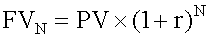
- FV = future value at time n
- PV = present value
- r = interest rate per period
- N = number of years
In order to receive a single future cash flow N years from now, you must make an investment today in the following amount:
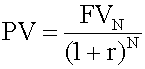
Notice that the future cash flow is discounted back to the present. Therefore, the interest rate is called the discount rate.
You should be able to calculate PVs and FVs using your calculator.
- N = number of periods
- I/Year = yield in market place or the required rate of return
- PV = present value
- PMT = payment amount per period
- FV = the future value of the investment
Example 1
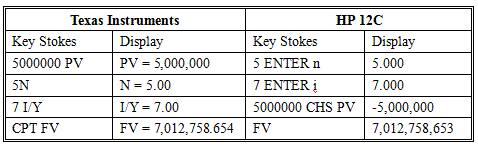
An analyst invests $5 million in a 5-year certificate of deposit (CD) at a local financial institution. The CD promises to pay 7% per year compounded annually. The institution also allows him to reinvest the interest at the same CD rate for the duration of the CD. How much will the analyst have at the end of five years if his money remains invested at 7% for five years with no withdrawals of interest?
Before using the Texas Instruments BAII PLUS and HP 12C calculator, it is essential to ensure that your settings are correct. The default settings on the calculator are not necessarily the settings you need when making the calculations. Follow these steps to ensure that your calculator is correctly set.
Texas Instruments BAII PLUS Settings
- Press 2nd QUIT 2nd [CLR TVM] to clear the worksheet.
- Press 2nd [P/Y] to enter payments per year and/or compounding periods per year.
- The P/Y label and current value are displayed. The default value is 12. You must now key in 1 and then ENTER since you want 1 payment per year.
- If the question says there are 12 payments per year, you would change this to 12.
- Turn the calculator on by pressing the ON key.
- Clear the memory and set decimals to 2 places by pressing the following keys:
- CLEAR REG f 2 - 0.00 will display.
- CLEAR FIN - this clears all the data in the financial mode.
The calculator keys to press are:
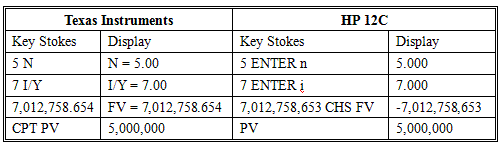
If you are given the FV and need to solve for PV, the calculator keys to press are:
When compounding periods are not annual
Some investments pay interest more than once a year. When you calculate these amounts, make sure that periodic interest rates correspond to the number of compounding periods in the year. For example, if time periods are quoted in quarters, quarterly interest rates should be used.
When compounding periods are other than annual
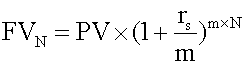
- rs = the quoted annual interest rate
- m = the number of compounding periods per year
- N = the number of years.
An analyst invests $5 million in a 5-year certificate of deposit (CD) at a local financial institution. The CD promises to pay 7% per year, compounded semi-annually. The institution also allows him to reinvest the interest at the same CD rate for the duration of the CD. How much will the analyst have at the end of five years if his money remains invested at 7% for five years with no withdrawals of interest?
The calculator keys to press are:
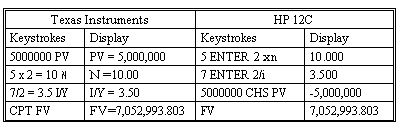
Note that the answer is greater than when the compounding was annual. This is because interest is earned twice a year instead of only once.
If the number of compounding periods becomes infinite, interest is compounding continuously. Accordingly, the future value N years from now is computed as follows:
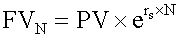
Summary
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |