Do you want BuboFlash to help you learning these things? Or do you want to add or correct something? Click here to log in or create user.
Tags
#has-images #quantitative-methods-basic-concepts #statistics
Question
The harmonic mean of n numbers xi (where i = 1, 2, ..., n) is:
XH = [...]
Answer
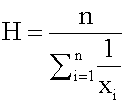
Tags
#has-images #quantitative-methods-basic-concepts #statistics
Question
The harmonic mean of n numbers xi (where i = 1, 2, ..., n) is:
XH = [...]
Answer
?
Tags
#has-images #quantitative-methods-basic-concepts #statistics
Question
The harmonic mean of n numbers xi (where i = 1, 2, ..., n) is:
XH = [...]
Answer
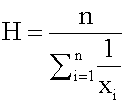
If you want to change selection, open original toplevel document below and click on "Move attachment"
Harmonic Mean The harmonic mean of n numbers x i (where i = 1, 2, ..., n) is: The special cases of n = 2 and n = 3 are given by: and so on.
, therefore, is not recommended for use as the only measure of central tendency. A further disadvantage of the mode is that many distributions have more than one mode. These distributions are called "multimodal." <span>Harmonic Mean The harmonic mean of n numbers x i (where i = 1, 2, ..., n) is: The special cases of n = 2 and n = 3 are given by: and so on. For n = 2, the harmonic mean is related to arithmetic mean A and geometric mean G by: The mean, median, and mode are equal in symmetric distributions. The mean is higher than the median in positively skewed distributions and lower than the median in negatively skewed dist
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itHarmonic Mean The harmonic mean of n numbers x i (where i = 1, 2, ..., n) is: The special cases of n = 2 and n = 3 are given by: and so on.
Original toplevel document
Subject 4. Measures of Center Tendency, therefore, is not recommended for use as the only measure of central tendency. A further disadvantage of the mode is that many distributions have more than one mode. These distributions are called "multimodal." <span>Harmonic Mean The harmonic mean of n numbers x i (where i = 1, 2, ..., n) is: The special cases of n = 2 and n = 3 are given by: and so on. For n = 2, the harmonic mean is related to arithmetic mean A and geometric mean G by: The mean, median, and mode are equal in symmetric distributions. The mean is higher than the median in positively skewed distributions and lower than the median in negatively skewed dist
Summary
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Details
No repetitionsDiscussion
Do you want to join discussion? Click here to log in or create user.