Edited, memorised or added to reading queue
on 26-Sep-2016 (Mon)
Do you want BuboFlash to help you learning these things? Click here to log in or create user.
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Abdo Pain
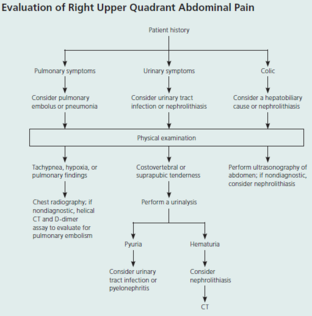
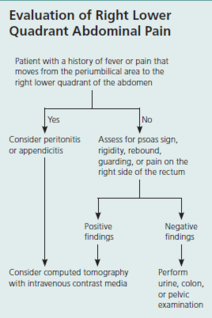
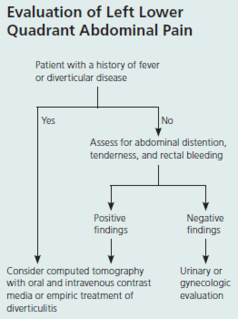
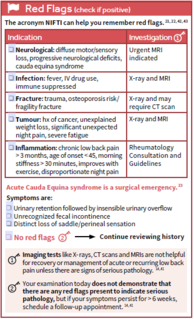
Abdominal Pain (acute and chronic) Subjective LOCATION of pain is starting point of abdo pain evaluation Is it pulm, urinary, or hepatobiliary? UTI/kidney stone → urinalysis colic/fever/steatorrhea/Murphy’s → u/s If suspected appendicitis, also get urgent surg consult Not just hx of fever/ds, physical findings too (e.g. distention, tenderness, rectal blood, etc) Onset, duration, severity, quality, exacerbating/remitting factors Pain relief w/ bowel mvnt, More freq stools w/ onset of pain, Loose stools w/ onset of pain, Passage of
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Abdo Pain
; Not just hx of fever/ds, physical findings too (e.g. distention, tenderness, rectal blood, etc) Onset, duration, severity, quality, exacerbating/remitting factors <span>Pain relief w/ bowel mvnt, More freq stools w/ onset of pain, Loose stools w/ onset of pain, Passage of mucus, Sensation of incomplete evacuation, abdo distention Manning criteria (3 or more of) for IBS Red flags New onset of pain, Change in pain, Altered bowel habits in elderly Check if all 3 are particular to elderly, or just the altered
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Abdo Pain
ief w/ bowel mvnt, More freq stools w/ onset of pain, Loose stools w/ onset of pain, Passage of mucus, Sensation of incomplete evacuation, abdo distention Manning criteria (3 or more of) for IBS <span>Red flags New onset of pain, Change in pain, Altered bowel habits in elderly Check if all 3 are particular to elderly, or just the altered bowel habits Wt loss (GI malignancy) Pain radiating to back (pancreatitis, AAA) Appendicitis (from highest to lowest PPV) RLQ PAIN, pain migration from periumbilical to RLQ, fever, anorexia Pain radiating to groin (testicular torsion, hernia, renal colic) Bleeding per rectum, melena stool (GI bleed, Meckel’s, malignancy in elderly) Anemia Supraclavicular nodes personal/family hx of serious bowel patho Pain waking pt at night Current abx/steroids (can mask peritoneal sx’s) Cardiac hx incl. Afib, HTN (ischemic bowel, AAA, MI) Bowel obstruction (highest to lowest PPV) CONSTIPATION, abdo distention, ↓ pain after vomiting, colic, prev abdo surg Antipsychotic use (ileus, obstruction, toxic megacolon) EtOH (risk factor for pancreatitis, varices) Sexually active (ectopic pregnancy, STIs) Cholecystitis (highest to lowest PPV) RUQ pain, fever, jaundice IBS algorithm Objective General inspection Change in men
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Abdo Pain
(risk factor for pancreatitis, varices) Sexually active (ectopic pregnancy, STIs) Cholecystitis (highest to lowest PPV) RUQ pain, fever, jaundice <span>IBS algorithm Objective General inspection Change in mental status (infection - UTI) Shock (perforated viscera, GI hemorrhage, severe panc
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Abdo Pain
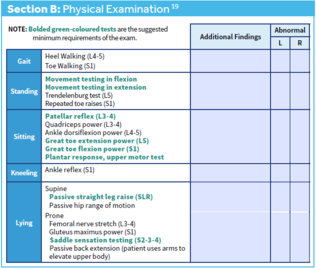
Cholecystitis (highest to lowest PPV) RUQ pain, fever, jaundice IBS algorithm <span>Objective General inspection Change in mental status (infection - UTI) Shock (perforated viscera, GI hemorrhage, severe pancreatitis, MI, sepsis) Vitals Upper abdo pain - pay attention to Cardiac (ischemia) & lung (pneumonia) exams Tachypneic (pneumonia) Abdo peritoneal signs Carnett’s sign (high ppv for abdo wall pain) ↑ pain when supine pt raises head & shoulder, tensing abdo wall Murphy’s sign (high ppv for choleycystitis) Psoas sign (high ppv for appendicitis) Sever pain out of proportion (ischemic bowel, pancreatitis) restless/writhing (biliary/renal colic, testicular torsion) LLQ tenderness (diverticulitis) Rectal & pelvic exams if lower abdo & pelvic pain DRE - fecal impaction, palpable mass, occult blood in stool Tenderness & fullness on R of rectum suggests retrocecal appendix Pelvic - vaginal discharge (vaginitis), cervical motion tenderness & peritoneal signs (ectopic pregnancy or other gyne complications e.g. tubo-ovarian abscess) S&S of surgical abdo Fever Protracted (prolonged) vomiting syncope/pre-syncope Evidence of GI blood loss
