Edited, memorised or added to reading queue
on 27-Jun-2016 (Mon)
Do you want BuboFlash to help you learning these things? Click here to log in or create user.
Flashcard 149669210
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itn the old fashioned view of banking regulation (or self-regulation), we look at the assets side: as long as the bank has a tenth* of its assets in liquid form (i.e. gold coins in the safe), it will probably do OK.
Original toplevel document
Mark Wadsworth: Banking made easyset.2. The traditional books explain how banks started off using 'fractional reserve banking', i.e. they take 100 gold coins as deposits and lend out 90 of them, keeping 10 in the safe in case depositors come round to make a withdrawal.3. So i<span>n the old fashioned view of banking regulation (or self-regulation), we look at the assets side: as long as the bank has a tenth* of its assets in liquid form (i.e. gold coins in the safe), it will probably do OK.4. The modern view of banking regulation (i.e. Basel rules), we look at the liabilities side, and say that share capital (a non-repayable liability or source of finance) should be at lea
Flashcard 150897079
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 150897089
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 150902234
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
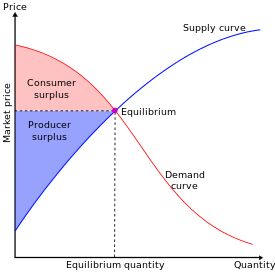
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itGraph illustrating consumer (red) and producer (blue) surpluses on a supply and demand chart.
Original toplevel document
Economic surplus - Wikipedia, the free encyclopediaFrom Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Jump to: navigation, search This article is about consumers' and producers' surplus. For information about other surpluses, see Surplus. <span>Graph illustrating consumer (red) and producer (blue) surpluses on a supply and demand chart In mainstream economics, economic surplus, also known as total welfare or Marshallian surplus (named after Alfred Marshall), refers to two related quantities. Consumer surplus or consume
Flashcard 150905371
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
What is Linux systemd ? A Neat Chart of its Components
| Reply More <span>systemd is a system and service manager that is designed specifically for Linux kernel. It replaces the init process to become the first process (PID = 1) that gets executed in user space during the Linux start-up process. In
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
What is Linux systemd ? A Neat Chart of its Components
More systemd is a system and service manager that is designed specifically for Linux kernel. It replaces the init process to become the first process (<span>PID = 1) that gets executed in user space during the Linux start-up process. In this article, we will study the basics of systemd. Note - The term init in this artic
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
What is Linux systemd ? A Neat Chart of its Components
More systemd is a system and service manager that is designed specifically for Linux kernel. It replaces the init process to become the first process (PID = 1) that <span>gets executed in user space during the Linux start-up process. In this article, we will study the basics of systemd. Note - The term init in this article refers to sysvinit. Why systemd? It is usually the first ques
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
What is Linux systemd ? A Neat Chart of its Components
Why systemd? It is usually the first question that comes into mind. To understand the answer, we need to first understand a bit about the init. If we just forget about systemd and the other similar systems, then itâs safe to say that <span>init is the first process started by kernel when you boot up any Linux or Unix computer. This means that all the other process are itâs children in one way or the other. Once the system is successfully brought up, the init process continues to run and waits for special
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
What is Linux systemd ? A Neat Chart of its Components
ât yet enabled the service by default. If you are an Ubuntu user, you can install systemd using this guide. Managing services with systemd Here is a list of some useful systemd utilities along with a brief description of what they do: <span>systemctl: Control the systemd system and services. journalctl: To manage journal, systemdâs own logging system hostnamectl: Control hostname. localectl: Configure system local and keyboard layout. timedatectl: Set time and date. systemd-cgls : Show cgroup contents. systemadm: Front-end for systemctl command. Letâs consider some basic examples that involve the systemctl utility. To display the status of everything systemd controls, just run the command with no options: $ systemctl To
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
What is Linux systemd ? A Neat Chart of its Components
e is currently running and 1 means it is not. To shutdown or reboot the system, you can use the following commands: systemctl halt systemctl poweroff systemctl reboot The concept of cgroups systemd organizes and manages processes with <span>cgroups -- a mechanism for limiting, accounting, and isolating Kernel resource usage. In laymanâs terms, it is a collection of processes that are bound by a common criteria. These groups can be hierarchical, and every group inherits limits from its parent. As new pr
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
What is Linux systemd ? A Neat Chart of its Components
$? If the result is 0, it means the service is currently running and 1 means it is not. To shutdown or reboot the system, you can use the following commands: systemctl halt systemctl poweroff systemctl reboot The concept of cgroups <span>systemd organizes and manages processes with cgroups -- a mechanism for limiting, accounting, and isolating Kernel resource usage. In laymanâs terms, it is a collection of processes that are bound by a common criteria. These groups can be hierarchical, and every group inherits limits from its parent. As new pr
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
What is Linux systemd ? A Neat Chart of its Components
ses are spawned they become members of the parent's cgroup. A cgroup is named for the service it belongs, and in case you need to kill a service, you can just kill its cgroup, killing all of its processes in one go. In cgroups vocabulary, <span>every system resource like CPU, memory, disk input/output, bandwidth is called a subsystem or resource controller. The Linux kernel provides access to various subsystems (like memory, CPU, and more) through these cgroups. The cgconfig service is used to manage hierarchies and cgroups on your syst