Do you want BuboFlash to help you learning these things? Or do you want to add or correct something? Click here to log in or create user.
Subject 2. Variance and Covariance of Returns
#cfa #cfa-level-1 #has-images #portfolio-management #risk-and-return-part-i
Investment is all about reward versus variability (risk). The return measures the reward of an investment and dispersion is a measure of investment risk.
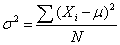
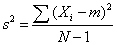
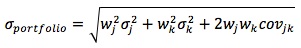
σ1 = 0.1, w1 = 0.5, σ2 = 0.1, w2 = 0.5, ρ12 = 1
Standard Deviation of Portfolio [0.52 x 0.12 + 0.52 x 0.12 + 2 x 0.5 x 0.5 x 0.01]1/2 = 0.10 (perfect correlation)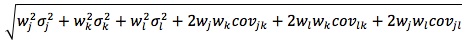
The variance is a measure of how spread out a distribution is. It is computed as the average squared deviation of each number from its mean. The formula for the variance in a population is:
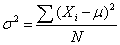
where μ is the mean and N is the number of scores.
To compute variance in a sample:
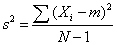
where m is the sample mean.
The formula for the standard deviation is very simple: it is the square root of the variance. It is the most commonly used measure of spread.
The standard deviation of a portfolio is a function of:
- The weighted average of the individual variances, plus
- The weighted covariances between all the assets in the portfolio.
In a two-asset portfolio:
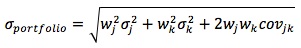
The maximum amount of risk reduction is predetermined by the correlation coefficient. Thus, the correlation coefficient is the engine that drives the whole theory of portfolio diversification.
Example with perfect positive correlation (assume equal weights):
What is the standard deviation of a portfolio (E), assuming the following data?
σ1 = 0.1, w1 = 0.5, σ2 = 0.1, w2 = 0.5, ρ12 = 1
Solution:
Cov12 = σ1 x σ2 x ρ12 = 0.1 x 0.1 x 1 = 0.01
Standard Deviation of Portfolio [0.52 x 0.12 + 0.52 x 0.12 + 2 x 0.5 x 0.5 x 0.01]1/2 = 0.10 (perfect correlation)
If there are three securities in the portfolio, its standard deviation is:
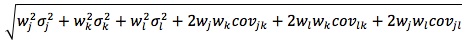
If you want to change selection, open original toplevel document below and click on "Move attachment"
Summary
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Details
Discussion
Do you want to join discussion? Click here to log in or create user.