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Abdo Pain
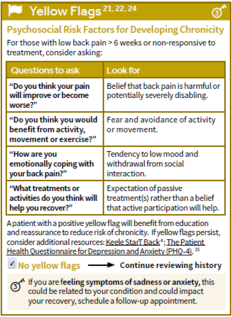
retrocecal appendix Pelvic - vaginal discharge (vaginitis), cervical motion tenderness & peritoneal signs (ectopic pregnancy or other gyne complications e.g. tubo-ovarian abscess) <span>S&S of surgical abdo Fever Protracted (prolonged) vomiting syncope/pre-syncope Evidence of GI blood loss Psychosocial factors assc w/ chr & recurrent abdo pain Assessment Common causes IBS (discomfort/pain assc w/ a
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Abdo Pain
Fever Protracted (prolonged) vomiting syncope/pre-syncope Evidence of GI blood loss Psychosocial factors assc w/ chr & recurrent abdo pain <span>Assessment Common causes IBS (discomfort/pain assc w/ altered bowel habits >3d/mo in prev 3 mo) Less common but important causes Appendicitis Acute cholecystitis Diverticulitis Acute pancreatitis Perforated ulcer Bowel infarction Plan (for acute abdo pain) - acute abdo = sudden, non-traumatic disorder needing urgent dx & tx Labs CBC (infection/blood loss)
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
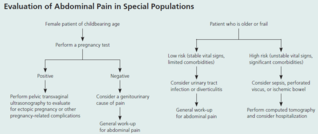
Abdo Pain
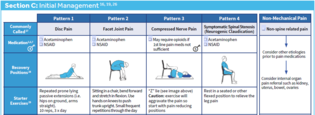
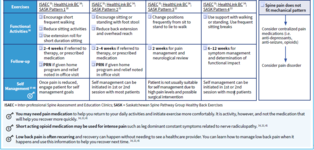
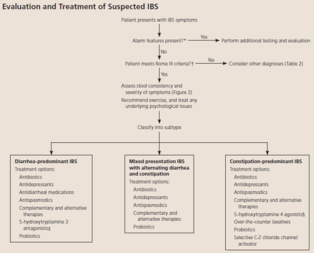
#13; Appendicitis Acute cholecystitis Diverticulitis Acute pancreatitis Perforated ulcer Bowel infarction <span>Plan (for acute abdo pain) - acute abdo = sudden, non-traumatic disorder needing urgent dx & tx Labs CBC (infection/blood loss) Amylase + lipase (pancreatitis) LFT (RUQ pain) Urinalysis (hematuria, dysuria, flank pain - UTI/kidney stone) Beta hcg (women in childbearing age) Chlamydia + gonorrhea (women @ risk of STIs) Imaging (based on location) U/S (RUQ pain) abdo/transvag ultrasound for pregnant women, even for LLQ/RLQ pain Transvag u/s for ectopic pregnancy CT w/ IV contrast media (adults w/ acute RLQ pain) CT w/ oral + IV contrast media (LLQ pain) - for sigmoid diverticulitis LUQ pain (many causes so depends) Suggested esophageal/gastric patho = endoscopy or upper GI series Others = CT (can image pancreas, spleen, kidneys, intestines, vasculature) Xray Free air under diaphragm (=perforation of GI tract) Abn calcifications (10% gallstones, 90% kidney stones) Mult dilated loops of bowel & air-fluid lvls (bowel obstruction) May see with paralytic ileus *occult UTI, perforated viscus, ischemic bowel ds* - potentially fatal, often missed or dx late in elderly pt CONSIDER IN ALL OLDER PTS w/ abdo pain Initial investigations & basic management for chr/recurrent abdo pain IBS Exercise: vigorous 3-5/week (all types of IBS)
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Abdo Pain
#13; *occult UTI, perforated viscus, ischemic bowel ds* - potentially fatal, often missed or dx late in elderly pt CONSIDER IN ALL OLDER PTS w/ abdo pain <span>Initial investigations & basic management for chr/recurrent abdo pain IBS Exercise: vigorous 3-5/week (all types of IBS) Laxatives: OTC (polyethylene glycol (PEG - osmotic) - Miralax); only helps w/ constipation Antidiarrheal: OTC loperamide (imodium); likely only helps diarrhea Probiotics: in some OTC supplements & yogurts (lactobacillus, bifidobacterium, streptococcus) To prevent worsening sx Abx Diarrheal/mixed: rifaximin (Xifaxan); prevent worsening global sx over 4wk Constipation: neomycin; improve constipation & bloating Antispasmodics: hyoscyamine (Levsin), dicyclomine (Bentyl) Selective C-2 chloride channel activators: lubiprostone (Amitiza) - constipation Antidepressants SSRI - citalopram (celexa), fluoxetine (prozac), paroxetine (paxil) TCA - amitriptyline, desipramine (norpramin), doxepin, imipramine (tofranil), trimipramine (surmontil) Other: relaxation, herbals, peppermint oil Not routinely recommended: CBC, lytes, thyroid, stool testing for ova & parasites, abdo img <span><body><html>
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |