Explain the images of the ARP example !
Let’s say that host A wants to communicate with host B for the first time. Host A knows the IP address of host B, but since this is the first time the two hosts communicate, the hardware (MAC) addresses are not known.
1. ARP Request + ARP Reply
ARP Request + ARP Reply => IP-MAC mapping learnt => ?
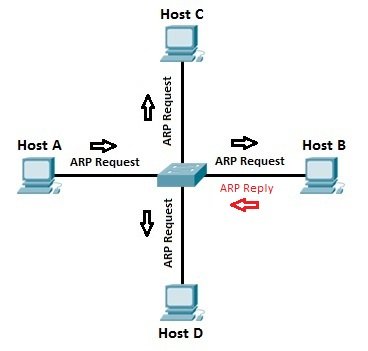
ARP Request
* Host A uses the ARP process to find out the MAC address of host B.
* switch knows the MAC address of the host A because of the ARP request.
* The switch forwards the ARP request out all ports except the port the host A is connected to.
* Host B receives the ARP request and responds with its MAC address.
* Host B also learns the MAC address of host A (because host A sent its MAC address in the ARP request).
* The switch learns which MAC addresses are associated with which port.
ARP Reply
* host B responded with the ARP reply that included its MAC address => switch knows the MAC address of host B => MAC address table got address
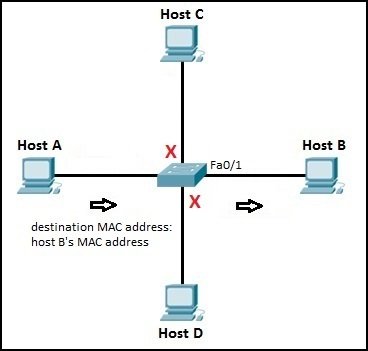
Learn IP-MAC mapping
* Now, when host A sends a packet to host B, the switch looks up in its MAC address table and forwards the frame only out Fa0/1 port, the port on which host B is connected.
Explain the images of the ARP example !
Let’s say that host A wants to communicate with host B for the first time. Host A knows the IP address of host B, but since this is the first time the two hosts communicate, the hardware (MAC) addresses are not known.
1. ARP Request + ARP Reply
ARP Request + ARP Reply => IP-MAC mapping learnt => ?
Explain the images of the ARP example !
Let’s say that host A wants to communicate with host B for the first time. Host A knows the IP address of host B, but since this is the first time the two hosts communicate, the hardware (MAC) addresses are not known.
1. ARP Request + ARP Reply
ARP Request + ARP Reply => IP-MAC mapping learnt => ?
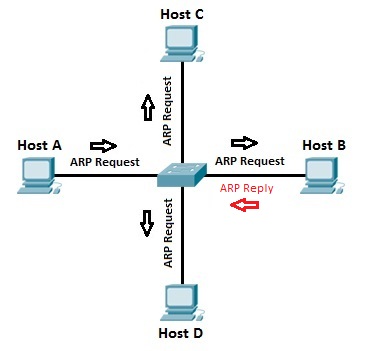
ARP Request
* Host A uses the ARP process to find out the MAC address of host B.
* switch knows the MAC address of the host A because of the ARP request.
* The switch forwards the ARP request out all ports except the port the host A is connected to.
* Host B receives the ARP request and responds with its MAC address.
* Host B also learns the MAC address of host A (because host A sent its MAC address in the ARP request).
* The switch learns which MAC addresses are associated with which port.
ARP Reply
* host B responded with the ARP reply that included its MAC address => switch knows the MAC address of host B => MAC address table got address
Learn IP-MAC mapping
* Now, when host A sends a packet to host B, the switch looks up in its MAC address table and forwards the frame only out Fa0/1 port, the port on which host B is connected.
Summary
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |