Edited, memorised or added to reading queue
on 29-Jul-2022 (Fri)
Do you want BuboFlash to help you learning these things? Click here to log in or create user.
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open it4. Unfocused: As one executive at a large financial-services company put it, “The association between survey-based scores and business outcomes is not well understood, and, as a result, many parts of the organization simply claim a business impact from their CX initiatives with no real evidence.” Several companies have recently come under fire for basing investment decisions on a survey-based score alone. Remarkably, of the CX leaders we surveyed, only 4 percent said that their
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itWe now present our general framework for data-driven agent-based modeling (DDABM), which we subsequently apply to the problem of modeling residential rooftop solar diffusion in San Diego county, California. The key features of this framework are: a) explicit division of data into “calibration” and “validation” to ensure sound and reliable model validation and b) automated agent model training and cross-validation. In this framework, we make three assumptions. The first is that time is discrete. While this assumption is not of fundamental importance, it will help in presenting the concepts, and i
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 7107920661772
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itOur third assumption is that each individual makes independent decisions at each time t, conditional on state x. Again, if x includes all features relevant to an agent’s decision, this assumption is relatively innocuous
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itn at the agent level, in contrast, enables us to leverage state-of-the-art machine learning techniques, as well as obtain more reliable, and interpretable, models at the individual agent level. <span>Recently, in field of ecology and sociology, there is rising interest to combine agent-based model with empirical methods [24]. Biophysical measurements, i.e., soil properties and socioeconomic surveys are used by Berger and Schreinemachers [4] to generate a landscape and agent populations which are consistent with empirical observation by Monte Carlo techniques. Notice that this is quite different application from ours, since we do not need to generate an agent population; rather we instantiate our multi-agent simulation with learned agents. <span>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 7107925642508
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itthetic sequential data — DoppelGANger. It is a framework based on Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) with some innovations that make possible the generation of synthetic versions of complex <span>sequential datasets. <span>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 7107927477516
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 7107932196108
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itDisadvantages of survey-based CX systems 4. Unfocused: As one executive at a large financial-services company put it, “The association between survey-based scores and business outcomes is not well understood, and, as a result, many parts o
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 7107934555404
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itWe offer instead a framework for data-driven agent-based modeling (DDABM), where agent models are learned from data about individual (typically, human) behavior, and the agent-based model is thereby fully data-driven, with no additional parameters to govern
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 7107939011852
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
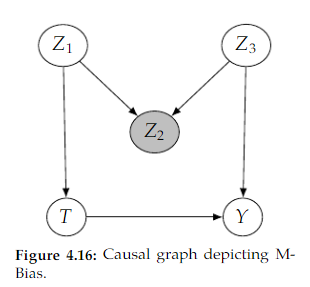
Open itThis is known as M-bias
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 7107941633292
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open it> Universal Framework for Agent based Models - 4 phases (1) Initialization (2) Experience(3) Training(4) Application In the last phase, Application, the trained Neural Network is used for decision making. Agents are reset to their original initial conditions so that the actions performed during the Experience phase have no direct influence on the Application phase. In each time step age
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 7107943468300
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itThere's no selection bias without selection. And selection is, of course, present in all studies. But for selection to cause bias under the null, it needs to be related to both treatment A and outcome Y.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 7107946089740
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |