History is the discovery, collection, organization, analysis and presentation of information about past events. History can also mean a continuous, typically chronological, record of important or public events or of a particular trend or institution. Scholars who write about history are called historians. It is a field of knowledge which uses a narrative to examine and analyse the sequence of events, and it sometimes attempts to investigate objectively the patterns of cause and effect that determine events. Historians debate the nature of history and its usefulness. This includes discussing the study of the discipline as an end in itself and as a way of providing "perspective" on the problems of the present. The stories common to a particular culture, but not supported by external sources (such as the legends surrounding King Arthur) are usually classified as cultural heritage rather than the "disinterested investigation" needed by the discipline of history. Events of the past prior to written record are considered prehistory. Amongst scholars, the fifth century BC Greek historian Herodotus is considered to be the "father of history", and, along with his contemporary Thucydides, forms the foundations for the modern study of history. Their influence, along with other historical traditions in other parts of their world, have spawned many different interpretations of the nature of history which has evolved over the centuries and are continuing to change. The modern study of history has many different fields including those that focus on certain regions and those which focus on certain topical or thematic elements of historical investigation. Often history is taught as part of primary and secondary education, and the academic study of history is a major discipline in university studies.
Selected article
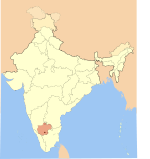
The Western Ganga Dynasty (350–1000 CE) (Kannada: ಪಶ್ಚಿಮ ಗಂಗ ಸಂಸ್ಥಾನ) was an important ruling dynasty of ancient Karnataka in India. They are known as Western Gangas to distinguish them from the Eastern Gangas who in later centuries ruled over modern Odisha. The general belief is the Western Gangas began their rule during a time when multiple native clans asserted their freedom due to the weakening of the Pallava empire in South India, a geo-political event sometimes attributed to the southern conquests of Samudra Gupta. The Western Ganga sovereignty lasted from about 350 to 550 CE, initially ruling from Kolar and later moving their capital to Talakad on the banks of the Kaveri River in modern Mysore district.
After the rise of the imperial Chalukyas of Badami, the Gangas accepted Chalukya overlordship and fought for the cause of their overlords against the Pallavas of Kanchi. The Chalukyas were replaced by the Rashtrakutas of Manyakheta in 753 CE as the dominant power in the Deccan. After a century of struggle for autonomy, the Western Gangas finally accepted Rashtrakuta overlordship and successfully fought alongside them against their foes, the Chola Dynasty of Tanjavur. In the late 10th century, north of Tungabhadra river, the Rashtrakutas were replaced by the emerging Western Chalukya Empire and the Chola Dynasty saw renewed power south of the Kaveri river. The defeat of the Western Gangas by Cholas around 1000 resulted in the end of the Ganga influence over the region. Selected biography
Jovan Vladimir or John Vladimir (Serbian Cyrillic: Јован Владимир; died 22 May 1016) was ruler of Duklja, the most powerful Serbian principality of the time, from around 1000 to 1016. He ruled during the protracted war between the Byzantine Empire and the First Bulgarian Empire. His close relationship with Byzantium did not save Duklja from the expansionist Tsar Samuel of Bulgaria, who conquered the principality in around 1010 and took Jovan Vladimir prisoner. A medieval chronicle asserts that Samuel's daughter, Theodora Kosara, fell in love with Vladimir and begged her father for his hand. The tsar allowed the marriage and returned Duklja to Vladimir, who ruled as his vassal.
Vladimir was acknowledged as a pious, just, and peaceful ruler. He took no part in his father-in-law's war efforts. The warfare culminated with Samuel's defeat by the Byzantines in 1014; the tsar died soon afterward. In 1016 Vladimir fell victim to a plot by Ivan Vladislav, the last ruler of the First Bulgarian Empire. He was beheaded in front of a church in Prespa, the empire's capital, and was buried there. He was soon recognized as a martyr and saint; his feast day is celebrated on 22 May. His widow, Kosara, reburied him in the Prečista Krajinska Church, near his court in southeastern Duklja. In 1381 his remains were preserved in the Church of Saint Jovan Vladimir near Elbasan, and since 1995 they have been kept in the Orthodox cathedral of Tirana, Albania. The saint's remains are considered relics, and attract many believers, especially on his feast day, when the relics are taken to the church near Elbasan for a celebration. Did you know...
Selected pictureBuzz Aldrin's footprint, taken by himself on Apollo 11, the first manned mission to the moon, on July 20, 1969. The print was part of an experiment to test the properties of the lunar regolith, but today it is known for being one of the most iconic things left on the moon by humans. On this dayJune 14: Liberation Day in the Falkland Islands and South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands (1982); Trooping the Colour and the Queen's Official Birthday in the United Kingdom and several other Commonwealth countries (2014); Flag Day in the United States
Selected quote
Selected portal"The ideas which now pass for brilliant innovations and advances are in fact mere revivals of ancient errors, and a further proof of the dictum that those who are ignorant of the past are condemned to repeat it." Things you can do
WikiProjectsAncient Near East • Australian History • Former countries • History of Canada • Chinese history • European history • Heraldry and vexillology • History of India • Jewish history • Medieval Scotland • Mesoamerica • Military history • Middle Ages • History of Science Composers • Political figures • Saints • United States Presidents Topics
CategoriesHistory • By period • By region • By topic • By ethnic group • Historiography • Archaeology • Books • Documents • Maps • Images • Magazines • Organizations • Fictional • Museums • Pseudohistory • Stubs • Timelines • Chronology • People • | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Portal:History - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
aImperial ChinaClassical CivilisationColonialismCrusadesDisastersHeraldry History of ScienceIndian independence movementKhitanMiddle AgesNew FranceRussian EmpireSoviet Union War edit The History Portal History by Frederick Dielman <span>History is the discovery, collection, organization, analysis and presentation of information about past events. History can also mean a continuous, typically chronological, record of important or public events or of a particular trend or institution. Scholars who write about history are called historians. It is a field of knowledge which uses a narrative to examine and analyse the sequence of events, and it sometimes attempts to investigate objectively the patterns of cause and effect that determine events. Historians debate the nature of history and its usefulness. This includes discussing the study of the discipline as an end in itself and as a way of providing "perspective" on the problems of the present. The stories common to a particular culture, but not supported by external sources (such as the legends surrounding King Arthur) are usually classified as cultural heritage rather than the "disinterested investigation" needed by the discipline of history. Events of the past prior to written record are considered prehistory. Amongst scholars, the fifth century BC Greek historian Herodotus is considered to be the "father of history", and, along with his contemporary Thucydides, forms the foundations for the modern study of history. Their influence, along with other historical traditions in other parts of their world, have spawned many different interpretations of the nature of history which has evolved over the centuries and are continuing to change. The modern study of history has many different fields including those that focus on certain regions and those which focus on certain topical or thematic elements of historical investigation. Often