Edited, memorised or added to reading queue
on 04-Jul-2022 (Mon)
Do you want BuboFlash to help you learning these things? Click here to log in or create user.
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 7101938535692
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
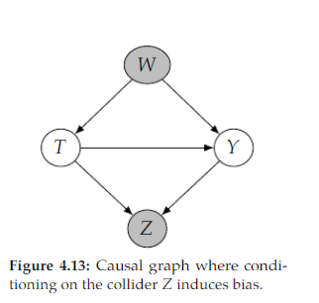
Open itan> Consider the following general kind of path, where → · · · → denotes a directed path: 𝑇 → · · · → 𝑍 ← · · · ← 𝑌 . Conditioning on 𝑍 , or any descendant of 𝑍 in a path like this, will induce <span>collider bias <span>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 7101940370700
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itWhy use a survey to ask customers about their experiences when data about customer interactions can be used to predict satisfaction?
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open it4. Unfocused: As one executive at a large financial-services company put it, “The association between survey-based scores and business outcomes is not well understood, and, as a result, many parts of the organization simply claim a business impact from their CX initiatives with no real evidence.” Several companies have recently come under fire for basing investment decisions on a survey-based score alone. Remarkably, of the CX leaders we surveyed, only 4 percent said that their
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 7101945613580
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itAssumptions of causal inference: 1. Unconfoundedness (Assumption 2.2) 2. Positivity (Assumption 2.3) 3. No interference (Assumption 2.4) 4. Consistency (Assumption 2.5)
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itThis is not a philosophy book. We remain agnostic about metaphysical concepts like causality and cause. Instead, we focus on the identification and estimation of causal effects in populations, that is, numerical quantities that measure changes in the distribution of an outcome under different interventions.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |