Edited, memorised or added to reading queue
on 07-Jun-2024 (Fri)
Do you want BuboFlash to help you learning these things? Click here to log in or create user.
Flashcard 7629863783692
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itthe most important take-home message: we need expert knowledge to determine if we should adjust for a variable. The statistical criteria are insufficient to characterize confounding and confounders.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 7629866405132
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itcs—often using several types of machine-learning algorithms—to understand and track what is influencing customer satisfaction and business performance, and to detect specific events in customer <span>journeys. <span>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 7629867453708
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itPredictive customer scores The company develops analytics—often using several types of machine-learning algorithms—to understand and track what is influencing customer satisfaction and business performance, and to detect specific events in customer journeys.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 7629868502284
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itPredictive customer scores The company develops analytics—often using several types of machine-learning algorithms—to understand and track what is influencing customer satisfaction and business <span>performance, and to detect specific events in customer journeys. <span>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
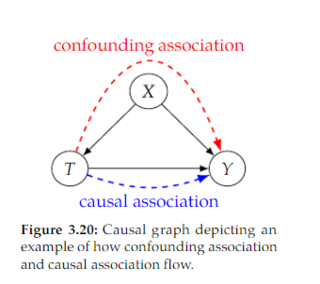
Open itWe refer to the flow of association along directed paths as causal association. A common type of non-causal association that makes total association not causation is confounding association. In the graph in Figure 3.20, we depict the confounding association in red and the causal association in blue
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 7629871910156
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itConsider the following general kind of path, where → · · · → denotes a directed path: 𝑇 → · · · → 𝑍 ← · · · ← 𝑌 . Conditioning on 𝑍 , or any descendant of 𝑍 in a path like this, will induce collider bias
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 7629873220876
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itTwo sources of bias: - common cause (confounding) - conditioning on common effect (selection bias)
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 7629874269452
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itTwo sources of bias: - common cause (confounding) - conditioning on common effect (selection bias)
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 7629876890892
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itWhy use a survey to ask customers about their experiences when data about customer interactions can be used to predict both satisfaction and the likelihood that a customer will remain loyal, bolt, or even increase business?
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 7629879250188
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
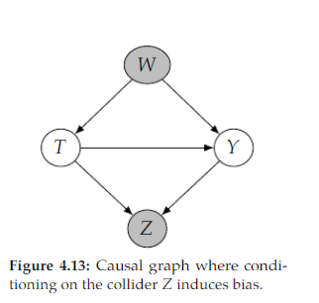
Open itIf we condition on a descendant of 𝑇 that isn’t a mediator, it could unblock a path from 𝑇 to 𝑌 that was blocked by a collider. For example, this is the case with conditioning on 𝑍 in Figure 4.13. This induces non-causal association between 𝑇 and 𝑌 , which biase
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 7629880560908
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open it𝔼[𝑌 | do(𝑡), 𝑍 = 𝑧] vs 𝔼[𝑌 | 𝑍 = 𝑧] 𝔼[𝑌 | 𝑍 = 𝑧] simply refers to the expected value in the (pre-intervention) population where individuals take whatever treatment they would normally take ( 𝑇 ). This distinction will become important when we get to counterfactuals...
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 7629883182348
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itIf all the paths between two nodes 𝑋 and 𝑌 are blocked, then we say that 𝑋 and 𝑌 are d-separated.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
How to delete all files before a certain date in Linux
How to delete all files before a certain date in Linux Posted on: September 15, 2015 If you have a list of files, but you only want to delete files older the a certain date, for example, a maildir folder with 5 years worth of email, and you want to delete everything older then 2 years, then run the following command. find . -type f -mtime +XXX -maxdepth 1 -exec rm {} \; The syntax of this is as follows. find – the command that finds the files . – the dot signifies the current folder. You can change this to something like /home/someuser/mail/somedomain/
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itformat that predictions will take. For example, below are some common predictive modeling problem types and the structure and standard activation function that you can use in the output layer: <span>Regression: Linear activation function, or linear , and the number of neurons matching the number of outputs. This is the default activation function used for neurons in the Dense layer. Binary Classification (2 class) : Logistic activation function, or sigmoid , and one neuron the output layer. Multiclass Classification (> 2 class) : Softmax activation function, or
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 7629890522380
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itA potential outcome 𝑌(𝑡) is distinct from the observed outcome 𝑌 in that not all potential outcomes are observed
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 7629891833100
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itHow to Force User to Change Password at Next Login in Linux User name: ravi # passwd --expire ravi
Original toplevel document
How to Force User to Change Password at Next Login in LinuxUser name: ravi # passwd --expire ravi How to Force User to Change Password at Next Login in Linux Using passwd Command To force a user to change his/her password, first of all the password must have expired and to cause a u
Flashcard 7629893668108
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itCausal edges assumption is asymmetric; “ 𝑋 is a cause of 𝑌 ” is not the same as saying “ 𝑌 is a cause of 𝑋
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 7629895503116
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itWhenever, do(𝑡) appears after the conditioning bar, it means that everything in that expression is in the post-intervention world where the intervention do(𝑡) occurs.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 7629896813836
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itPositivity is the condition that all subgroups of the data with different covariates have some probability of receiving any value of treatment