history is taught as part of primary and secondary education, and the academic study of history is a major discipline in university studies. More about History… View new selections below (purge) edit Selected article The Western Ganga Dynasty (350–1000 CE) (Kannada: ಪಶ್ಚಿಮ ಗಂಗ ಸಂಸ್ಥಾನ) was an important ruling dynasty of ancient Karnataka in India. They are known as Western Gangas to distinguish them from the Eastern Gangas who in later centuries ruled over modern Odisha. The general belief is the Western Gangas began their rule during a time when multiple native clans asserted their freedom due to the weakening of the Pallava empire in South India, a geo-political event sometimes attributed to the southern conquests of Samudra Gupta. The Western Ganga sovereignty lasted from about 350 to 550 CE, initially ruling from Kolar and later moving their capital to Talakad on the banks of the Kaveri River in modern Mysore district. After the rise of the imperial Chalukyas of Badami, the Gangas accepted Chalukya overlordship and fought for the cause of their overlords against the Pallavas of Kanchi. The Chalukyas were replaced by the Rashtrakutas of Manyakheta in 753 CE as the dominant power in the Deccan. After a century of struggle for autonomy, the Western Gangas finally accepted Rashtrakuta overlordship and successfully fought alongside them against their foes, the Chola Dynasty of Tanjavur. In the late 10th century, north of Tungabhadra river, the Rashtrakutas were replaced by the emerging Western Chalukya Empire and the Chola Dynasty saw renewed power south of the Kaveri river. The defeat of the Western Gangas by Cholas around 1000 resulted in the end of the Ganga influence over the region. ...Archive/Nominations Read more... edit Selected biography Jovan Vladimir or John Vladimir (Serbian Cyrillic: Јован Владимир; died 22 May 1016) was ruler of Duklja, the most powerful Serbian principality of the time, from around 1000 to 1016. He ruled during the protracted war between the Byzantine Empire and the First Bulgarian Empire. His close relationship with Byzantium did not save Duklja from the expansionist Tsar Samuel of Bulgaria, who conquered the principality in around 1010 and took Jovan Vladimir prisoner. A medieval chronicle asserts that Samuel's daughter, Theodora Kosara, fell in love with Vladimir and begged her father for his hand. The tsar allowed the marriage and returned Duklja to Vladimir, who ruled as his vassal. Vladimir was acknowledged as a pious, just, and peaceful ruler. He took no part in his father-in-law's war efforts. The warfare culminated with Samuel's defeat by the Byzantines in 1014; the tsar died soon afterward. In 1016 Vladimir fell victim to a plot by Ivan Vladislav, the last ruler of the First Bulgarian Empire. He was beheaded in front of a church in Prespa, the empire's capital, and was buried there. He was soon recognized as a martyr and saint; his feast day is celebrated on 22 May. His widow, Kosara, reburied him in the Prečista Krajinska Church, near his court in southeastern Duklja. In 1381 his remains were preserved in the Church of Saint Jovan Vladimir near Elbasan, and since 1995 they have been kept in the Orthodox cathedral of Tirana, Albania. The saint's remains are considered relics, and attract many believers, especially on his feast day, when the relics are taken to the church near Elbasan for a celebration. ...Archive/Nominations Read more... edit Did you know... ... that the underground Fortress of Mimoyecques (pictured) was built by Nazi Germany to bombard London with 10 shells a minute using the V-3 supergun?... that Howard P. Perry was the first African American recruit in the United States Marine Corps?... that the Chester city walls form the most complete circuit of Roman and medieval defensive town walls in Britain?... that China's first female director was adopted by the first Premier of the People's Republic of China?... that the Medieval Merchant's House in Southampton was being used as a brothel when bomb damage during the Blitz revealed the building's important medieval architecture?... that the Sumerian "river of paradise", the Hubur, derived partly from real geography before becoming a demonic fantasy?... that Bill Foley's photograph "The Last Smile" shows Anwar Sadat only moments before his assassination?... that the 1911 Sarez earthquake triggered a huge landslide, forming the tallest dam in the world? ...Archive/Nominations More... edit Selected picture Buzz Aldrin's footprint, taken by himself on Apollo 11, the first manned mission to the moon, on July 20, 1969. The print was part of an experiment to test the properties of the lunar regolith, but today it is known for being one of the most iconic things left on the moon by humans. ...Archive/Nominations Read more... edit On this day June 14: Liberation Day in the Falkland Islands and South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands (1982); Trooping the Colour and the Queen's Official Birthday in the United Kingdom and several other Commonwealth countries (2014); Flag Day in the United States 1285 – Forces led by Prince Trần Quang Khải of Vietnam's Trần dynasty destroyed most of the invading Mongol naval fleet in a battle at Chuong Duong.1846 – Anglo-American settlers in the Town of Sonoma began a rebellion against Mexico, proclaiming the California Republic and eventually raising a homemade flag with a bear and star (digital reproduction pictured).1940 – Four days after the French government fled Paris, German forces occupied the French capital, essentially ending the Battle of France.1982 – Argentine forces surrendered to the British, essentially ending the Falklands War.1994 – After the Vancouver Canucks lost to the New York Rangers in ice hockey's Stanley Cup Finals, a riot ensued in Downtown Vancouver, causing C$1.1 million in damage. More anniversaries: June 13 – June 14 – June 15 Archive – By email – List of historical anniversaries It is now June 14, 2014 (UTC) – Reload this page edit Selected quote What we find in books is like the fire in our hearths. We fetch it from our neighbors, we kindle it at home, we communicate it to others, and it becomes the property of all. —Voltaire, 18th century French philosopher ...Archive More... edit Selected portal Classical Civilisation "The ideas which now pass for brilliant innovations and advances are in fact mere revivals of ancient errors, and a further proof of the dictum that those who are ignorant of the past are condemned to repeat it." — Henry Hazlitt ...Archive/Nominations Read more... edit Things you can do Here are some Open Tasks : Copy/edit: Hongwu Emperor, Indian independence movement, Modern history, More...Wikify:Merge: More...Requests: , More...Stubs: Greco-Roman, Java War, Leopold II of Austria, Panhellenic Liberation Movement, Rio Protocol, Social history, Golden Age of Piracy, More...Requested pictures - of history topicsAre you a historian, i.e. one who studies and writes history, and who has a keen interest in writing outstanding articles? Join our fine group by adding Category:Wikipedian historians to the bottom of your user page. edit WikiProjects History Ancient Near East • Australian History • Former countries • History of Canada • Chinese history • European history • Heraldry and vexillology • History of India • Jewish history • Medieval Scotland • Mesoamerica • Military history • Middle Ages • History of Science Time Days of the Year • Years Biography Composers • Political figures • Saints • United States Presidents Topics vte Social sciences Primary AnthropologyArchaeologyEconomicsGeography human HistoryLawLinguisticsPolitical science international relationspolitical economypublic administration PsychologySociology criminal justicecriminologydemographyrural Interdisciplinary AnthrozoologyArea studiesCommunication studiesCommunity studiesCultural studiesDevelopment studiesEducationEnvironmental (social sciencestudies)Food studiesGender studiesGlobal studiesHuman ecologyInformation scienceInternational studiesMedia studiesPlanning land useregionalurban Political ecologyPublic healthRegional scienceScience and technology studiesScience studies Other categorizations HumanitiesGeisteswissenschaftHuman science IndexJournalsOutlinePortalWikiProjectWikiversity vte Humanities HistoryLinguisticsLawLiteraturePerforming artsPoliticsPhilosophyReligious studiesVisual arts vte Time Key concepts Past historydeep time PresentFuture futurology Eternity arguments forEternal return Immortality Time portal Measurement and standards Chronometry UTCUTTAIUnit of timePlanck timeSecondMinuteHourDayWeekMonthYearDecadeCenturyMillenniumTropical yearSolar yearSidereal year Systems of measurement Time zone12-hour clock24-hour clockDaylight saving timeSolar timeSidereal timeMetric timeDecimal timeHexadecimal time Calendars