "leaning on the trade." Possible costs are:
- Cost of the cash discount (if any) forgone.
- Late payment penalties or interest.
- Deterioration in credit rating.
Trade discounts should be evaluated by computing the implicit rate of return:
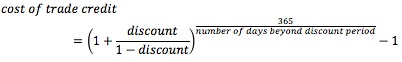
Example
Today, June 10, you purchased $5,000 worth of materials from one of your suppliers. The terms of the sale are 3/15, net 45.
- Discounted price: $5,000 x (1 - 0.03) = $4,850
- Last day to receive discount: June 10 + 15 days = June 25
- Days credit: 45 - 15 = 30
- Implicit interest: 0.03 x $5,000 = $150
- Cost of credit (effective annual rate): (1 + 0.03/0.97)365/30 - 1 = 44.86%
Analysts often use the number of days of payables and payables turnover to evaluate accounts payable management.
- Payables turnover = Cost of goods sold / Accounts payables
- Number of days of payables = # of days in period / Payables turnover = Accounts payable / Average day's purchase
If you want to change selection, open original toplevel document below and click on "Move attachment"
Summary
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Details
Discussion
Do you want to join discussion? Click here to log in or create user.