Edited, memorised or added to reading queue
on 18-Sep-2020 (Fri)
Do you want BuboFlash to help you learning these things? Click here to log in or create user.
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Carbon cycle - Wikipedia
des. It remains unclear if carbon absorption will continue at this rate.[7] Epiphytes on electric wires. This kind of plant takes both CO 2 and water from the atmosphere for living and growing. <span>Carbon in the Earth's atmosphere exists in two main forms: carbon dioxide and methane. Both of these gases absorb and retain heat in the atmosphere and are partially responsible for the greenhouse effect.[4] Methane produces a larger greenhouse effect per volume as compared to carbon dioxide, but it exists in much lower concentrations and is more short-lived than carbon dioxide, making carbon dioxide the more important greenhouse gas of the two.[8] Carbon dioxide is removed from the atmosphere primarily through photosynthesis and enters the terrestrial and oceanic biospheres. Carbon dioxide also dissolves directly from the atmosph
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Carbon cycle - Wikipedia
illion years into the future.[12][full citation needed] Terrestrial biosphere[edit] Main article: Terrestrial biological carbon cycle A portable soil respiration system measuring soil CO 2 flux <span>The terrestrial biosphere includes the organic carbon in all land-living organisms, both alive and dead, as well as carbon stored in soils. About 500 gigatons of carbon are stored above ground in plants and other living organisms,[5] while soil holds approximately 1,500 gigatons of carbon.[13] Most carbon in the terrestrial biosphere is organic carbon,[14] while about a third of soil carbon is stored in inorganic forms, such as calcium carbonate.[15] Organic carbon is a
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
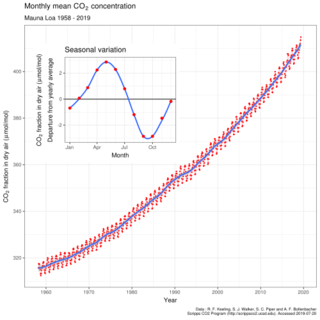
Keeling Curve - Wikipedia
ia Keeling Curve From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia (Redirected from Keeling curve) Jump to navigation Jump to search "Keeling" redirects here. For other uses, see Keeling (disambiguation). <span>Atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO 2) concentrations from 1958 to 2019 The Keeling Curve is a graph of the accumulation of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere based on continuous measurements taken at the Mauna Loa Observatory on the island of Hawaii