Edited, memorised or added to reading queue
on 01-Aug-2014 (Fri)
Do you want BuboFlash to help you learning these things? Click here to log in or create user.
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Greeks (finance) - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
or4.2 Speed4.3 Ultima4.4 Zomma 5 Greeks for multi-asset options6 Formulas for European option Greeks7 Related measures 7.1 Bond duration and convexity7.2 Beta7.3 Fugit 8 See also9 Notes10 References11 External links Use of the Greeks[edit] <span>Spot Price (S)Volatility ()Time to Expiry ()Value (V) Delta Vega ThetaDelta () GammaVannaCharmVega () VannaVommaVetaGamma () SpeedZommaColorVomma UltimaTotto Definition of Greeks as the sensitivity of an option's price and risk (in the first column) to the underlying parameter (in the first row). First-order Greeks are in blue, second-order Greeks are in green, and third-order Greeks are in yellow. Note that vanna appears twice as it should, and rho is left out as it is not as important as the rest. The Greeks are vital tools in risk management. Each Greek measures the sensitivity of the value of a portfolio to a small change in a given underlying parameter, so that component risks
Flashcard 149625984
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 149626363
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itFor most practical calculations, the Macaulay duration is calculated using the yield to maturity
Original toplevel document
Bond duration - Wikipedia, the free encyclopediaey are and the final large circle including the final principal repayment. If these circles were put on a balance beam, the fulcrum of the beam would represent the weighted average distance (time to payment), which is 1.78 years in this case. <span>For most practical calculations, the Macaulay duration is calculated using the yield to maturity to calculate the : (2) (3) where: indexes the cash flows, is the present value of the th cash payment from an asset, is the cash flow of the th payment from an asset, is the y
Flashcard 149626370
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itDV01 is the ratio of a price change in output (dollars) to unit change in input (a basis point of yield).
Original toplevel document
Bond duration - Wikipedia, the free encyclopediato yield: so that it is the product of the modified duration and the price (value): ($ per 1 percentage point change in yield) or ($ per 1 basis point change in yield) The DV01 is analogous to the delta in derivative pricing (The Greeks) – <span>it is the ratio of a price change in output (dollars) to unit change in input (a basis point of yield). Dollar duration or DV01 is the change in price in dollars, not in percentage. It gives the dollar variation in a bond's value per unit change in the yield. It is often measured per 1 bas
Flashcard 149626377
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itDV01 is the ratio of a price change in output (dollars) to unit change in input (a basis point of yield).
Original toplevel document
Bond duration - Wikipedia, the free encyclopediato yield: so that it is the product of the modified duration and the price (value): ($ per 1 percentage point change in yield) or ($ per 1 basis point change in yield) The DV01 is analogous to the delta in derivative pricing (The Greeks) – <span>it is the ratio of a price change in output (dollars) to unit change in input (a basis point of yield). Dollar duration or DV01 is the change in price in dollars, not in percentage. It gives the dollar variation in a bond's value per unit change in the yield. It is often measured per 1 bas
Flashcard 149626385
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itDollar duration or DV01 is the change in price in dollars, not in percentage.
Original toplevel document
Bond duration - Wikipedia, the free encyclopediae point change in yield) or ($ per 1 basis point change in yield) The DV01 is analogous to the delta in derivative pricing (The Greeks) – it is the ratio of a price change in output (dollars) to unit change in input (a basis point of yield). <span>Dollar duration or DV01 is the change in price in dollars, not in percentage. It gives the dollar variation in a bond's value per unit change in the yield. It is often measured per 1 basis point - DV01 is short for "dollar value of an 01" (or 1 basis poi
Flashcard 149626396
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itDollar duration or DV01 is the change in price in dollars, not in percentage.
Original toplevel document
Bond duration - Wikipedia, the free encyclopediae point change in yield) or ($ per 1 basis point change in yield) The DV01 is analogous to the delta in derivative pricing (The Greeks) – it is the ratio of a price change in output (dollars) to unit change in input (a basis point of yield). <span>Dollar duration or DV01 is the change in price in dollars, not in percentage. It gives the dollar variation in a bond's value per unit change in the yield. It is often measured per 1 basis point - DV01 is short for "dollar value of an 01" (or 1 basis poi
Flashcard 149626407
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itDollar duration or DV01 is the change in price in dollars, not in percentage.
