Do you want BuboFlash to help you learning these things? Or do you want to add or correct something? Click here to log in or create user.
#cfa-level-1 #economics #has-images #microeconomics #reading-15-demand-and-supply-analysis-the-firm #section-3-analysis-of-revenue-costs-and-profit #study-session-4
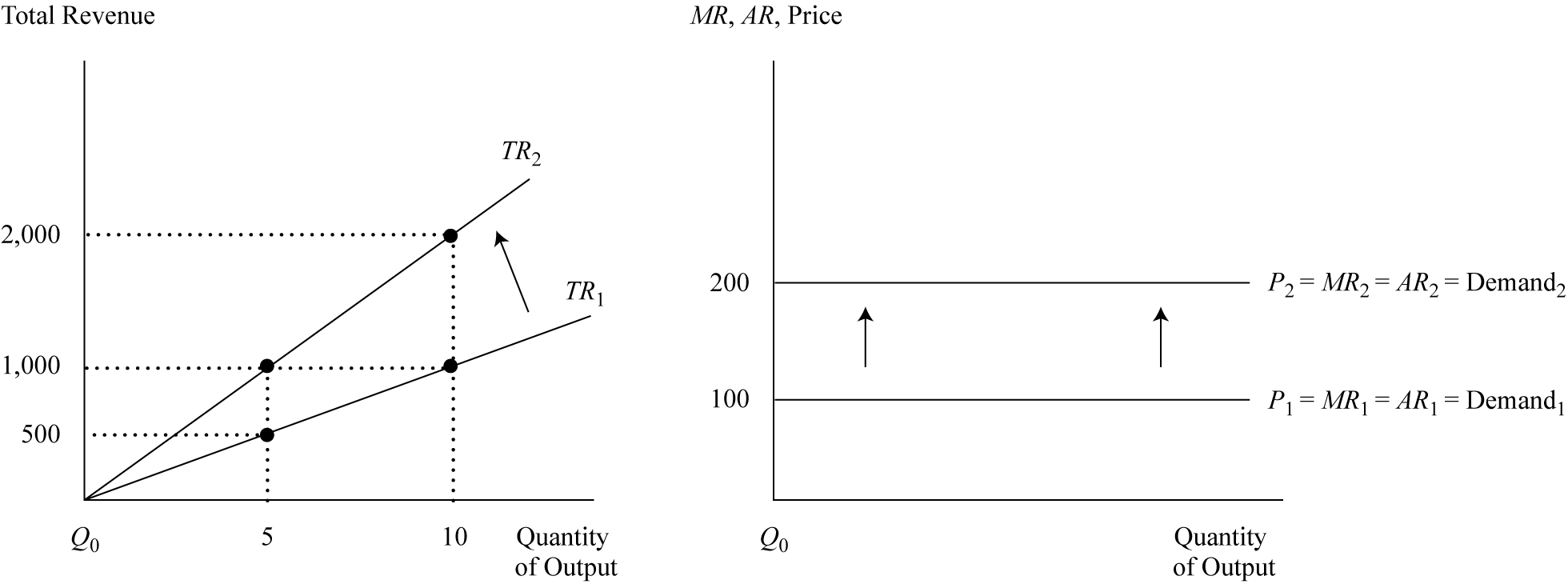

Here at a price of 100, P1 = MR1 = AR1 = Demand1.
Marginal revenue, average revenue, and the firm’s price remain constant until market demand and supply factors cause a change in price.
If price increases to 200 because of an increase in market demand, the firm’s demand curve shifts from Demand1 to Demand2 with corresponding increases in MR and AR as well.
Marginal revenue, average revenue, and the firm’s price remain constant until market demand and supply factors cause a change in price.
If price increases to 200 because of an increase in market demand, the firm’s demand curve shifts from Demand1 to Demand2 with corresponding increases in MR and AR as well.
If you want to change selection, open document below and click on "Move attachment"
Exhibit 5. Total Revenue, Average Revenue, and Marginal Revenue under Perfect Competition
mpetition, MR equals AR and both are equal to a price that stays the same across all levels of output. Because price is fixed to the individual seller, the firm’s demand curve is a horizontal line at the point where the market sets the price. <span>In Exhibit 5, at a price of 100, P 1 = MR 1 = AR 1 = Demand 1 . Marginal revenue, average revenue, and the firm’s price remain constant until market demand and supply factors cause a change in price. For instance, if price increases to 200 because of an increase in market demand, the firm’s demand curve shifts from Demand 1 to Demand 2 with corresponding increases in MR and AR as well. Total revenue increases from TR 1 to TR 2 when price increases from 100 to 200. At a price of 100, total revenue at 10 units is 1,000; however, at a price of 200, total revenue would
Exhibit 5. Total Revenue, Average Revenue, and Marginal Revenue under Perfect Competition
mpetition, MR equals AR and both are equal to a price that stays the same across all levels of output. Because price is fixed to the individual seller, the firm’s demand curve is a horizontal line at the point where the market sets the price. <span>In Exhibit 5, at a price of 100, P 1 = MR 1 = AR 1 = Demand 1 . Marginal revenue, average revenue, and the firm’s price remain constant until market demand and supply factors cause a change in price. For instance, if price increases to 200 because of an increase in market demand, the firm’s demand curve shifts from Demand 1 to Demand 2 with corresponding increases in MR and AR as well. Total revenue increases from TR 1 to TR 2 when price increases from 100 to 200. At a price of 100, total revenue at 10 units is 1,000; however, at a price of 200, total revenue would
Summary
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Details
Discussion
Do you want to join discussion? Click here to log in or create user.