Do you want BuboFlash to help you learning these things? Or do you want to add or correct something? Click here to log in or create user.
#has-images #ir #peds
Sleep Requirements
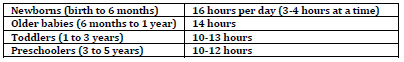
Newborns
• Should sleep on back in crib with flat surface, no pillows or soft items
• In parents’ room for first 6 months
Older babies
• Maintain regular daytime and bedtime schedule
• Start consistent bedtime routine
• Avoid putting baby to bed with a bottle
Sleep Problems
Night terrors
• Parasomnia that occurs in first third of night
• High to extreme autonomic agitation
• High arousal threshold, agitated if awakened
• No daytime sleepiness or recall of event
Nightmares
• Occur in last third of night during REM sleep
• Mild to high autonomic arousal/agitation
• Low arousal threshold, agitated after event
• Can have daytime sleepiness and frequent, vivid recall of event
• Very common
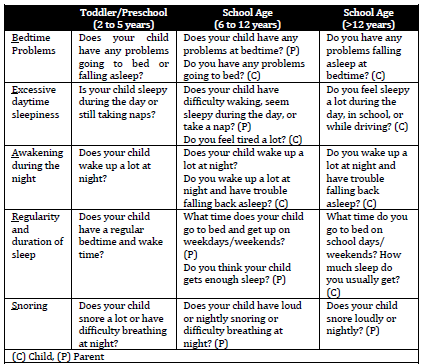
BEARS Screening Tool for Pediatric Sleep Disorders
Sleep associations
• Infant or toddler child has learned to fall asleep only under certain
conditions or has specific sleep associations that require parental
intervention, such as being rocked or fed, which are usually readily
available at bedtime
• During the night, when the infant or toddler awakens, they are not able
to get back to sleep ("self‐soothe") unless those same conditions are
available
90
o The infant then "signals" the caregiver by crying or coming into the
parents' bedroom if the child is no longer in a crib until the
necessary associations are provided
o Ferber method advocates that at bedtime child is put in bed while
they are drowsy, but still awake, to help them learn how to fall
asleep on their own (self‐soothe)

Newborns
• Should sleep on back in crib with flat surface, no pillows or soft items
• In parents’ room for first 6 months
Older babies
• Maintain regular daytime and bedtime schedule
• Start consistent bedtime routine
• Avoid putting baby to bed with a bottle
Sleep Problems
Night terrors
• Parasomnia that occurs in first third of night
• High to extreme autonomic agitation
• High arousal threshold, agitated if awakened
• No daytime sleepiness or recall of event
Nightmares
• Occur in last third of night during REM sleep
• Mild to high autonomic arousal/agitation
• Low arousal threshold, agitated after event
• Can have daytime sleepiness and frequent, vivid recall of event
• Very common
BEARS Screening Tool for Pediatric Sleep Disorders

Sleep associations
• Infant or toddler child has learned to fall asleep only under certain
conditions or has specific sleep associations that require parental
intervention, such as being rocked or fed, which are usually readily
available at bedtime
• During the night, when the infant or toddler awakens, they are not able
to get back to sleep ("self‐soothe") unless those same conditions are
available
90
o The infant then "signals" the caregiver by crying or coming into the
parents' bedroom if the child is no longer in a crib until the
necessary associations are provided
o Ferber method advocates that at bedtime child is put in bed while
they are drowsy, but still awake, to help them learn how to fall
asleep on their own (self‐soothe)
If you want to change selection, open document below and click on "Move attachment"
Development
least a few should be present to indicate the child is ready for toilet training - Average age for a child to be toilet trained is between 2 to 3 years old - Advise parents to expect accidents during initial training <span>Sleep Requirements Newborns • Should sleep on back in crib with flat surface, no pillows or soft items • In parents’ room for first 6 months Older babies • Maintain regular daytime and bedtime schedule • Start consistent bedtime routine • Avoid putting baby to bed with a bottle Sleep Problems Night terrors • Parasomnia that occurs in first third of night • High to extreme autonomic agitation • High arousal threshold, agitated if awakened • No daytime sleepiness or recall of event Nightmares • Occur in last third of night during REM sleep • Mild to high autonomic arousal/agitation • Low arousal threshold, agitated after event • Can have daytime sleepiness and frequent, vivid recall of event • Very common BEARS Screening Tool for Pediatric Sleep Disorders Sleep associations • Infant or toddler child has learned to fall asleep only under certain conditions or has specific sleep associations that require parental intervention, such as being rocked or fed, which are usually readily available at bedtime • During the night, when the infant or toddler awakens, they are not able to get back to sleep ("self‐soothe") unless those same conditions are available 90 o The infant then "signals" the caregiver by crying or coming into the parents' bedroom if the child is no longer in a crib until the necessary associations are provided o Ferber method advocates that at bedtime child is put in bed while they are drowsy, but still awake, to help them learn how to fall asleep on their own (self‐soothe) Colic Syllabus: Cohen et al. Colic. Pediatrics in Review. 2012;33(7):332. • Infantile colic is defined as o paroxysms of irritability, fussiness or crying that
Development
least a few should be present to indicate the child is ready for toilet training - Average age for a child to be toilet trained is between 2 to 3 years old - Advise parents to expect accidents during initial training <span>Sleep Requirements Newborns • Should sleep on back in crib with flat surface, no pillows or soft items • In parents’ room for first 6 months Older babies • Maintain regular daytime and bedtime schedule • Start consistent bedtime routine • Avoid putting baby to bed with a bottle Sleep Problems Night terrors • Parasomnia that occurs in first third of night • High to extreme autonomic agitation • High arousal threshold, agitated if awakened • No daytime sleepiness or recall of event Nightmares • Occur in last third of night during REM sleep • Mild to high autonomic arousal/agitation • Low arousal threshold, agitated after event • Can have daytime sleepiness and frequent, vivid recall of event • Very common BEARS Screening Tool for Pediatric Sleep Disorders Sleep associations • Infant or toddler child has learned to fall asleep only under certain conditions or has specific sleep associations that require parental intervention, such as being rocked or fed, which are usually readily available at bedtime • During the night, when the infant or toddler awakens, they are not able to get back to sleep ("self‐soothe") unless those same conditions are available 90 o The infant then "signals" the caregiver by crying or coming into the parents' bedroom if the child is no longer in a crib until the necessary associations are provided o Ferber method advocates that at bedtime child is put in bed while they are drowsy, but still awake, to help them learn how to fall asleep on their own (self‐soothe) Colic Syllabus: Cohen et al. Colic. Pediatrics in Review. 2012;33(7):332. • Infantile colic is defined as o paroxysms of irritability, fussiness or crying that
Summary
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Details
Discussion
Do you want to join discussion? Click here to log in or create user.