Edited, memorised or added to reading queue
on 02-Oct-2016 (Sun)
Do you want BuboFlash to help you learning these things? Click here to log in or create user.
Flashcard 1402802933004
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
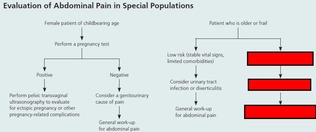
Open itGeneral inspection Change in mental status (infection - UTI) Shock (perforated viscera, GI hemorrhage, severe pancreatitis, MI, sepsis)
Original toplevel document
Abdo PainCholecystitis (highest to lowest PPV) RUQ pain, fever, jaundice IBS algorithm <span>Objective General inspection Change in mental status (infection - UTI) Shock (perforated viscera, GI hemorrhage, severe pancreatitis, MI, sepsis) Vitals Upper abdo pain - pay attention to Cardiac (ischemia) & lung (pneumonia) exams Tachypneic (pneumonia) Abdo peritoneal signs Carnett’s sign (high ppv for abdo wall pain) ↑ pain when supine pt raises head & shoulder, tensing abdo wall Murphy’s sign (high ppv for choleycystitis) Psoas sign (high ppv for appendicitis) Sever pain out of proportion (ischemic bowel, pancreatitis) restless/writhing (biliary/renal colic, testicular torsion) LLQ tenderness (diverticulitis) Rectal & pelvic exams if lower abdo & pelvic pain DRE - fecal impaction, palpable mass, occult blood in stool Tenderness & fullness on R of rectum suggests retrocecal appendix Pelvic - vaginal discharge (vaginitis), cervical motion tenderness & peritoneal signs (ectopic pregnancy or other gyne complications e.g. tubo-ovarian abscess) S&S of surgical abdo Fever Protracted (prolonged) vomiting syncope/pre-syncope Evidence of GI blood loss
Flashcard 1402805292300
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itAbdo peritoneal signs Carnett’s sign (high ppv for abdo wall pain) ↑ pain when supine pt raises head & shoulder, tensing abdo wall Murphy’s sign (high ppv for choleycystitis) Psoas sign (high ppv for appendicitis) Sever pain out of proportion (ischemic bowel, pancreatitis) restless/writhing (biliary/renal colic, testicular torsion) LLQ tenderness (diverticulitis)
Original toplevel document
Abdo PainCholecystitis (highest to lowest PPV) RUQ pain, fever, jaundice IBS algorithm <span>Objective General inspection Change in mental status (infection - UTI) Shock (perforated viscera, GI hemorrhage, severe pancreatitis, MI, sepsis) Vitals Upper abdo pain - pay attention to Cardiac (ischemia) & lung (pneumonia) exams Tachypneic (pneumonia) Abdo peritoneal signs Carnett’s sign (high ppv for abdo wall pain) ↑ pain when supine pt raises head & shoulder, tensing abdo wall Murphy’s sign (high ppv for choleycystitis) Psoas sign (high ppv for appendicitis) Sever pain out of proportion (ischemic bowel, pancreatitis) restless/writhing (biliary/renal colic, testicular torsion) LLQ tenderness (diverticulitis) Rectal & pelvic exams if lower abdo & pelvic pain DRE - fecal impaction, palpable mass, occult blood in stool Tenderness & fullness on R of rectum suggests retrocecal appendix Pelvic - vaginal discharge (vaginitis), cervical motion tenderness & peritoneal signs (ectopic pregnancy or other gyne complications e.g. tubo-ovarian abscess) S&S of surgical abdo Fever Protracted (prolonged) vomiting syncope/pre-syncope Evidence of GI blood loss
Flashcard 1402809224460
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itRectal & pelvic exams if lower abdo & pelvic pain DRE - fecal impaction, palpable mass, occult blood in stool Tenderness & fullness on R of rectum suggests retrocecal appendix
Original toplevel document
Abdo PainCholecystitis (highest to lowest PPV) RUQ pain, fever, jaundice IBS algorithm <span>Objective General inspection Change in mental status (infection - UTI) Shock (perforated viscera, GI hemorrhage, severe pancreatitis, MI, sepsis) Vitals Upper abdo pain - pay attention to Cardiac (ischemia) & lung (pneumonia) exams Tachypneic (pneumonia) Abdo peritoneal signs Carnett’s sign (high ppv for abdo wall pain) ↑ pain when supine pt raises head & shoulder, tensing abdo wall Murphy’s sign (high ppv for choleycystitis) Psoas sign (high ppv for appendicitis) Sever pain out of proportion (ischemic bowel, pancreatitis) restless/writhing (biliary/renal colic, testicular torsion) LLQ tenderness (diverticulitis) Rectal & pelvic exams if lower abdo & pelvic pain DRE - fecal impaction, palpable mass, occult blood in stool Tenderness & fullness on R of rectum suggests retrocecal appendix Pelvic - vaginal discharge (vaginitis), cervical motion tenderness & peritoneal signs (ectopic pregnancy or other gyne complications e.g. tubo-ovarian abscess) S&S of surgical abdo Fever Protracted (prolonged) vomiting syncope/pre-syncope Evidence of GI blood loss
Flashcard 1402811583756
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itRectal & pelvic exams if lower abdo & pelvic pain DRE - fecal impaction, palpable mass, occult blood in stool Tenderness & fullness on R of rectum suggests retrocecal appendix Pelvic - vaginal discharge (vaginitis), cervical motion tenderness & peritoneal signs (
Original toplevel document
Abdo PainCholecystitis (highest to lowest PPV) RUQ pain, fever, jaundice IBS algorithm <span>Objective General inspection Change in mental status (infection - UTI) Shock (perforated viscera, GI hemorrhage, severe pancreatitis, MI, sepsis) Vitals Upper abdo pain - pay attention to Cardiac (ischemia) & lung (pneumonia) exams Tachypneic (pneumonia) Abdo peritoneal signs Carnett’s sign (high ppv for abdo wall pain) ↑ pain when supine pt raises head & shoulder, tensing abdo wall Murphy’s sign (high ppv for choleycystitis) Psoas sign (high ppv for appendicitis) Sever pain out of proportion (ischemic bowel, pancreatitis) restless/writhing (biliary/renal colic, testicular torsion) LLQ tenderness (diverticulitis) Rectal & pelvic exams if lower abdo & pelvic pain DRE - fecal impaction, palpable mass, occult blood in stool Tenderness & fullness on R of rectum suggests retrocecal appendix Pelvic - vaginal discharge (vaginitis), cervical motion tenderness & peritoneal signs (ectopic pregnancy or other gyne complications e.g. tubo-ovarian abscess) S&S of surgical abdo Fever Protracted (prolonged) vomiting syncope/pre-syncope Evidence of GI blood loss
Flashcard 1402813943052
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itRectal & pelvic exams if lower abdo & pelvic pain DRE - fecal impaction, palpable mass, occult blood in stool Tenderness & fullness on R of rectum suggests retrocecal appendix Pelvic - vaginal discharge (vaginitis), cervical motion tenderness & peritoneal signs (ectopic pregnancy or other gyne complications e.g. tubo-ovarian abscess) <
Original toplevel document
Abdo PainCholecystitis (highest to lowest PPV) RUQ pain, fever, jaundice IBS algorithm <span>Objective General inspection Change in mental status (infection - UTI) Shock (perforated viscera, GI hemorrhage, severe pancreatitis, MI, sepsis) Vitals Upper abdo pain - pay attention to Cardiac (ischemia) & lung (pneumonia) exams Tachypneic (pneumonia) Abdo peritoneal signs Carnett’s sign (high ppv for abdo wall pain) ↑ pain when supine pt raises head & shoulder, tensing abdo wall Murphy’s sign (high ppv for choleycystitis) Psoas sign (high ppv for appendicitis) Sever pain out of proportion (ischemic bowel, pancreatitis) restless/writhing (biliary/renal colic, testicular torsion) LLQ tenderness (diverticulitis) Rectal & pelvic exams if lower abdo & pelvic pain DRE - fecal impaction, palpable mass, occult blood in stool Tenderness & fullness on R of rectum suggests retrocecal appendix Pelvic - vaginal discharge (vaginitis), cervical motion tenderness & peritoneal signs (ectopic pregnancy or other gyne complications e.g. tubo-ovarian abscess) S&S of surgical abdo Fever Protracted (prolonged) vomiting syncope/pre-syncope Evidence of GI blood loss
Flashcard 1402816302348
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itms if lower abdo & pelvic pain DRE - fecal impaction, palpable mass, occult blood in stool Tenderness & fullness on R of rectum suggests retrocecal appendix Pelvic - <span>vaginal discharge (vaginitis), cervical motion tenderness & peritoneal signs (ectopic pregnancy or other gyne complications e.g. tubo-ovarian abscess) <span><body><html>
Original toplevel document
Abdo PainCholecystitis (highest to lowest PPV) RUQ pain, fever, jaundice IBS algorithm <span>Objective General inspection Change in mental status (infection - UTI) Shock (perforated viscera, GI hemorrhage, severe pancreatitis, MI, sepsis) Vitals Upper abdo pain - pay attention to Cardiac (ischemia) & lung (pneumonia) exams Tachypneic (pneumonia) Abdo peritoneal signs Carnett’s sign (high ppv for abdo wall pain) ↑ pain when supine pt raises head & shoulder, tensing abdo wall Murphy’s sign (high ppv for choleycystitis) Psoas sign (high ppv for appendicitis) Sever pain out of proportion (ischemic bowel, pancreatitis) restless/writhing (biliary/renal colic, testicular torsion) LLQ tenderness (diverticulitis) Rectal & pelvic exams if lower abdo & pelvic pain DRE - fecal impaction, palpable mass, occult blood in stool Tenderness & fullness on R of rectum suggests retrocecal appendix Pelvic - vaginal discharge (vaginitis), cervical motion tenderness & peritoneal signs (ectopic pregnancy or other gyne complications e.g. tubo-ovarian abscess) S&S of surgical abdo Fever Protracted (prolonged) vomiting syncope/pre-syncope Evidence of GI blood loss
Flashcard 1402822855948
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1402827574540
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1402830458124
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1402835963148
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1402838846732
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1402844351756
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open it*occult UTI, perforated viscus, ischemic bowel ds* - potentially fatal, often missed or dx late in elderly pt CONSIDER IN ALL OLDER PTS w/ abdo pain
Original toplevel document
Abdo Pain#13; Appendicitis Acute cholecystitis Diverticulitis Acute pancreatitis Perforated ulcer Bowel infarction <span>Plan (for acute abdo pain) - acute abdo = sudden, non-traumatic disorder needing urgent dx & tx Labs CBC (infection/blood loss) Amylase + lipase (pancreatitis) LFT (RUQ pain) Urinalysis (hematuria, dysuria, flank pain - UTI/kidney stone) Beta hcg (women in childbearing age) Chlamydia + gonorrhea (women @ risk of STIs) Imaging (based on location) U/S (RUQ pain) abdo/transvag ultrasound for pregnant women, even for LLQ/RLQ pain Transvag u/s for ectopic pregnancy CT w/ IV contrast media (adults w/ acute RLQ pain) CT w/ oral + IV contrast media (LLQ pain) - for sigmoid diverticulitis LUQ pain (many causes so depends) Suggested esophageal/gastric patho = endoscopy or upper GI series Others = CT (can image pancreas, spleen, kidneys, intestines, vasculature) Xray Free air under diaphragm (=perforation of GI tract) Abn calcifications (10% gallstones, 90% kidney stones) Mult dilated loops of bowel & air-fluid lvls (bowel obstruction) May see with paralytic ileus *occult UTI, perforated viscus, ischemic bowel ds* - potentially fatal, often missed or dx late in elderly pt CONSIDER IN ALL OLDER PTS w/ abdo pain Initial investigations & basic management for chr/recurrent abdo pain IBS Exercise: vigorous 3-5/week (all types of IBS)
Flashcard 1402847759628
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1402849594636
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1402852478220
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1402854313228
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1402856148236
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1402858507532
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itMigraine management -acute meds -monitor for med overuse -prophy meds if: ---HA >3d/mo and acute meds not effective OR ---HA >8d/mo b/c risk of overuse OR ---disability despite acute meds behavioural management -HA diary - freq, intensity, triggers, meds -lifesty
Flashcard 1402860080396
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itMigraine management -acute meds -monitor for med overuse -prophy meds if: ---HA >3d/mo and acute meds not effective OR ---HA >8d/mo b/c risk of overuse OR ---disability despite acute meds behavioural management -HA diary - freq, intensity, triggers, meds -lifestyle factors - reduce caffeine, regular exercise, r
Flashcard 1402861653260
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itl>Migraine management -acute meds -monitor for med overuse -prophy meds if: ---HA >3d/mo and acute meds not effective OR ---HA >8d/mo b/c risk of overuse OR ---disability despite acute meds behavioural management -HA diary - freq, intensity, triggers, meds -lifestyle factors - reduce caffeine, regular exercise, regular/adequate sleep/meals -stress management
Flashcard 1402863226124
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open it-monitor for med overuse -prophy meds if: ---HA >3d/mo and acute meds not effective OR ---HA >8d/mo b/c risk of overuse OR ---disability despite acute meds behavioural management -HA diary - <span>freq, intensity, triggers, meds -lifestyle factors - reduce caffeine, regular exercise, regular/adequate sleep/meals -stress management strategies - relaxation training, CBT, pacing activity, biofeedback</s
Flashcard 1402864798988
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open it>3d/mo and acute meds not effective OR ---HA >8d/mo b/c risk of overuse OR ---disability despite acute meds behavioural management -HA diary - freq, intensity, triggers, meds -lifestyle factors - <span>reduce caffeine, regular exercise, regular/adequate sleep/meals -stress management strategies - relaxation training, CBT, pacing activity, biofeedback<span><body><html>
Flashcard 1402866371852
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open it---disability despite acute meds behavioural management -HA diary - freq, intensity, triggers, meds -lifestyle factors - reduce caffeine, regular exercise, regular/adequate sleep/meals -stress management strategies - <span>relaxation training, CBT, pacing activity, biofeedback<span><body><html>
Flashcard 1402880789772
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1402882624780
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1402884459788
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1402886294796
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1402888129804
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1402889964812
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1402891799820
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1402893634828
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1402895469836
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1402897304844
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1402899139852
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1402900974860
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1402902809868
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1402904644876
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1402906479884
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1402908314892
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1402910149900
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1402911984908
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1402913819916
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1402915654924
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1402917489932
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1402919324940
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1402921159948
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1402923519244
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1402925354252
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1402927189260
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1402929024268
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1402930859276
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1402932694284
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1402937937164
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1402942131468
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1402946325772
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1402950520076
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1402954714380
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1402958908684
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1402963102988
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1402967297292
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1402973588748
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1402977783052
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1402981977356
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1402986171660
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1402992463116
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1402996657420
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1403000851724
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1403005046028
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1403009240332
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1403013958924
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1403018677516
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1403020512524
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1403022347532
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1403024182540
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1403026017548
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1403027852556
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1403029687564
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1403031784716
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1403033619724
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1403035454732
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1403044367628
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1403045678348
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1403049872652
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1403054066956
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1403059047692
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itSubjective “Does it feel like either the room is spinning or that you are spinning?” and/or “Is it triggered or worsened by turning your head or rolling over in bed?” Yes = vertigo BENIGN PAROXYSMAL POSITIONAL VERTIGO (most common) brief, recurrent episodes (seconds to minutes), +/- nausea and vomiti
Original toplevel document
Dizziness/VertigoDizziness/Vertigo Approach to patient with Dizziness Subjective “Does it feel like either the room is spinning or that you are spinning?” and/or “Is it triggered or worsened by turning your head or rolling over in bed?” Yes = vertigo BENIGN PAROXYSMAL POSITIONAL VERTIGO (most common) brief, recurrent episodes (seconds to minutes), +/- nausea and vomiting Vestibular Neuritis rapid onset, severe, persistent (days), N/V, imbalance Ménière’s Disease recurrent episodes (minutes to hours), fluctuating hearing loss, tinnitus, and sensation of aural fullness Vestibular Toxicity aminoglycosides (eg. gentamycin), loop diuretics, ASA, NSAIDs, amiodarone, quinine, cisplatin No = other forms of dizziness Presyncopal Dizziness – “feels like nearly fainting or blacking out” ECG Triggered by exertion? Chest pain/palpitations? Known structural heart dz? FmHx of sudden death? Abnormal ECG? (if pt stable, fax ECG for urgent advice) If yes to any, suspect cardiac etiology. Refer to Emergency If no, orthostatic hypotension? Yes = investigate underlying cause. meds/alcohol? Consider CBC/lytes No = likely vasovagal/situational etiology. If recurrent episodes or pt is at risk of injury, consider referral for tilt test (+/- carotid sinus massage if >40 yo) Disequilibrium Dizziness – “unsteadiness while walking” Often multifactorial, common in elderly, risk of falls. Complete neuro and MSK exams to rule out peripheral neuropathy, Parkinsonism, MSK d/o, CVA, etc Nonspecific Dizziness – “woozy”, “giddy”, “light-headed” DDx: hypoglycemic (glucose), thyroid disease (TSH), pregnancy (β-HCG), meds, psychiatric disorders, alcohol/drugs, menstruation, previous head trauma Ask about: onset, duration, nausea, vomiting, hearing loss, tinnitus, headache, imbalance, aural fullness, ear pain, rash, facial paralysis, medications Objective Assessment viral labyrinthitis benign positional vertigo Eustachian tube dysfunction (often with s
Flashcard 1403061406988
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itSubjective “Does it feel like either the room is spinning or that you are spinning?” and/or “Is it triggered or worsened by turning your head or rolling over in bed?” Yes = vertigo <span>BENIGN PAROXYSMAL POSITIONAL VERTIGO (most common) brief, recurrent episodes (seconds to minutes), +/- nausea and vomiting Vestibular Neuritis rapid onset, severe, persistent (days), N/V, imbalance Ménière’s Disease recurrent episodes (minutes to hours), fluctuating hearing loss, tinnitus, and sensation of aural fullness Vestibular Toxicity aminoglycosides (eg. gentamycin), loop diuretics, ASA, NSAIDs, amiodarone, quinine, cisplatin No = other forms of dizziness Presyncopal Dizziness – “feels like nearly fainting or blacking out” ECG Triggered