GregorianJulianHebrewIslamicLunarSolar HijriMayanIntercalationLeap secondLeap year Clocks AstrariumHistory of timekeeping devicesHorologyMarine chronometerSundialWater clockAtomic clockQuantum clock Chronology / history / archaeology / geology Astronomical chronology / Calendar eraChronicleTimelinePeriodizationRegnal yearBig History / Dating methodologies / Geological timeGeochronologyGeological historyDeep timeEonEraPeriodEpochAgeChron Religion and mythology DreamtimeKālaKalachakraProphecyTime and fate deitiesWheel of time Philosophy A-series and B-seriesB-theory of timeCausalityDurationEndurantismEternal returnEternalismEventPerdurantismPresentismTemporal finitismTemporal partsThe Unreality of Time Physics Absolute time and spaceArrow of timeChrononCoordinate timeImaginary timePlanck epochPlanck timeProper timeRateSpacetimeTheory of relativityTime dilation gravitational Time domainT-symmetry Biology / psychology / sociology / economics / accounting / management ChronobiologyCircadian rhythms / Mental chronometrySpecious presentTime perception / Time discipline / Time use researchTime value of moneyTime-based currencyTime bankingTerm / Accounting periodFiscal year / Time managementPunctualityProcrastinationTime clockTimesheetTime tracking software Related topics Carpe diemClock positionSpaceSystem timeTempus fugitTime capsuleTime complexityTime signatureTime travel vte Chronology Key topics TimeAstronomyGeologyPaleontologyArchaeologyHistory ErasEpochs Calendar eras Human EraAb urbe conditaAnno Domini / Common EraAnno MundiByzantine eraSpanish eraBefore PresentHijriEgyptianSothic cycleHindu units of timeHindu Yugas Regnal year Canon of KingsLists of kingsLimmuSeleucid era Era names ChineseJapaneseKoreanVietnamese Calendars Pre-Julian / Julian Pre-Julian RomanOriginal JulianProleptic JulianRevised Julian Gregorian GregorianProleptic GregorianOld Style and New Style dates Astronomical LunisolarSolarLunarAstronomical year numbering Others Chinese sexagenary cycleGeologic CalendarHebrewIranianIslamicISO week date Astronomic time Cosmic CalendarEphemerisGalactic yearMetonic cycleMilankovitch cycles Geologic time Concepts Deep timeGeological history of EarthGeological time units Standards Global Standard Stratigraphic Age (GSSA)Global Boundary Stratotype Section and Point (GSSP) Methods ChronostratigraphyGeochronologyIsotope geochemistryLaw of superpositionOptical datingSamarium-neodymium dating Archaeological methods Absolute dating Amino acid racemisationArchaeomagnetic datingDendrochronologyGlottochronologyIce coreIncremental datingLichenometryPaleomagnetismRadiocarbon datingRadiometric datingTephrochronologyThermoluminescence datingUranium-lead dating Relative dating Fluorine absorptionObsidian hydrationSeriationStratigraphy Genetic methods Molecular clock Related topics ChronicleNew ChronologyPeriodizationSynchronoptic viewTimelineYear ZeroCircaFloruitTerminus post quemASPRO chronology Portal edit Categories History • By period • By region • By topic • By ethnic group • Historiography • Archaeology • Books • Documents • Maps • Images • Magazines • Organizations • Fictional • Museums • Pseudohistory • Stubs • Timelines • Chronology • People • Wikipedia historians ▼ History ► History by ethnic group ► History by location ► History by period ► History by topic ► Fields of history ► History-related lists ► Historical eras ► Prehistory ► History awards ► Commemoration ► Historical controversies ► Historical documents ► History education ► Events ► Historical geography ► Historical geology ► Historians ► Historiography ► Legacies ► Nostalgia ► History organizations ► History painters ► Philosophy of history ► Historic preservation ► Historical timelines ► Historical works ► Works about history ► Wikipedia books on history ► History images ► History portals ► History stubs Associated Wikimedia History on Wikibooks History on Wikimedia CommonsHistory on Wikinews History on Wikiquote History on Wikisource History on Wikiversity History on Wikivoyage History on Wiktionary History on Wikidata Manuals and booksImages and mediaNewsQuotationsTextsLearning resourcesTravel guidesDefinitionsDatabase What are portals?List of portalsFeatured portals Retrieved from "http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Portal:History&oldid=611767654" Categories: History portalHistory portalsHistoryHidden categorie
Summary
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |