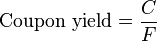Edited, memorised or added to reading queue
on 03-Jul-2014 (Thu)
Do you want BuboFlash to help you learning these things? Click here to log in or create user.
Flashcard 149623398
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
calculating asset swap spread (par-par)
Asset swap (type: market - same structure as par-par but at different price) is a difference between bond quoted price and implied strip price of the same bond (implied price of cashflows against a specific yield curve), quoted as the spread on the floating swap
Asset swap (type: market - same structure as par-par but at different price) is a difference between bond quoted price and implied strip price of the same bond (implied price of cashflows against a specific yield curve), quoted as the spread on the floating swap
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Bond valuation - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
ices are often quoted in terms of YTM. To achieve a return equal to YTM, i.e. where it is the required return on the bond, the bond owner must: buy the bond at price ,hold the bond until maturity, andredeem the bond at par. Coupon yield[edit] <span>The coupon yield is simply the coupon payment as a percentage of the face value . Coupon yield is also called nominal yield. Current yield[edit] The current yield is simply the coupon payment as a percentage of the (current) bond price . Relationship[edit] The concept of current yield is closely related to o
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Bond valuation - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
of the bond's price with respect to discount rates. For example, for small interest rate changes, the duration is the approximate percentage by which the value of the bond will fall for a 1% per annum increase in market interest rate. So the <span>market price of a 17-year bond with a duration of 7 would fall about 7% if the market interest rate (or more precisely the corresponding force of interest) increased by 1% per annum. Convexity is a measure of the "curvature" of price changes. It is needed because the price is not a linear function of the discount rate, but rather a convex function of the di
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Yield to maturity - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
ds6 See also7 References8 External links Main assumptions[edit] The main underlying assumptions used concerning the traditional yield measures are: The bond will be held to maturity.All coupon and principal payments will be made on schedule.<span>All the coupons are reinvested at an interest rate equal to the yield-to-maturity.[3]The yield is usually quoted without making any allowance for tax paid by the investor on the return, and is then known as "gross redemption yield". It also does not make an
Flashcard 149624199
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itmarket price of a 17-year bond with a duration of 7 would fall about 7% if the market interest rate increased by 1% per annum.
Original toplevel document
Bond valuation - Wikipedia, the free encyclopediaof the bond's price with respect to discount rates. For example, for small interest rate changes, the duration is the approximate percentage by which the value of the bond will fall for a 1% per annum increase in market interest rate. So the <span>market price of a 17-year bond with a duration of 7 would fall about 7% if the market interest rate (or more precisely the corresponding force of interest) increased by 1% per annum. Convexity is a measure of the "curvature" of price changes. It is needed because the price is not a linear function of the discount rate, but rather a convex function of the di
Flashcard 149624206
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itmarket price of a 17-year bond with a duration of 7 would fall about 7% if the market interest rate increased by 1% per annum.
Original toplevel document
Bond valuation - Wikipedia, the free encyclopediaof the bond's price with respect to discount rates. For example, for small interest rate changes, the duration is the approximate percentage by which the value of the bond will fall for a 1% per annum increase in market interest rate. So the <span>market price of a 17-year bond with a duration of 7 would fall about 7% if the market interest rate (or more precisely the corresponding force of interest) increased by 1% per annum. Convexity is a measure of the "curvature" of price changes. It is needed because the price is not a linear function of the discount rate, but rather a convex function of the di
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itIf a bond's coupon rate is less than its YTM, then the bond is selling at a discount.If a bond's coupon rate is more than its YTM, then the bond is selling at a premium.If a bond's coupon rate is equal to its YTM, then the bond is selling at par. </bod
Original toplevel document
Yield to maturity - Wikipedia, the free encyclopediausually quoted without making any allowance for tax paid by the investor on the return, and is then known as "gross redemption yield". It also does not make any allowance for the dealing costs incurred by the purchaser (or seller). <span>Coupon rate vs. YTM[edit] If a bond's coupon rate is less than its YTM, then the bond is selling at a discount.If a bond's coupon rate is more than its YTM, then the bond is selling at a premium.If a bond's coupon rate is equal to its YTM, then the bond is selling at par. Variants of yield to maturity[edit] As some bonds have different characteristics, there are some variants of YTM: Yield to call: when a bond is callable (can be repurchased by the issuer
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itIf a bond's coupon rate is less than its YTM, then the bond is selling at a discount.If a bond's coupon rate is more than its YTM, then the bond is selling at a premium.If a bond's coupon rate is equal to its YTM, then the bond is selling at par.
Original toplevel document
Yield to maturity - Wikipedia, the free encyclopediausually quoted without making any allowance for tax paid by the investor on the return, and is then known as "gross redemption yield". It also does not make any allowance for the dealing costs incurred by the purchaser (or seller). <span>Coupon rate vs. YTM[edit] If a bond's coupon rate is less than its YTM, then the bond is selling at a discount.If a bond's coupon rate is more than its YTM, then the bond is selling at a premium.If a bond's coupon rate is equal to its YTM, then the bond is selling at par. Variants of yield to maturity[edit] As some bonds have different characteristics, there are some variants of YTM: Yield to call: when a bond is callable (can be repurchased by the issuer
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itIf a bond's coupon rate is less than its YTM, then the bond is selling at a discount.If a bond's coupon rate is more than its YTM, then the bond is selling at a premium.If a bond's coupon rate is equal to its YTM, then the bond is selling at par.
Original toplevel document
Yield to maturity - Wikipedia, the free encyclopediausually quoted without making any allowance for tax paid by the investor on the return, and is then known as "gross redemption yield". It also does not make any allowance for the dealing costs incurred by the purchaser (or seller). <span>Coupon rate vs. YTM[edit] If a bond's coupon rate is less than its YTM, then the bond is selling at a discount.If a bond's coupon rate is more than its YTM, then the bond is selling at a premium.If a bond's coupon rate is equal to its YTM, then the bond is selling at par. Variants of yield to maturity[edit] As some bonds have different characteristics, there are some variants of YTM: Yield to call: when a bond is callable (can be repurchased by the issuer
Flashcard 149624240
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itThe current yield is simply the coupon payment as a percentage of the (current) bond price .
Original toplevel document
Bond valuation - Wikipedia, the free encyclopediathe bond at price ,hold the bond until maturity, andredeem the bond at par. Coupon yield[edit] The coupon yield is simply the coupon payment as a percentage of the face value . Coupon yield is also called nominal yield. Current yield[edit] <span>The current yield is simply the coupon payment as a percentage of the (current) bond price . Relationship[edit] The concept of current yield is closely related to other bond concepts, including yield to maturity, and coupon yield. The relationship between yield to maturity and t
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itThe coupon yield is simply the coupon payment as a percentage of the face value . Coupon yield is also called nominal yield.
Original toplevel document
Bond valuation - Wikipedia, the free encyclopediaices are often quoted in terms of YTM. To achieve a return equal to YTM, i.e. where it is the required return on the bond, the bond owner must: buy the bond at price ,hold the bond until maturity, andredeem the bond at par. Coupon yield[edit] <span>The coupon yield is simply the coupon payment as a percentage of the face value . Coupon yield is also called nominal yield. Current yield[edit] The current yield is simply the coupon payment as a percentage of the (current) bond price . Relationship[edit] The concept of current yield is closely related to o
Flashcard 149624256
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itCoupon yield is also called nominal yield.
Original toplevel document
Bond valuation - Wikipedia, the free encyclopediaices are often quoted in terms of YTM. To achieve a return equal to YTM, i.e. where it is the required return on the bond, the bond owner must: buy the bond at price ,hold the bond until maturity, andredeem the bond at par. Coupon yield[edit] <span>The coupon yield is simply the coupon payment as a percentage of the face value . Coupon yield is also called nominal yield. Current yield[edit] The current yield is simply the coupon payment as a percentage of the (current) bond price . Relationship[edit] The concept of current yield is closely related to o
Flashcard 149624263
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itCoupon yield is also called nominal yield.
Original toplevel document
Bond valuation - Wikipedia, the free encyclopediaices are often quoted in terms of YTM. To achieve a return equal to YTM, i.e. where it is the required return on the bond, the bond owner must: buy the bond at price ,hold the bond until maturity, andredeem the bond at par. Coupon yield[edit] <span>The coupon yield is simply the coupon payment as a percentage of the face value . Coupon yield is also called nominal yield. Current yield[edit] The current yield is simply the coupon payment as a percentage of the (current) bond price . Relationship[edit] The concept of current yield is closely related to o
Flashcard 149624274
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itThe coupon yield is simply the coupon payment as a percentage of the face value .
Original toplevel document
Bond valuation - Wikipedia, the free encyclopediaices are often quoted in terms of YTM. To achieve a return equal to YTM, i.e. where it is the required return on the bond, the bond owner must: buy the bond at price ,hold the bond until maturity, andredeem the bond at par. Coupon yield[edit] <span>The coupon yield is simply the coupon payment as a percentage of the face value . Coupon yield is also called nominal yield. Current yield[edit] The current yield is simply the coupon payment as a percentage of the (current) bond price . Relationship[edit] The concept of current yield is closely related to o
 as a percentage of the face value
as a percentage of the face value 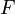 .
.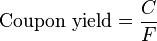


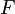 .
.