Original toplevel document
Bond duration - Wikipedia, the free encyclopediae point change in yield) or ($ per 1 basis point change in yield) The DV01 is analogous to the delta in derivative pricing (The Greeks) – it is the ratio of a price change in output (dollars) to unit change in input (a basis point of yield). <span>Dollar duration or DV01 is the change in price in dollars, not in percentage. It gives the dollar variation in a bond's value per unit change in the yield. It is often measured per 1 basis point - DV01 is short for "dollar value of an 01" (or 1 basis poi
Flashcard 149626419
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itGiven a single series of nominal cash flows (like a riskless bond). If these payments are discounted to net present value with a static treasury yield curve the sum of their values will tend to overestimate the market price of the priced instrument. The parallel shift, which, if applied to the yield curve makes the NPV of the ant
Original toplevel document
Z-spread - Wikipedia, the free encyclopediaage-backed securities, a model of typical repayment rates tends to be given; for example, the PSA formula for a particular Fannie Mae MBS might equate a particular group of mortgages to an 8 year amortizing bond with a 5% mortality per annum. <span>This gives a single series of nominal cash flows (like a riskless bond). If these payments are discounted to net present value with a static treasury yield curve the sum of their values will tend to overestimate the market price of the MBS. The parallel shift, which, if applied to the yield curve makes the NPV of the anticipated receipts equal to the market price is the Yield curve spread. The Z-spread of a bond is the number of basis points one needs to add to the Treasury spot rates yield curve, so that the NPV of the bond cash flows (using the adjusted yield curve) equa
Flashcard 149626426
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itGiven a single series of nominal cash flows (like a riskless bond). If these payments are discounted to net present value with a static treasury yield curve the sum of their values will tend to overestimate the market price of the priced instrument. The parallel shift, which, if applied to the yield curve makes the NPV of the anticipated receipts equal to the market price is the Yield curve
Original toplevel document
Z-spread - Wikipedia, the free encyclopediaage-backed securities, a model of typical repayment rates tends to be given; for example, the PSA formula for a particular Fannie Mae MBS might equate a particular group of mortgages to an 8 year amortizing bond with a 5% mortality per annum. <span>This gives a single series of nominal cash flows (like a riskless bond). If these payments are discounted to net present value with a static treasury yield curve the sum of their values will tend to overestimate the market price of the MBS. The parallel shift, which, if applied to the yield curve makes the NPV of the anticipated receipts equal to the market price is the Yield curve spread. The Z-spread of a bond is the number of basis points one needs to add to the Treasury spot rates yield curve, so that the NPV of the bond cash flows (using the adjusted yield curve) equa
Flashcard 149626437
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itgle series of nominal cash flows (like a riskless bond). If these payments are discounted to net present value with a static treasury yield curve the sum of their values will tend to overestimate the market price of the priced instrument. The <span>parallel shift, which, if applied to the yield curve makes the NPV of the anticipated receipts equal to the market price is the Yield curve spread (aka Z-spread).<span><body><html>
Original toplevel document
Z-spread - Wikipedia, the free encyclopediaage-backed securities, a model of typical repayment rates tends to be given; for example, the PSA formula for a particular Fannie Mae MBS might equate a particular group of mortgages to an 8 year amortizing bond with a 5% mortality per annum. <span>This gives a single series of nominal cash flows (like a riskless bond). If these payments are discounted to net present value with a static treasury yield curve the sum of their values will tend to overestimate the market price of the MBS. The parallel shift, which, if applied to the yield curve makes the NPV of the anticipated receipts equal to the market price is the Yield curve spread. The Z-spread of a bond is the number of basis points one needs to add to the Treasury spot rates yield curve, so that the NPV of the bond cash flows (using the adjusted yield curve) equa
Flashcard 149626455
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itMacaulay duration is a weighted average time until repayment (measured in units of time such as years)
Original toplevel document
Bond duration - Wikipedia, the free encyclopediathe asset. This gives the well-known relation between Macaulay duration and modified duration quoted above. It should be remembered that, even though Macaulay duration and modified duration are closely related, they are conceptually distinct. <span>Macaulay duration is a weighted average time until repayment (measured in units of time such as years) while modified duration is a price sensitivity measure when the price is treated as a function of yield, the percentage change in price with respect to yield. Units[edit] For modified du
Flashcard 149626468
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itmodified duration is a price sensitivity measure when the price is treated as a function of yield, the percentage change in price with respect to yield.
Original toplevel document
Bond duration - Wikipedia, the free encyclopediat should be remembered that, even though Macaulay duration and modified duration are closely related, they are conceptually distinct. Macaulay duration is a weighted average time until repayment (measured in units of time such as years) while <span>modified duration is a price sensitivity measure when the price is treated as a function of yield, the percentage change in price with respect to yield. Units[edit] For modified duration the common units are the percent change in price per one percentage point change in yield per year (for example yield going from 8% per year (y = 0.08)
Flashcard 149626487
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itConventionally, the zero rates for calculating Z-spread are determined from the Treasury curve, with semi-annual compounding.
Original toplevel document
Z-spread - Wikipedia, the free encyclopediaonal factors such as liquidity and credit risk. The Z-spread quantifies the impact of these additional factors. It is the spread you need to add to the curve you are discounting with in order to generate a price that matches the market price. <span>Conventionally, the zero rates are determined from the Treasury curve, with semi-annual compounding. The Problem with YTM spreads[edit] Coupon Paying bonds are essentially portfolios of Zero Coupon Bond components and the Yield to Maturity of such instruments can be thought of as being
Flashcard 149626507
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 149626518
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 149626529
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 149626540
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 149626551
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 149626566
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 149626577
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 149626604
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Article 149626615
Joshua Bloch "Effective Java"
#bloch-effective-java-2ed #java
Book on effective use of Java, must-read when you prepare for an interview as a Java programmer. I was reading the book and every flashcard or article I created were annotated like this: #bloch-effective-java-2ed #java #pXX, where XX is page number. The book can be found in amazon.co.uk
Flashcard 149626624
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 149626651
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 149626678
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Article 149626689
#bloch-effective-java-2ed #java #p109
A class or interface whose declaration has one or more type parameters is a generic class or interface.
Flashcard 149626698
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Open it
A class or interface whose declaration has one or more type parameters is a generic class or interface.
A class or interface whose declaration has one or more type parameters is a generic class or interface.
Flashcard 149626705
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Open it
A class or interface whose declaration has one or more type parameters is a generic class or interface.
A class or interface whose declaration has one or more type parameters is a generic class or interface.
Flashcard 149626721
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Article 149626728
#bloch-effective-java-2ed #java #p109
Each generic type defines a set of parameterized types, which consist of the class or interface name followed by an angle-bracketed list of actual type parameters corresponding to the generic type’s formal type parameters.
Flashcard 149626737
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Open it
Each generic type defines a set of parameterized types, which consist of the class or interface name followed by an angle-bracketed list of actual type parameters corresponding to the generic type’s formal type parameters.</bo
Each generic type defines a set of parameterized types, which consist of the class or interface name followed by an angle-bracketed list of actual type parameters corresponding to the generic type’s formal type parameters.</bo
Flashcard 149626744
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Open it
Each generic type defines a set of parameterized types, which consist of the class or interface name followed by an angle-bracketed list of actual type parameters corresponding to the generic type’s formal type parameters.
Each generic type defines a set of parameterized types, which consist of the class or interface name followed by an angle-bracketed list of actual type parameters corresponding to the generic type’s formal type parameters.
Article 149626755
#bloch-effective-java-2ed #java #p109
Each generic type defines a raw type, which is the name of the generic type used without any accompanying actual type parameters
Flashcard 149626764
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Open it
Each generic type defines a raw type, which is the name of the generic type used without any accompanying actual type parameters
Each generic type defines a raw type, which is the name of the generic type used without any accompanying actual type parameters
Flashcard 149626771
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Open it
Each generic type defines a raw type, which is the name of the generic type used without any accompanying actual type parameters
Each generic type defines a raw type, which is the name of the generic type used without any accompanying actual type parameters
Flashcard 149626778
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 149626789
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Article 149626800
generics terms quick reference
#bloch-effective-java-2ed #java #p115
TermExampleParameterized typeList<String>Actual type parameterStringGeneric typeList<E>Formal type parameterEUnbounded wildcard typeList<?>Raw typeListBounded type parameter<E extends Number>Recursive type bound<T extends Comparable<T>>Bounded wildcard typeList<? extends Number>Generic method static<E> List<E> asList(E[] a)Type tokenString.class
Flashcard 149626809
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
generics terms quick reference
TermExampleParameterized typeListActual type parameterStringGeneric typeListFormal type parameterEUnbounded wildcard typeListRaw typeListBounded type parameterRecursive type bound>Bounded wildcard typeListGeneric
TermExampleParameterized typeListActual type parameterStringGeneric typeListFormal type parameterEUnbounded wildcard typeListRaw typeListBounded type parameterRecursive type bound>Bounded wildcard typeListGeneric
Flashcard 149626816
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
generics terms quick reference
TermExampleParameterized typeListActual type parameterStringGeneric typeListFormal type parameterEUnbounded wildcard typeListRaw typeListBounded type parameterRecursive type bound>Bounded wildcard typeListGeneric method static List asLis
TermExampleParameterized typeListActual type parameterStringGeneric typeListFormal type parameterEUnbounded wildcard typeListRaw typeListBounded type parameterRecursive type bound>Bounded wildcard typeListGeneric method static List asLis
Flashcard 149626823
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
generics terms quick reference
TermExampleParameterized typeListActual type parameterStringGeneric typeListFormal type parameterEUnbounded wildcard typeListRaw typeListBounded type parameterRecursive type bound>Bounded wildcard typeListGeneric method static List asList(E[] a)Type token
TermExampleParameterized typeListActual type parameterStringGeneric typeListFormal type parameterEUnbounded wildcard typeListRaw typeListBounded type parameterRecursive type bound>Bounded wildcard typeListGeneric method static List asList(E[] a)Type token
Flashcard 149626830
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
generics terms quick reference
TermExampleParameterized typeListActual type parameterStringGeneric typeListFormal type parameterEUnbounded wildcard typeListRaw typeListBounded type parameterRecursive type bound>Bounded wildcard typeListGeneric method static List asList(E[] a)Type tokenString.class
TermExampleParameterized typeListActual type parameterStringGeneric typeListFormal type parameterEUnbounded wildcard typeListRaw typeListBounded type parameterRecursive type bound>Bounded wildcard typeListGeneric method static List asList(E[] a)Type tokenString.class
Flashcard 149626837
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
generics terms quick reference
TermExampleParameterized typeListActual type parameterStringGeneric typeListFormal type parameterEUnbounded wildcard typeListRaw typeListBounded type parameterRecursive type bound>Bounded wildcard typeListGeneric method static List asList(E[] a)Type tokenString.class
TermExampleParameterized typeListActual type parameterStringGeneric typeListFormal type parameterEUnbounded wildcard typeListRaw typeListBounded type parameterRecursive type bound>Bounded wildcard typeListGeneric method static List asList(E[] a)Type tokenString.class
Flashcard 149626844
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
generics terms quick reference
TermExampleParameterized typeListActual type parameterStringGeneric typeListFormal type parameterEUnbounded wildcard typeListRaw typeListBounded type parameterRecursive type bound>Bounded wildcard typeListGeneric method static List asList(E[] a)Type tokenString.class
TermExampleParameterized typeListActual type parameterStringGeneric typeListFormal type parameterEUnbounded wildcard typeListRaw typeListBounded type parameterRecursive type bound>Bounded wildcard typeListGeneric method static List asList(E[] a)Type tokenString.class
Flashcard 149626851
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
generics terms quick reference
TermExampleParameterized typeListActual type parameterStringGeneric typeListFormal type parameterEUnbounded wildcard typeListRaw typeListBounded type parameterRecursive type bound>Bounded wildcard typeListGeneric method static List asList(E[] a)Type tokenString.class
TermExampleParameterized typeListActual type parameterStringGeneric typeListFormal type parameterEUnbounded wildcard typeListRaw typeListBounded type parameterRecursive type bound>Bounded wildcard typeListGeneric method static List asList(E[] a)Type tokenString.class
Flashcard 149626858
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
generics terms quick reference
TermExampleParameterized typeListActual type parameterStringGeneric typeListFormal type parameterEUnbounded wildcard typeListRaw typeListBounded type parameterRecursive type bound>Bounded wildcard typeListGeneric method static List asList(E[] a)Type tokenString.class
TermExampleParameterized typeListActual type parameterStringGeneric typeListFormal type parameterEUnbounded wildcard typeListRaw typeListBounded type parameterRecursive type bound>Bounded wildcard typeListGeneric method static List asList(E[] a)Type tokenString.class
Flashcard 149626865
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
generics terms quick reference
TermExampleParameterized typeListActual type parameterStringGeneric typeListFormal type parameterEUnbounded wildcard typeListRaw typeListBounded type parameterRecursive type bound>Bounded wildcard typeListGeneric method static List asList(E[] a)Type tokenString.class
TermExampleParameterized typeListActual type parameterStringGeneric typeListFormal type parameterEUnbounded wildcard typeListRaw typeListBounded type parameterRecursive type bound>Bounded wildcard typeListGeneric method static List asList(E[] a)Type tokenString.class
Flashcard 149626872
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
generics terms quick reference
tml>TermExampleParameterized typeListActual type parameterStringGeneric typeListFormal type parameterEUnbounded wildcard typeListRaw typeListBounded type parameterRecursive type bound>Bounded wildcard typeListGeneric method static List asList(E[] a)Type tokenString.class<html>
tml>TermExampleParameterized typeListActual type parameterStringGeneric typeListFormal type parameterEUnbounded wildcard typeListRaw typeListBounded type parameterRecursive type bound>Bounded wildcard typeListGeneric method static List asList(E[] a)Type tokenString.class<html>
Flashcard 149626879
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
generics terms quick reference
xampleParameterized typeListActual type parameterStringGeneric typeListFormal type parameterEUnbounded wildcard typeListRaw typeListBounded type parameterRecursive type bound>Bounded wildcard typeListGeneric method static List asList(E[] a)<span>Type tokenString.class<span><body><html>
xampleParameterized typeListActual type parameterStringGeneric typeListFormal type parameterEUnbounded wildcard typeListRaw typeListBounded type parameterRecursive type bound>Bounded wildcard typeListGeneric method static List asList(E[] a)<span>Type tokenString.class<span><body><html>
Flashcard 149626886
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
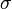 )
)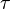 )
)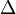
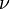
 )
) 
 )
)