Original toplevel document
Dizziness/VertigoDizziness/Vertigo Approach to patient with Dizziness Subjective “Does it feel like either the room is spinning or that you are spinning?” and/or “Is it triggered or worsened by turning your head or rolling over in bed?” Yes = vertigo BENIGN PAROXYSMAL POSITIONAL VERTIGO (most common) brief, recurrent episodes (seconds to minutes), +/- nausea and vomiting Vestibular Neuritis rapid onset, severe, persistent (days), N/V, imbalance Ménière’s Disease recurrent episodes (minutes to hours), fluctuating hearing loss, tinnitus, and sensation of aural fullness Vestibular Toxicity aminoglycosides (eg. gentamycin), loop diuretics, ASA, NSAIDs, amiodarone, quinine, cisplatin No = other forms of dizziness Presyncopal Dizziness – “feels like nearly fainting or blacking out” ECG Triggered by exertion? Chest pain/palpitations? Known structural heart dz? FmHx of sudden death? Abnormal ECG? (if pt stable, fax ECG for urgent advice) If yes to any, suspect cardiac etiology. Refer to Emergency If no, orthostatic hypotension? Yes = investigate underlying cause. meds/alcohol? Consider CBC/lytes No = likely vasovagal/situational etiology. If recurrent episodes or pt is at risk of injury, consider referral for tilt test (+/- carotid sinus massage if >40 yo) Disequilibrium Dizziness – “unsteadiness while walking” Often multifactorial, common in elderly, risk of falls. Complete neuro and MSK exams to rule out peripheral neuropathy, Parkinsonism, MSK d/o, CVA, etc Nonspecific Dizziness – “woozy”, “giddy”, “light-headed” DDx: hypoglycemic (glucose), thyroid disease (TSH), pregnancy (β-HCG), meds, psychiatric disorders, alcohol/drugs, menstruation, previous head trauma Ask about: onset, duration, nausea, vomiting, hearing loss, tinnitus, headache, imbalance, aural fullness, ear pain, rash, facial paralysis, medications Objective Assessment viral labyrinthitis benign positional vertigo Eustachian tube dysfunction (often with s
Flashcard 1403063766284
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itSubjective “Does it feel like either the room is spinning or that you are spinning?” and/or “Is it triggered or worsened by turning your head or rolling over in bed?” Yes = vertigo <span>BENIGN PAROXYSMAL POSITIONAL VERTIGO (most common) brief, recurrent episodes (seconds to minutes), +/- nausea and vomiting Vestibular Neuritis rapid onset, severe, persistent (days), N/V, imbalance Ménière’s Disease recurren
Original toplevel document
Dizziness/VertigoDizziness/Vertigo Approach to patient with Dizziness Subjective “Does it feel like either the room is spinning or that you are spinning?” and/or “Is it triggered or worsened by turning your head or rolling over in bed?” Yes = vertigo BENIGN PAROXYSMAL POSITIONAL VERTIGO (most common) brief, recurrent episodes (seconds to minutes), +/- nausea and vomiting Vestibular Neuritis rapid onset, severe, persistent (days), N/V, imbalance Ménière’s Disease recurrent episodes (minutes to hours), fluctuating hearing loss, tinnitus, and sensation of aural fullness Vestibular Toxicity aminoglycosides (eg. gentamycin), loop diuretics, ASA, NSAIDs, amiodarone, quinine, cisplatin No = other forms of dizziness Presyncopal Dizziness – “feels like nearly fainting or blacking out” ECG Triggered by exertion? Chest pain/palpitations? Known structural heart dz? FmHx of sudden death? Abnormal ECG? (if pt stable, fax ECG for urgent advice) If yes to any, suspect cardiac etiology. Refer to Emergency If no, orthostatic hypotension? Yes = investigate underlying cause. meds/alcohol? Consider CBC/lytes No = likely vasovagal/situational etiology. If recurrent episodes or pt is at risk of injury, consider referral for tilt test (+/- carotid sinus massage if >40 yo) Disequilibrium Dizziness – “unsteadiness while walking” Often multifactorial, common in elderly, risk of falls. Complete neuro and MSK exams to rule out peripheral neuropathy, Parkinsonism, MSK d/o, CVA, etc Nonspecific Dizziness – “woozy”, “giddy”, “light-headed” DDx: hypoglycemic (glucose), thyroid disease (TSH), pregnancy (β-HCG), meds, psychiatric disorders, alcohol/drugs, menstruation, previous head trauma Ask about: onset, duration, nausea, vomiting, hearing loss, tinnitus, headache, imbalance, aural fullness, ear pain, rash, facial paralysis, medications Objective Assessment viral labyrinthitis benign positional vertigo Eustachian tube dysfunction (often with s
Flashcard 1403066125580
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itYes = vertigo BENIGN PAROXYSMAL POSITIONAL VERTIGO (most common) brief, recurrent episodes (seconds to minutes), +/- nausea and vomiting <span>Vestibular Neuritis rapid onset, severe, persistent (days), N/V, imbalance Ménière’s Disease recurrent episodes (minutes to hours), fluctuating hearing loss, tinnitus, and sensation of aural fullness Ves
Original toplevel document
Dizziness/VertigoDizziness/Vertigo Approach to patient with Dizziness Subjective “Does it feel like either the room is spinning or that you are spinning?” and/or “Is it triggered or worsened by turning your head or rolling over in bed?” Yes = vertigo BENIGN PAROXYSMAL POSITIONAL VERTIGO (most common) brief, recurrent episodes (seconds to minutes), +/- nausea and vomiting Vestibular Neuritis rapid onset, severe, persistent (days), N/V, imbalance Ménière’s Disease recurrent episodes (minutes to hours), fluctuating hearing loss, tinnitus, and sensation of aural fullness Vestibular Toxicity aminoglycosides (eg. gentamycin), loop diuretics, ASA, NSAIDs, amiodarone, quinine, cisplatin No = other forms of dizziness Presyncopal Dizziness – “feels like nearly fainting or blacking out” ECG Triggered by exertion? Chest pain/palpitations? Known structural heart dz? FmHx of sudden death? Abnormal ECG? (if pt stable, fax ECG for urgent advice) If yes to any, suspect cardiac etiology. Refer to Emergency If no, orthostatic hypotension? Yes = investigate underlying cause. meds/alcohol? Consider CBC/lytes No = likely vasovagal/situational etiology. If recurrent episodes or pt is at risk of injury, consider referral for tilt test (+/- carotid sinus massage if >40 yo) Disequilibrium Dizziness – “unsteadiness while walking” Often multifactorial, common in elderly, risk of falls. Complete neuro and MSK exams to rule out peripheral neuropathy, Parkinsonism, MSK d/o, CVA, etc Nonspecific Dizziness – “woozy”, “giddy”, “light-headed” DDx: hypoglycemic (glucose), thyroid disease (TSH), pregnancy (β-HCG), meds, psychiatric disorders, alcohol/drugs, menstruation, previous head trauma Ask about: onset, duration, nausea, vomiting, hearing loss, tinnitus, headache, imbalance, aural fullness, ear pain, rash, facial paralysis, medications Objective Assessment viral labyrinthitis benign positional vertigo Eustachian tube dysfunction (often with s
Flashcard 1403068484876
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open it; brief, recurrent episodes (seconds to minutes), +/- nausea and vomiting Vestibular Neuritis rapid onset, severe, persistent (days), N/V, imbalance <span>Ménière’s Disease recurrent episodes (minutes to hours), fluctuating hearing loss, tinnitus, and sensation of aural fullness Vestibular Toxicity aminoglycosides (eg. gentamycin), loop diuretics, ASA, NSAIDs, amiodarone, quinine, cisplatin No = o
Original toplevel document
Dizziness/VertigoDizziness/Vertigo Approach to patient with Dizziness Subjective “Does it feel like either the room is spinning or that you are spinning?” and/or “Is it triggered or worsened by turning your head or rolling over in bed?” Yes = vertigo BENIGN PAROXYSMAL POSITIONAL VERTIGO (most common) brief, recurrent episodes (seconds to minutes), +/- nausea and vomiting Vestibular Neuritis rapid onset, severe, persistent (days), N/V, imbalance Ménière’s Disease recurrent episodes (minutes to hours), fluctuating hearing loss, tinnitus, and sensation of aural fullness Vestibular Toxicity aminoglycosides (eg. gentamycin), loop diuretics, ASA, NSAIDs, amiodarone, quinine, cisplatin No = other forms of dizziness Presyncopal Dizziness – “feels like nearly fainting or blacking out” ECG Triggered by exertion? Chest pain/palpitations? Known structural heart dz? FmHx of sudden death? Abnormal ECG? (if pt stable, fax ECG for urgent advice) If yes to any, suspect cardiac etiology. Refer to Emergency If no, orthostatic hypotension? Yes = investigate underlying cause. meds/alcohol? Consider CBC/lytes No = likely vasovagal/situational etiology. If recurrent episodes or pt is at risk of injury, consider referral for tilt test (+/- carotid sinus massage if >40 yo) Disequilibrium Dizziness – “unsteadiness while walking” Often multifactorial, common in elderly, risk of falls. Complete neuro and MSK exams to rule out peripheral neuropathy, Parkinsonism, MSK d/o, CVA, etc Nonspecific Dizziness – “woozy”, “giddy”, “light-headed” DDx: hypoglycemic (glucose), thyroid disease (TSH), pregnancy (β-HCG), meds, psychiatric disorders, alcohol/drugs, menstruation, previous head trauma Ask about: onset, duration, nausea, vomiting, hearing loss, tinnitus, headache, imbalance, aural fullness, ear pain, rash, facial paralysis, medications Objective Assessment viral labyrinthitis benign positional vertigo Eustachian tube dysfunction (often with s
Flashcard 1403070844172
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itstent (days), N/V, imbalance Ménière’s Disease recurrent episodes (minutes to hours), fluctuating hearing loss, tinnitus, and sensation of aural fullness <span>Vestibular Toxicity aminoglycosides (eg. gentamycin), loop diuretics, ASA, NSAIDs, amiodarone, quinine, cisplatin No = other forms of dizziness Presyncopal Dizziness – “feels like nearly fainting or blacking out” ECG Triggered
Original toplevel document
Dizziness/VertigoDizziness/Vertigo Approach to patient with Dizziness Subjective “Does it feel like either the room is spinning or that you are spinning?” and/or “Is it triggered or worsened by turning your head or rolling over in bed?” Yes = vertigo BENIGN PAROXYSMAL POSITIONAL VERTIGO (most common) brief, recurrent episodes (seconds to minutes), +/- nausea and vomiting Vestibular Neuritis rapid onset, severe, persistent (days), N/V, imbalance Ménière’s Disease recurrent episodes (minutes to hours), fluctuating hearing loss, tinnitus, and sensation of aural fullness Vestibular Toxicity aminoglycosides (eg. gentamycin), loop diuretics, ASA, NSAIDs, amiodarone, quinine, cisplatin No = other forms of dizziness Presyncopal Dizziness – “feels like nearly fainting or blacking out” ECG Triggered by exertion? Chest pain/palpitations? Known structural heart dz? FmHx of sudden death? Abnormal ECG? (if pt stable, fax ECG for urgent advice) If yes to any, suspect cardiac etiology. Refer to Emergency If no, orthostatic hypotension? Yes = investigate underlying cause. meds/alcohol? Consider CBC/lytes No = likely vasovagal/situational etiology. If recurrent episodes or pt is at risk of injury, consider referral for tilt test (+/- carotid sinus massage if >40 yo) Disequilibrium Dizziness – “unsteadiness while walking” Often multifactorial, common in elderly, risk of falls. Complete neuro and MSK exams to rule out peripheral neuropathy, Parkinsonism, MSK d/o, CVA, etc Nonspecific Dizziness – “woozy”, “giddy”, “light-headed” DDx: hypoglycemic (glucose), thyroid disease (TSH), pregnancy (β-HCG), meds, psychiatric disorders, alcohol/drugs, menstruation, previous head trauma Ask about: onset, duration, nausea, vomiting, hearing loss, tinnitus, headache, imbalance, aural fullness, ear pain, rash, facial paralysis, medications Objective Assessment viral labyrinthitis benign positional vertigo Eustachian tube dysfunction (often with s
Flashcard 1403073203468
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open it13; Vestibular Toxicity aminoglycosides (eg. gentamycin), loop diuretics, ASA, NSAIDs, amiodarone, quinine, cisplatin No = other forms of dizziness <span>Presyncopal Dizziness – “feels like nearly fainting or blacking out” ECG Triggered by exertion? Chest pain/palpitations? Known structural heart dz? FmHx of sudden death? Abnormal ECG? (if pt stable, fax ECG for urgent advice) If yes to any, suspect cardiac etiology. Refer to Emergency If no, orthostatic hypotension? Yes = investigate underlying cause. meds/alcohol? Consider CBC/lytes No = likely vasovagal/situational etiology. If recurrent episodes or pt is at risk of injury, consider referral for tilt test (+/- carotid sinus massage if >40 yo) Disequilibrium Dizziness – “unsteadiness while walking” Often multifactorial, common in elderly, risk of falls. Complete neuro and MSK exams to rule out peripheral neuropathy, Parkinsonism, MSK d/o, CVA, etc Nonspecific Dizziness – “woozy”, “giddy”, “light-headed” DDx: hypoglycemic (glucose), thyroid disease (TSH), pregnancy (β-HCG), meds, psychiatric disorders, alcohol/drugs, menstruation, previous head trauma Ask about: onset, duration, nausea, vomiting, hearing loss, tinnitus, headache, imbalance, aural fullness, ear pain, rash, facial paralysis, medications &
Original toplevel document
