Do you want BuboFlash to help you learning these things? Or do you want to add or correct something? Click here to log in or create user.
Subject 7. The Maturity Structure of Interest Rates
#basic-concepts #cfa #cfa-level-1 #fixed-income #has-images #reading-54-introduction-to-fixed-income-valuation
A yield curve is typically constructed on the basis of observed yields and maturities. There are different types of yield curves.
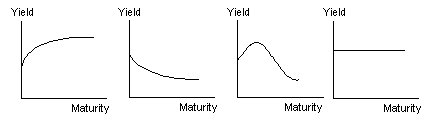
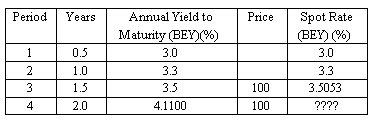
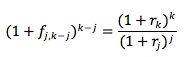
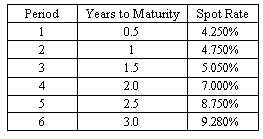

The most common type is the upward-sloping yield curve. The longer maturity issues have higher yields than the shorter maturity issues.
A spot rate is the yield on a zero-coupon bond. A series of spot rates (spot curve) can be used to discount the cash flows of a bond.
Default-free spot rates can be derived from the Treasury par yield curve by a method called bootstrapping. The basic principle of bootstrapping is that the value of a Treasury coupon security should be equal to the value of the package of zero-coupon Treasury securities that duplicate the coupon bond's cash flows.
Example
Determine the spot rate for the fourth period cash flow. The coupon rate is 4.11%, paid semi-annually.

The coupon for each period should be discounted at the corresponding spot rate.
100 = 2.055/(1+0.03/2)1 + 2.055/(1+0.033/2)2 + 2.055/(1+0.035053/2)3 + 102.055/(1+i/2)4 = 2.0246 + 1.9888 + 1.9506 + 102.055/(1+i/2)4
i = 2.0669% and the annualized spot rate is 4.1339%.
A par curve is a sequence of yields-to-maturity in which each bond is priced at par value. A par curve is obtained from a spot curve. All bonds used to derive the par curve are assumed to have the same credit risk, periodicity, currency, liquidity, tax status, and annual yields.
A forward rate refers to the interest rate on a loan beginning some time in the future. In contrast, a spot rate is the interest rate on a loan beginning immediately. For example, the two-year forward rate one year from now is 4%. This means that if you borrow a two-year loan one year from now, you will pay an interest of 4%.
A forward curve is a series of forward rates, each with the same time frame.
Forward rate calculations are usually based on a theoretical spot rate curve. They are sometimes referred to as implicit forward rates.
Given spot rates for maturities of j and k years, you can compute the forward rate (fj, k-j) that applies for the period from year j to year k using the relationship:
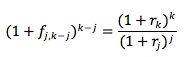
Example
Compute the annualized six-month forward rate two years from now.

In order to compute the six-month forward rate two years from now, first determine the spot rate for the fifth period (0.087) and the spot rate for the fourth period (0.0700). Then complete the following calculation: [(1 + 0.0875/2)5/(1 + 0.0700/2)4] - 1 = 7.95%.
Similarly, implied spot rates can be calculated as geometric average of forward rates.
If you want to change selection, open original toplevel document below and click on "Move attachment"
Summary
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Details
Discussion
Do you want to join discussion? Click here to log in or create user.