Subject 5. The Total Probability Rule
#has-images #reading-9-probability-concepts
If we have an event or scenario S, the event not-S, called the complement of S, is written SC. Note that P(S) + P(SC) = 1, as either S or not-S must occur.
The total probability rule explains the unconditional probability of an event in terms of probabilities conditional on the scenarios.
- P(A) = P(A|S)P(S) + P(A|SC)P(SC)
- P(A) = P(A|S1)P(S1) + P(A|S2)P(S2) + ... + P(A|Sn)P(Sn)
- The first equation is just a special case of the second equation.
- The second equation states the following: the probability of any event [P(A)] can be expressed as a weighted average of the probabilities of the event, given scenarios [terms such as P(A|S1)]; the weights applied to these conditional probabilities are the respective probabilities of the scenarios [terms such as P(A1multiplying P(A|S1)], and the scenarios must be mutually exclusive and exhaustive.
- Event A: IBM's revenue will increase.
- Event B: the economy is going into an expansion. P(B) = 0.6, and therefore P(Bc) = 0.4.
The probability of an increase in IBM's revenue given no economic expansion is P(A|Bc) = 0.7.
Using the total probability rule, we can compute the probability of an increase in IBM's revenue: P(A) = P(A|B) x P(B) + P(A|Bc) x P(Bc) = 0.8 x 0.6 + 0.7 x 0.4 = 0.76.
Typical exam question
An analyst constructs the following probability table for the market and Company X's stock:
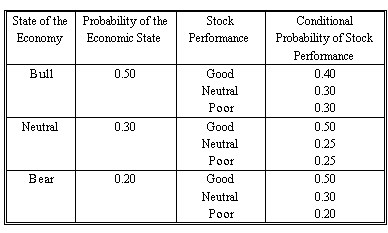
1. Compute the total probability of good performance for Company X's stock.
Here we are asked to find the total probability of good performance. This means we have to find the joint probability of one stock outcome. To do this we multiply and add.
We take Σ (probability of economic state x good conditional probability): Joint probability = (0.5 x 0.4) + (0.3 x 0.5) + (0.2 x 0.5) = 45%
2. Compute the probability of simultaneously realizing a bull economy and poor stock performance for Company X.
This question asks you to determine the probability of a specific branch. If we follow the branch and multiply the probabilities, we will arrive at the correct answer as follows.
Bull economy: 0.5
Poor stock: 0.3
Probability = 0.5 x 0.3 = 0.15 = 15%