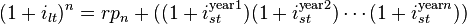The Liquidity Premium Theory is an offshoot of the Pure Expectations Theory. The Liquidity Premium Theory asserts that long-term interest rates not only reflect investors’ assumptions about future interest rates but also include a premium for holding long-term bonds (investors prefer short term bonds to long term bonds), called the term premium or the liquidity premium. This premium compensates investors for the added risk of having their money tied up for a longer period, including the greater price uncertainty. Because of the term premium, long-term bond yields tend to be higher than short-term yields, and the yield curve slopes upward. Long term yields are also higher not just because of the liquidity premium, but also because of the risk premium added by the risk of default from holding a security over the long term. The market expectations hypothesis is combined with the liquidity premium theory:
Where 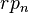 is the risk premium associated with an
is the risk premium associated with an 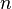 year bond.
year bond.
Yield curve - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
stence in the shape of the yield curve. Shortcomings of expectations theory: Neglects the risks inherent in investing in bonds (because forward rates are not perfect predictors of future rates). 1) Interest rate risk 2) Reinvestment rate risk <span>Liquidity premium theory[edit] The Liquidity Premium Theory is an offshoot of the Pure Expectations Theory. The Liquidity Premium Theory asserts that long-term interest rates not only reflect investors’ assumptions about future interest rates but also include a premium for holding long-term bonds (investors prefer short term bonds to long term bonds), called the term premium or the liquidity premium. This premium compensates investors for the added risk of having their money tied up for a longer period, including the greater price uncertainty. Because of the term premium, long-term bond yields tend to be higher than short-term yields, and the yield curve slopes upward. Long term yields are also higher not just because of the liquidity premium, but also because of the risk premium added by the risk of default from holding a security over the long term. The market expectations hypothesis is combined with the liquidity premium theory: Where is the risk premium associated with an year bond. Market segmentation theory[edit] This theory is also called the segmented market hypothesis. In this theory, financial instruments of different terms are not substitutable. As a result,
Summary
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |