Do you want BuboFlash to help you learning these things? Or do you want to add or correct something? Click here to log in or create user.
#has-images #ir #peds
Bullying
Syllabus: Lamb et al. Approach to Bullying and Victimization. Canadian Family
Physician. 2009;55(4):356.
Introduction
• Defined as the use of power or aggression to cause distress or control
of another
• Can be direct (face‐to‐face) or indirect (gossip, exclusion)
• Negative actions can include:
o Physical actions (punching, kicking, biting)
o Verbal actions (threats, name calling, insults)
o Social exclusion (spreading rumours, gossiping, excluding)
• Actions are repeated and the intensity or duration establishes
dominance
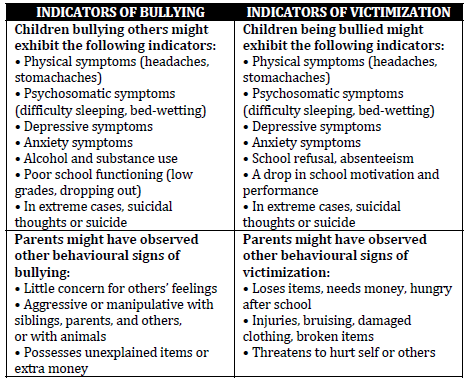
History
• When a physician identifies a possible bullying situation, the following
questions can help determine what type of help may be appropriate
o Who do you bully/who bullys you?
o What do you do to others/what do others do to you? (e.g. gossiping,
insults, hitting, etc.)
o When and how often do you bully/are you bullied?
o Where do you bully/where are you bullied?
o Why do you bully others/why do you think you are bullied?
o How do you think the kids feel when you bully them or how do you
feel when you are bullied?
Management
• Comprehensive strategies that encompass the school, family and
community are most likely to be effective
o establish a social school environment that promotes safety
o provide access to health and mental health services
o integrate school, family and community prevention efforts
o provide training to enable school staff to promote safety and
prevent violence effectively
Syllabus: Lamb et al. Approach to Bullying and Victimization. Canadian Family
Physician. 2009;55(4):356.
Introduction
• Defined as the use of power or aggression to cause distress or control
of another
• Can be direct (face‐to‐face) or indirect (gossip, exclusion)
• Negative actions can include:
o Physical actions (punching, kicking, biting)
o Verbal actions (threats, name calling, insults)
o Social exclusion (spreading rumours, gossiping, excluding)
• Actions are repeated and the intensity or duration establishes
dominance

History
• When a physician identifies a possible bullying situation, the following
questions can help determine what type of help may be appropriate
o Who do you bully/who bullys you?
o What do you do to others/what do others do to you? (e.g. gossiping,
insults, hitting, etc.)
o When and how often do you bully/are you bullied?
o Where do you bully/where are you bullied?
o Why do you bully others/why do you think you are bullied?
o How do you think the kids feel when you bully them or how do you
feel when you are bullied?
Management
• Comprehensive strategies that encompass the school, family and
community are most likely to be effective
o establish a social school environment that promotes safety
o provide access to health and mental health services
o integrate school, family and community prevention efforts
o provide training to enable school staff to promote safety and
prevent violence effectively
If you want to change selection, open document below and click on "Move attachment"
Development
been identified as exceptional by the IPRC process. An IEP is a written plan that describes the strengths and needs of the student, services established to meet that student’s needs, and how these should be delivered <span>Bullying Syllabus: Lamb et al. Approach to Bullying and Victimization. Canadian Family Physician. 2009;55(4):356. Introduction • Defined as the use of power or aggression to cause distress or control of another • Can be direct (face‐to‐face) or indirect (gossip, exclusion) • Negative actions can include: o Physical actions (punching, kicking, biting) o Verbal actions (threats, name calling, insults) o Social exclusion (spreading rumours, gossiping, excluding) • Actions are repeated and the intensity or duration establishes dominance History • When a physician identifies a possible bullying situation, the following questions can help determine what type of help may be appropriate o Who do you bully/who bullys you? o What do you do to others/what do others do to you? (e.g. gossiping, insults, hitting, etc.) o When and how often do you bully/are you bullied? o Where do you bully/where are you bullied? o Why do you bully others/why do you think you are bullied? o How do you think the kids feel when you bully them or how do you feel when you are bullied? Management • Comprehensive strategies that encompass the school, family and community are most likely to be effective o establish a social school environment that promotes safety o provide access to health and mental health services o integrate school, family and community prevention efforts o provide training to enable school staff to promote safety and prevent violence effectively Toilet Training Syllabus: Clifford et al. Toilet Learning: Anticipatory Guidance with a child‐oriented approach. Paediatrics and Child Health. 2000;5(6):333. F
Development
been identified as exceptional by the IPRC process. An IEP is a written plan that describes the strengths and needs of the student, services established to meet that student’s needs, and how these should be delivered <span>Bullying Syllabus: Lamb et al. Approach to Bullying and Victimization. Canadian Family Physician. 2009;55(4):356. Introduction • Defined as the use of power or aggression to cause distress or control of another • Can be direct (face‐to‐face) or indirect (gossip, exclusion) • Negative actions can include: o Physical actions (punching, kicking, biting) o Verbal actions (threats, name calling, insults) o Social exclusion (spreading rumours, gossiping, excluding) • Actions are repeated and the intensity or duration establishes dominance History • When a physician identifies a possible bullying situation, the following questions can help determine what type of help may be appropriate o Who do you bully/who bullys you? o What do you do to others/what do others do to you? (e.g. gossiping, insults, hitting, etc.) o When and how often do you bully/are you bullied? o Where do you bully/where are you bullied? o Why do you bully others/why do you think you are bullied? o How do you think the kids feel when you bully them or how do you feel when you are bullied? Management • Comprehensive strategies that encompass the school, family and community are most likely to be effective o establish a social school environment that promotes safety o provide access to health and mental health services o integrate school, family and community prevention efforts o provide training to enable school staff to promote safety and prevent violence effectively Toilet Training Syllabus: Clifford et al. Toilet Learning: Anticipatory Guidance with a child‐oriented approach. Paediatrics and Child Health. 2000;5(6):333. F
Summary
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Details
Discussion
Do you want to join discussion? Click here to log in or create user.