Dizziness/VertigoDizziness/Vertigo Approach to patient with Dizziness Subjective “Does it feel like either the room is spinning or that you are spinning?” and/or “Is it triggered or worsened by turning your head or rolling over in bed?” Yes = vertigo BENIGN PAROXYSMAL POSITIONAL VERTIGO (most common) brief, recurrent episodes (seconds to minutes), +/- nausea and vomiting Vestibular Neuritis rapid onset, severe, persistent (days), N/V, imbalance Ménière’s Disease recurrent episodes (minutes to hours), fluctuating hearing loss, tinnitus, and sensation of aural fullness Vestibular Toxicity aminoglycosides (eg. gentamycin), loop diuretics, ASA, NSAIDs, amiodarone, quinine, cisplatin No = other forms of dizziness Presyncopal Dizziness – “feels like nearly fainting or blacking out” ECG Triggered by exertion? Chest pain/palpitations? Known structural heart dz? FmHx of sudden death? Abnormal ECG? (if pt stable, fax ECG for urgent advice) If yes to any, suspect cardiac etiology. Refer to Emergency If no, orthostatic hypotension? Yes = investigate underlying cause. meds/alcohol? Consider CBC/lytes No = likely vasovagal/situational etiology. If recurrent episodes or pt is at risk of injury, consider referral for tilt test (+/- carotid sinus massage if >40 yo) Disequilibrium Dizziness – “unsteadiness while walking” Often multifactorial, common in elderly, risk of falls. Complete neuro and MSK exams to rule out peripheral neuropathy, Parkinsonism, MSK d/o, CVA, etc Nonspecific Dizziness – “woozy”, “giddy”, “light-headed” DDx: hypoglycemic (glucose), thyroid disease (TSH), pregnancy (β-HCG), meds, psychiatric disorders, alcohol/drugs, menstruation, previous head trauma Ask about: onset, duration, nausea, vomiting, hearing loss, tinnitus, headache, imbalance, aural fullness, ear pain, rash, facial paralysis, medications Objective Assessment viral labyrinthitis benign positional vertigo Eustachian tube dysfunction (often with s
Flashcard 1403075562764
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open ituretics, ASA, NSAIDs, amiodarone, quinine, cisplatin No = other forms of dizziness Presyncopal Dizziness – “feels like nearly fainting or blacking out” <span>ECG Triggered by exertion? Chest pain/palpitations? Known structural heart dz? FmHx of sudden death? Abnormal ECG? (if pt stable, fax ECG for urgent advice) If y
Original toplevel document
Dizziness/VertigoDizziness/Vertigo Approach to patient with Dizziness Subjective “Does it feel like either the room is spinning or that you are spinning?” and/or “Is it triggered or worsened by turning your head or rolling over in bed?” Yes = vertigo BENIGN PAROXYSMAL POSITIONAL VERTIGO (most common) brief, recurrent episodes (seconds to minutes), +/- nausea and vomiting Vestibular Neuritis rapid onset, severe, persistent (days), N/V, imbalance Ménière’s Disease recurrent episodes (minutes to hours), fluctuating hearing loss, tinnitus, and sensation of aural fullness Vestibular Toxicity aminoglycosides (eg. gentamycin), loop diuretics, ASA, NSAIDs, amiodarone, quinine, cisplatin No = other forms of dizziness Presyncopal Dizziness – “feels like nearly fainting or blacking out” ECG Triggered by exertion? Chest pain/palpitations? Known structural heart dz? FmHx of sudden death? Abnormal ECG? (if pt stable, fax ECG for urgent advice) If yes to any, suspect cardiac etiology. Refer to Emergency If no, orthostatic hypotension? Yes = investigate underlying cause. meds/alcohol? Consider CBC/lytes No = likely vasovagal/situational etiology. If recurrent episodes or pt is at risk of injury, consider referral for tilt test (+/- carotid sinus massage if >40 yo) Disequilibrium Dizziness – “unsteadiness while walking” Often multifactorial, common in elderly, risk of falls. Complete neuro and MSK exams to rule out peripheral neuropathy, Parkinsonism, MSK d/o, CVA, etc Nonspecific Dizziness – “woozy”, “giddy”, “light-headed” DDx: hypoglycemic (glucose), thyroid disease (TSH), pregnancy (β-HCG), meds, psychiatric disorders, alcohol/drugs, menstruation, previous head trauma Ask about: onset, duration, nausea, vomiting, hearing loss, tinnitus, headache, imbalance, aural fullness, ear pain, rash, facial paralysis, medications Objective Assessment viral labyrinthitis benign positional vertigo Eustachian tube dysfunction (often with s
Flashcard 1403077922060
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itdarone, quinine, cisplatin No = other forms of dizziness Presyncopal Dizziness – “feels like nearly fainting or blacking out” ECG <span>Triggered by exertion? Chest pain/palpitations? Known structural heart dz? FmHx of sudden death? Abnormal ECG? (if pt stable, fax ECG for urgent advice) If yes to any, suspect cardiac etiology. Refer to Emergency If no, orthostatic hypotension? Yes = investigate underlying cause. med
Original toplevel document
Dizziness/VertigoDizziness/Vertigo Approach to patient with Dizziness Subjective “Does it feel like either the room is spinning or that you are spinning?” and/or “Is it triggered or worsened by turning your head or rolling over in bed?” Yes = vertigo BENIGN PAROXYSMAL POSITIONAL VERTIGO (most common) brief, recurrent episodes (seconds to minutes), +/- nausea and vomiting Vestibular Neuritis rapid onset, severe, persistent (days), N/V, imbalance Ménière’s Disease recurrent episodes (minutes to hours), fluctuating hearing loss, tinnitus, and sensation of aural fullness Vestibular Toxicity aminoglycosides (eg. gentamycin), loop diuretics, ASA, NSAIDs, amiodarone, quinine, cisplatin No = other forms of dizziness Presyncopal Dizziness – “feels like nearly fainting or blacking out” ECG Triggered by exertion? Chest pain/palpitations? Known structural heart dz? FmHx of sudden death? Abnormal ECG? (if pt stable, fax ECG for urgent advice) If yes to any, suspect cardiac etiology. Refer to Emergency If no, orthostatic hypotension? Yes = investigate underlying cause. meds/alcohol? Consider CBC/lytes No = likely vasovagal/situational etiology. If recurrent episodes or pt is at risk of injury, consider referral for tilt test (+/- carotid sinus massage if >40 yo) Disequilibrium Dizziness – “unsteadiness while walking” Often multifactorial, common in elderly, risk of falls. Complete neuro and MSK exams to rule out peripheral neuropathy, Parkinsonism, MSK d/o, CVA, etc Nonspecific Dizziness – “woozy”, “giddy”, “light-headed” DDx: hypoglycemic (glucose), thyroid disease (TSH), pregnancy (β-HCG), meds, psychiatric disorders, alcohol/drugs, menstruation, previous head trauma Ask about: onset, duration, nausea, vomiting, hearing loss, tinnitus, headache, imbalance, aural fullness, ear pain, rash, facial paralysis, medications Objective Assessment viral labyrinthitis benign positional vertigo Eustachian tube dysfunction (often with s
Flashcard 1403080281356
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itdarone, quinine, cisplatin No = other forms of dizziness Presyncopal Dizziness – “feels like nearly fainting or blacking out” ECG <span>Triggered by exertion? Chest pain/palpitations? Known structural heart dz? FmHx of sudden death? Abnormal ECG? (if pt stable, fax ECG for urgent advice) If yes to any, suspect cardiac etiology. Refer to Emergency If no, orthostatic hypotension? Yes = investigate underlying cause. meds/alcohol? Consider CBC/lytes No = likely vasovagal/situat
Original toplevel document
Dizziness/VertigoDizziness/Vertigo Approach to patient with Dizziness Subjective “Does it feel like either the room is spinning or that you are spinning?” and/or “Is it triggered or worsened by turning your head or rolling over in bed?” Yes = vertigo BENIGN PAROXYSMAL POSITIONAL VERTIGO (most common) brief, recurrent episodes (seconds to minutes), +/- nausea and vomiting Vestibular Neuritis rapid onset, severe, persistent (days), N/V, imbalance Ménière’s Disease recurrent episodes (minutes to hours), fluctuating hearing loss, tinnitus, and sensation of aural fullness Vestibular Toxicity aminoglycosides (eg. gentamycin), loop diuretics, ASA, NSAIDs, amiodarone, quinine, cisplatin No = other forms of dizziness Presyncopal Dizziness – “feels like nearly fainting or blacking out” ECG Triggered by exertion? Chest pain/palpitations? Known structural heart dz? FmHx of sudden death? Abnormal ECG? (if pt stable, fax ECG for urgent advice) If yes to any, suspect cardiac etiology. Refer to Emergency If no, orthostatic hypotension? Yes = investigate underlying cause. meds/alcohol? Consider CBC/lytes No = likely vasovagal/situational etiology. If recurrent episodes or pt is at risk of injury, consider referral for tilt test (+/- carotid sinus massage if >40 yo) Disequilibrium Dizziness – “unsteadiness while walking” Often multifactorial, common in elderly, risk of falls. Complete neuro and MSK exams to rule out peripheral neuropathy, Parkinsonism, MSK d/o, CVA, etc Nonspecific Dizziness – “woozy”, “giddy”, “light-headed” DDx: hypoglycemic (glucose), thyroid disease (TSH), pregnancy (β-HCG), meds, psychiatric disorders, alcohol/drugs, menstruation, previous head trauma Ask about: onset, duration, nausea, vomiting, hearing loss, tinnitus, headache, imbalance, aural fullness, ear pain, rash, facial paralysis, medications Objective Assessment viral labyrinthitis benign positional vertigo Eustachian tube dysfunction (often with s
Flashcard 1403082640652
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itdarone, quinine, cisplatin No = other forms of dizziness Presyncopal Dizziness – “feels like nearly fainting or blacking out” ECG <span>Triggered by exertion? Chest pain/palpitations? Known structural heart dz? FmHx of sudden death? Abnormal ECG? (if pt stable, fax ECG for urgent advice) If yes to any, suspect cardiac etiology. Refer to Emergency If no, orthostatic hypotension? Yes = investigate underlying cause. meds/alcohol? Consider CBC/lytes No = likely vasovagal/situational etiology. If recurrent episodes or pt is at risk of injur
Original toplevel document
Dizziness/VertigoDizziness/Vertigo Approach to patient with Dizziness Subjective “Does it feel like either the room is spinning or that you are spinning?” and/or “Is it triggered or worsened by turning your head or rolling over in bed?” Yes = vertigo BENIGN PAROXYSMAL POSITIONAL VERTIGO (most common) brief, recurrent episodes (seconds to minutes), +/- nausea and vomiting Vestibular Neuritis rapid onset, severe, persistent (days), N/V, imbalance Ménière’s Disease recurrent episodes (minutes to hours), fluctuating hearing loss, tinnitus, and sensation of aural fullness Vestibular Toxicity aminoglycosides (eg. gentamycin), loop diuretics, ASA, NSAIDs, amiodarone, quinine, cisplatin No = other forms of dizziness Presyncopal Dizziness – “feels like nearly fainting or blacking out” ECG Triggered by exertion? Chest pain/palpitations? Known structural heart dz? FmHx of sudden death? Abnormal ECG? (if pt stable, fax ECG for urgent advice) If yes to any, suspect cardiac etiology. Refer to Emergency If no, orthostatic hypotension? Yes = investigate underlying cause. meds/alcohol? Consider CBC/lytes No = likely vasovagal/situational etiology. If recurrent episodes or pt is at risk of injury, consider referral for tilt test (+/- carotid sinus massage if >40 yo) Disequilibrium Dizziness – “unsteadiness while walking” Often multifactorial, common in elderly, risk of falls. Complete neuro and MSK exams to rule out peripheral neuropathy, Parkinsonism, MSK d/o, CVA, etc Nonspecific Dizziness – “woozy”, “giddy”, “light-headed” DDx: hypoglycemic (glucose), thyroid disease (TSH), pregnancy (β-HCG), meds, psychiatric disorders, alcohol/drugs, menstruation, previous head trauma Ask about: onset, duration, nausea, vomiting, hearing loss, tinnitus, headache, imbalance, aural fullness, ear pain, rash, facial paralysis, medications Objective Assessment viral labyrinthitis benign positional vertigo Eustachian tube dysfunction (often with s
Flashcard 1403084999948
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itden death? Abnormal ECG? (if pt stable, fax ECG for urgent advice) If yes to any, suspect cardiac etiology. Refer to Emergency If no, orthostatic hypotension? <span>Yes = investigate underlying cause. meds/alcohol? Consider CBC/lytes No = likely vasovagal/situational etiology. If recurrent episodes or pt is at risk of injury, consider referral for tilt test (+/- carotid sinus massage if >40 yo)
Original toplevel document
Dizziness/VertigoDizziness/Vertigo Approach to patient with Dizziness Subjective “Does it feel like either the room is spinning or that you are spinning?” and/or “Is it triggered or worsened by turning your head or rolling over in bed?” Yes = vertigo BENIGN PAROXYSMAL POSITIONAL VERTIGO (most common) brief, recurrent episodes (seconds to minutes), +/- nausea and vomiting Vestibular Neuritis rapid onset, severe, persistent (days), N/V, imbalance Ménière’s Disease recurrent episodes (minutes to hours), fluctuating hearing loss, tinnitus, and sensation of aural fullness Vestibular Toxicity aminoglycosides (eg. gentamycin), loop diuretics, ASA, NSAIDs, amiodarone, quinine, cisplatin No = other forms of dizziness Presyncopal Dizziness – “feels like nearly fainting or blacking out” ECG Triggered by exertion? Chest pain/palpitations? Known structural heart dz? FmHx of sudden death? Abnormal ECG? (if pt stable, fax ECG for urgent advice) If yes to any, suspect cardiac etiology. Refer to Emergency If no, orthostatic hypotension? Yes = investigate underlying cause. meds/alcohol? Consider CBC/lytes No = likely vasovagal/situational etiology. If recurrent episodes or pt is at risk of injury, consider referral for tilt test (+/- carotid sinus massage if >40 yo) Disequilibrium Dizziness – “unsteadiness while walking” Often multifactorial, common in elderly, risk of falls. Complete neuro and MSK exams to rule out peripheral neuropathy, Parkinsonism, MSK d/o, CVA, etc Nonspecific Dizziness – “woozy”, “giddy”, “light-headed” DDx: hypoglycemic (glucose), thyroid disease (TSH), pregnancy (β-HCG), meds, psychiatric disorders, alcohol/drugs, menstruation, previous head trauma Ask about: onset, duration, nausea, vomiting, hearing loss, tinnitus, headache, imbalance, aural fullness, ear pain, rash, facial paralysis, medications Objective Assessment viral labyrinthitis benign positional vertigo Eustachian tube dysfunction (often with s
Flashcard 1403087359244
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itIf yes to any, suspect cardiac etiology. Refer to Emergency If no, orthostatic hypotension? Yes = investigate underlying cause. meds/alcohol? Consider CBC/lytes <span>No = likely vasovagal/situational etiology. If recurrent episodes or pt is at risk of injury, consider referral for tilt test (+/- carotid sinus massage if >40 yo) Disequilibrium Dizziness – “unsteadiness while walking” Often multifactorial, common in elderly, risk of falls. Complete neuro and MSK exams to rule out periph
Original toplevel document
Dizziness/VertigoDizziness/Vertigo Approach to patient with Dizziness Subjective “Does it feel like either the room is spinning or that you are spinning?” and/or “Is it triggered or worsened by turning your head or rolling over in bed?” Yes = vertigo BENIGN PAROXYSMAL POSITIONAL VERTIGO (most common) brief, recurrent episodes (seconds to minutes), +/- nausea and vomiting Vestibular Neuritis rapid onset, severe, persistent (days), N/V, imbalance Ménière’s Disease recurrent episodes (minutes to hours), fluctuating hearing loss, tinnitus, and sensation of aural fullness Vestibular Toxicity aminoglycosides (eg. gentamycin), loop diuretics, ASA, NSAIDs, amiodarone, quinine, cisplatin No = other forms of dizziness Presyncopal Dizziness – “feels like nearly fainting or blacking out” ECG Triggered by exertion? Chest pain/palpitations? Known structural heart dz? FmHx of sudden death? Abnormal ECG? (if pt stable, fax ECG for urgent advice) If yes to any, suspect cardiac etiology. Refer to Emergency If no, orthostatic hypotension? Yes = investigate underlying cause. meds/alcohol? Consider CBC/lytes No = likely vasovagal/situational etiology. If recurrent episodes or pt is at risk of injury, consider referral for tilt test (+/- carotid sinus massage if >40 yo) Disequilibrium Dizziness – “unsteadiness while walking” Often multifactorial, common in elderly, risk of falls. Complete neuro and MSK exams to rule out peripheral neuropathy, Parkinsonism, MSK d/o, CVA, etc Nonspecific Dizziness – “woozy”, “giddy”, “light-headed” DDx: hypoglycemic (glucose), thyroid disease (TSH), pregnancy (β-HCG), meds, psychiatric disorders, alcohol/drugs, menstruation, previous head trauma Ask about: onset, duration, nausea, vomiting, hearing loss, tinnitus, headache, imbalance, aural fullness, ear pain, rash, facial paralysis, medications Objective Assessment viral labyrinthitis benign positional vertigo Eustachian tube dysfunction (often with s
Flashcard 1403089718540
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itNo = likely vasovagal/situational etiology. If recurrent episodes or pt is at risk of injury, consider referral for tilt test (+/- carotid sinus massage if >40 yo) <span>Disequilibrium Dizziness – “unsteadiness while walking” Often multifactorial, common in elderly, risk of falls. Complete neuro and MSK exams to rule out peripheral neuropathy, Parkinsonism, MSK d/o, CVA, etc Nonspecific Dizziness – “woozy”, “giddy”, “light-headed” DDx: hypoglycemic (glucose), thyroid disease (TSH), pregnancy (β-HCG), meds, psychiatric disorders, al
Original toplevel document
Dizziness/VertigoDizziness/Vertigo Approach to patient with Dizziness Subjective “Does it feel like either the room is spinning or that you are spinning?” and/or “Is it triggered or worsened by turning your head or rolling over in bed?” Yes = vertigo BENIGN PAROXYSMAL POSITIONAL VERTIGO (most common) brief, recurrent episodes (seconds to minutes), +/- nausea and vomiting Vestibular Neuritis rapid onset, severe, persistent (days), N/V, imbalance Ménière’s Disease recurrent episodes (minutes to hours), fluctuating hearing loss, tinnitus, and sensation of aural fullness Vestibular Toxicity aminoglycosides (eg. gentamycin), loop diuretics, ASA, NSAIDs, amiodarone, quinine, cisplatin No = other forms of dizziness Presyncopal Dizziness – “feels like nearly fainting or blacking out” ECG Triggered by exertion? Chest pain/palpitations? Known structural heart dz? FmHx of sudden death? Abnormal ECG? (if pt stable, fax ECG for urgent advice) If yes to any, suspect cardiac etiology. Refer to Emergency If no, orthostatic hypotension? Yes = investigate underlying cause. meds/alcohol? Consider CBC/lytes No = likely vasovagal/situational etiology. If recurrent episodes or pt is at risk of injury, consider referral for tilt test (+/- carotid sinus massage if >40 yo) Disequilibrium Dizziness – “unsteadiness while walking” Often multifactorial, common in elderly, risk of falls. Complete neuro and MSK exams to rule out peripheral neuropathy, Parkinsonism, MSK d/o, CVA, etc Nonspecific Dizziness – “woozy”, “giddy”, “light-headed” DDx: hypoglycemic (glucose), thyroid disease (TSH), pregnancy (β-HCG), meds, psychiatric disorders, alcohol/drugs, menstruation, previous head trauma Ask about: onset, duration, nausea, vomiting, hearing loss, tinnitus, headache, imbalance, aural fullness, ear pain, rash, facial paralysis, medications Objective Assessment viral labyrinthitis benign positional vertigo Eustachian tube dysfunction (often with s
Flashcard 1403092077836
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open its – “unsteadiness while walking” Often multifactorial, common in elderly, risk of falls. Complete neuro and MSK exams to rule out peripheral neuropathy, Parkinsonism, MSK d/o, CVA, etc <span>Nonspecific Dizziness – “woozy”, “giddy”, “light-headed” DDx: hypoglycemic (glucose), thyroid disease (TSH), pregnancy (β-HCG), meds, psychiatric disorders, alcohol/drugs, menstruation, previous head trauma Ask about: onset, duration, nausea, vomiting, hearing loss, tinnitus, headache, imbalance, aural fullness, ear pain, rash, facial paralysis, medications &
Original toplevel document
Dizziness/VertigoDizziness/Vertigo Approach to patient with Dizziness Subjective “Does it feel like either the room is spinning or that you are spinning?” and/or “Is it triggered or worsened by turning your head or rolling over in bed?” Yes = vertigo BENIGN PAROXYSMAL POSITIONAL VERTIGO (most common) brief, recurrent episodes (seconds to minutes), +/- nausea and vomiting Vestibular Neuritis rapid onset, severe, persistent (days), N/V, imbalance Ménière’s Disease recurrent episodes (minutes to hours), fluctuating hearing loss, tinnitus, and sensation of aural fullness Vestibular Toxicity aminoglycosides (eg. gentamycin), loop diuretics, ASA, NSAIDs, amiodarone, quinine, cisplatin No = other forms of dizziness Presyncopal Dizziness – “feels like nearly fainting or blacking out” ECG Triggered by exertion? Chest pain/palpitations? Known structural heart dz? FmHx of sudden death? Abnormal ECG? (if pt stable, fax ECG for urgent advice) If yes to any, suspect cardiac etiology. Refer to Emergency If no, orthostatic hypotension? Yes = investigate underlying cause. meds/alcohol? Consider CBC/lytes No = likely vasovagal/situational etiology. If recurrent episodes or pt is at risk of injury, consider referral for tilt test (+/- carotid sinus massage if >40 yo) Disequilibrium Dizziness – “unsteadiness while walking” Often multifactorial, common in elderly, risk of falls. Complete neuro and MSK exams to rule out peripheral neuropathy, Parkinsonism, MSK d/o, CVA, etc Nonspecific Dizziness – “woozy”, “giddy”, “light-headed” DDx: hypoglycemic (glucose), thyroid disease (TSH), pregnancy (β-HCG), meds, psychiatric disorders, alcohol/drugs, menstruation, previous head trauma Ask about: onset, duration, nausea, vomiting, hearing loss, tinnitus, headache, imbalance, aural fullness, ear pain, rash, facial paralysis, medications Objective Assessment viral labyrinthitis benign positional vertigo Eustachian tube dysfunction (often with s