Do you want BuboFlash to help you learning these things? Or do you want to add or correct something? Click here to log in or create user.
Tags
#causality #has-images #statistics
Question
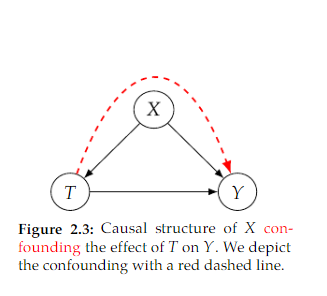
We do not have [...] in the data because 𝑋 is a common cause of 𝑇 and 𝑌 . We illustrate this in Figure 2.3. Because 𝑋 is a common cause of 𝑇 and 𝑌 , there is non-causal association between 𝑇 and 𝑌 . This non-causal association flows along the 𝑇 ← 𝑋 → 𝑌 path; we depict this with a red dashed arc
Answer
exchangeability
Tags
#causality #has-images #statistics

Question
We do not have [...] in the data because 𝑋 is a common cause of 𝑇 and 𝑌 . We illustrate this in Figure 2.3. Because 𝑋 is a common cause of 𝑇 and 𝑌 , there is non-causal association between 𝑇 and 𝑌 . This non-causal association flows along the 𝑇 ← 𝑋 → 𝑌 path; we depict this with a red dashed arc
Answer
?
Tags
#causality #has-images #statistics

Question
We do not have [...] in the data because 𝑋 is a common cause of 𝑇 and 𝑌 . We illustrate this in Figure 2.3. Because 𝑋 is a common cause of 𝑇 and 𝑌 , there is non-causal association between 𝑇 and 𝑌 . This non-causal association flows along the 𝑇 ← 𝑋 → 𝑌 path; we depict this with a red dashed arc
Answer
exchangeability
If you want to change selection, open original toplevel document below and click on "Move attachment"
We do not have exchangeability in the data because 𝑋 is a common cause of 𝑇 and 𝑌 . We illustrate this in Figure 2.3. Because 𝑋 is a common cause of 𝑇 and 𝑌 , there is non-causal association between 𝑇 and 𝑌 . This no
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itWe do not have exchangeability in the data because 𝑋 is a common cause of 𝑇 and 𝑌 . We illustrate this in Figure 2.3. Because 𝑋 is a common cause of 𝑇 and 𝑌 , there is non-causal association between 𝑇 and 𝑌 . This no
Original toplevel document (pdf)
owner: crocodile - (no access) - Introduction_to_Causal_Inference-Nov19_2020-Neal.pdf, p19Summary
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Details
No repetitionsDiscussion
Do you want to join discussion? Click here to log in or create user.