Edited, memorised or added to reading queue
on 08-May-2022 (Sun)
Do you want BuboFlash to help you learning these things? Click here to log in or create user.
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
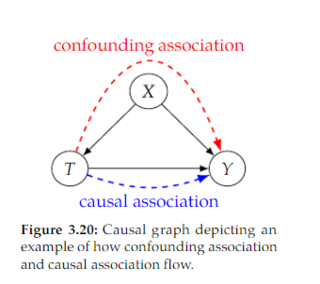
Open itWe refer to the flow of association along directed paths as causal association. A common type of non-causal association that makes total association not causation is confounding association. In the graph in Figure 3.20, we depict the confounding association in red
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itCausal graphs are special in that we additionally assume that the edges have causal meaning (causal edges assumption, Assumption 3.3). This assumption is what introduces causality into our models, and it makes one type of path take on a whole new meaning: directed paths. This assumption endows directed paths with the unique role of carrying causation along them. Additionally, this assumption is asymmetric; “ 𝑋 is a cause of 𝑌 ” is not the same as saying
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itThe Positivity-Unconfoundedness Tradeoff Although conditioning on more covariates could lead to a higher chance of satisfying unconfoundedness, it can lead to a higher chance of violating positivity. As we increase the dimension of the covariates, we make the subgroups for any level 𝑥 of the covariates smaller.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 7082270395660
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itAs we discussed in Section 4.2, the graph for the interventional distribution 𝑃(𝑌 | do(𝑡)) is the same as the graph for the observational distribution 𝑃(𝑌, 𝑇, 𝑋) , but with the incoming edges to 𝑇 removed.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itened node has no causal parents is that the intervened node is set to a constant value, so it no longer depends on any of the variables it depends on in the observational setting (its parents). <span>The graph with edges removed is known as the manipulated graph <span>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 7082274327820
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
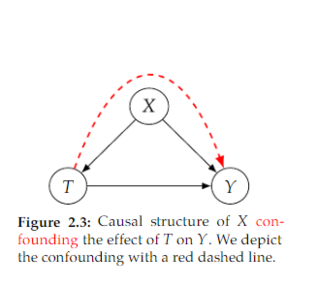
Open itThis non-causal association flows along the 𝑇 ← 𝑋 → 𝑌 path
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |