Do you want BuboFlash to help you learning these things? Or do you want to add or correct something? Click here to log in or create user.
Subject 9. Put-Call Parity
#cfa #cfa-level-1 #derivatives #has-images #los-59-i #reading-59-basics-of-derivative-pricing-and-valuation
First, consider an option strategy referred to as a fiduciary call, which consists of a European call and a risk-free bond that matures on the option expiration day and has a face value (X) equal to the exercise price of the call.

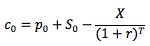
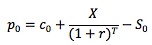
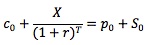
- If the price of the underlying is below X at expiration, the call expires worthless and the bond is worth X.
- If the price of the underlying is above X at expiration, the call expires and is worth ST (the underlying price) - X.
At expiration the fiduciary call will end with X or ST, whichever is greater. This combination allows protection against downside losses and is thus faithful to the notion of preserving capital.
Then, consider an option strategy known as a protective put, which consists of a European put and the underlying asset.
- If the price of the underlying is below X at expiration, the put expires and is worth X - ST and the underlying is worth ST.
- If the price of the underlying is above X at expiration, the put expires with no value and the underlying is worth ST.
So, at expiration, the protective put is worth X or ST, whichever is greater.
Thus, the fiduciary call and protective put end up with the same value. They are therefore identical combinations. To avoid arbitrage, their values today must be the same.

This equation is called put-call parity. It does not say that the puts and calls are equivalent, but it does show an equivalence (parity) of a call/bond portfolio and a put/underlying portfolio. Note that the put and call must have the same underlying, exercise price and expiration date.
By re-arranging the above equation:
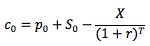
Because the right side of this equation is equivalent to a call, it is often referred to as a synthetic call. It consists of a long put, a long position in the underlying, and a short position in the risk-free bond.
There are numerous other combinations that can be constructed. For example, the put can be isolated as:
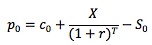
The right side is a synthetic put, which consists of a long call, a short position in the underlying, and a long position in the risk-free bond.
Another example is
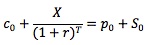
Synthetic positions enable investors to price options, because they produce the same results as options and have known prices. Consider the following example: a European call with an exercise price of $30 expires in 90 days. A European put with the same exercise price, expiration date and underlying is selling for $6. The underlying is selling for $40, and the risk-free rate is 10%. Based on the information, you can compute the value of the synthetic call: c0 = p0 + S0 - X/(1 + r)T = 6 + 40 - 30/(1 + 10%)90/365 = $16.7 (Note the time to expiration T = 90/365 = 0.2466). Since the synthetic call and the actual call have the same payoff, they must have the same price as well. Therefore, the price of the call should be $16.70.
Synthetic positions also tell how to exploit mispricing of options relative to their underlying assets. Continue with the above example. If the market price of the call is $10, the call is then underpriced. You can make a risk-free profit of $6.70 by selling the synthetic call for $16.7.
You cannot only synthesize a call or a put, but also synthesize the underlying or the bond.
Violations of put-call parity for European options:
Recall that the basic put-call parity equation is: c0 + X/(1 + r)T (fiduciary call )= p0 + S0 (protective put). Violations of put-call parity occur when one side of the equation is not equal to the other.
- An arbitrageur can buy the lower-priced side and simultaneously sell the higher-priced side, thereby making a profit on the price difference. Since the fiduciary call and protective put have the same payoff, the arbitrageur's positions will perfectly offset at expiration.
- As more and more arbitrageurs perform these transactions, the price of the lower-priced portfolio will increase and the price of the higher-priced portfolio will decrease, until put-call parity is restored.
Example
Consider the following example involving call options with an exercise price of $100 expiring in half a year (T = 0.5). The risk-free rate is 10%. The call is priced at $7.5, and the put is priced at $4.25. The underlying price is $99.
- Analysis: The left side of the put-call parity equation is c0 + X / (1 + r)T = 7.5 + 100/(1.10)0.5 = 102.85. The right side is p0 + S0 = 4.25 + 99 = 103.25. This means the protective put is overpriced.
- Our strategy: You sell the protective put. This means you sell the put and sell short the underlying. Doing so will generate a cash inflow of $103.25. You buy fiduciary call, paying out $102,85, netting a cash inflow of $0.4. At expiration, if the price of the underlying is above 100:
- The bond matures, paying $100.
- Use the $100 to exercise call, receiving the underlying.
- Deliver the underlying to cover the short sale.
- The put expires with no value.
- Net effect: no money in or out.
- What would you do if the price of the underlying is below 100 at expiration?
- So, $0.4 is received up front and nothing has to be paid out. The position is perfectly hedged and represents an arbitrage profit. The combined effects of other investors performing this transaction will result in the value of the protective put going down and/or the value of the covered call going up until the two strategies are equivalent in value.
If you want to change selection, open original toplevel document below and click on "Move attachment"
Summary
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Details
Discussion
Do you want to join discussion? Click here to log in or create user.