Do you want BuboFlash to help you learning these things? Or do you want to add or correct something? Click here to log in or create user.
Macaulay duration
#bonds #duration #finance #has-images
Macaulay duration, is the weighted average maturity of cash flows. Consider some set of fixed cash flows. The present value of these cash flows is:
Macaulay duration is defined as:[1][2][3] [4]
- (1)
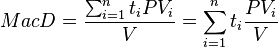
where:
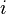 indexes the cash flows,
indexes the cash flows,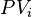 is the present value of the
is the present value of the 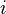 th cash payment from an asset,
th cash payment from an asset,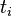 is the time in years until the
is the time in years until the 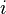 th payment will be received,
th payment will be received,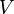 is the present value of all future cash payments from the asset.
is the present value of all future cash payments from the asset.
If you want to change selection, open document below and click on "Move attachment"
Bond duration - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Dollar duration, DV01 6.1 Application to Value-at-Risk (VaR) 7 Embedded options and effective duration8 Spread duration9 Average duration10 Convexity11 See also12 Notes13 References14 Further reading15 External links Macaulay duration[edit] <span>Macaulay duration, named for Frederick Macaulay who introduced the concept, is the weighted average maturity of cash flows. Consider some set of fixed cash flows. The present value of these cash flows is: Macaulay duration is defined as:[1][2][3] [4] (1) where: indexes the cash flows, is the present value of the th cash payment from an asset, is the time in years until the th payment will be received, is the present value of all future cash payments from the asset. In the second expression the fractional term is the ratio of the cash flow to the total PV. These terms add to 1.0 and serve as weights for a weighted average. Thus the overall expressi
Bond duration - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Dollar duration, DV01 6.1 Application to Value-at-Risk (VaR) 7 Embedded options and effective duration8 Spread duration9 Average duration10 Convexity11 See also12 Notes13 References14 Further reading15 External links Macaulay duration[edit] <span>Macaulay duration, named for Frederick Macaulay who introduced the concept, is the weighted average maturity of cash flows. Consider some set of fixed cash flows. The present value of these cash flows is: Macaulay duration is defined as:[1][2][3] [4] (1) where: indexes the cash flows, is the present value of the th cash payment from an asset, is the time in years until the th payment will be received, is the present value of all future cash payments from the asset. In the second expression the fractional term is the ratio of the cash flow to the total PV. These terms add to 1.0 and serve as weights for a weighted average. Thus the overall expressi
Summary
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Details
Discussion
Do you want to join discussion? Click here to log in or create user.