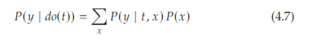Edited, memorised or added to reading queue
on 18-May-2022 (Wed)
Do you want BuboFlash to help you learning these things? Click here to log in or create user.
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 7070797663500
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itan> The idea is that although the treatment and potential outcomes may be unconditionally associated (due to confounding), within levels of 𝑋 , they are not associated. In other words, there is <span>no confounding within levels of 𝑋 because controlling for 𝑋 has made the treatment groups comparable. <span>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 7088143207692
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itAssociation flows along all unblocked paths. In causal graphs, causation flows along directed paths. Recall from Section 1.3.2 that not only is association not causation, but causation is a sub-category of association. That’s why association and causation both flow along directed paths.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 7088156052748
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itThe minimal building blocks of DAGs consist of chains, forks, immoralities, two unconnected nodes, and two connected nodes.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 7088157887756
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itThe main reason for moving from exchangeability (Assumption 2.1) to conditional exchangeability (Assumption 2.2) was that it seemed like a more realistic assumption
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 7088159722764
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itDefinition 3.4 (d-separation) Two (sets of) nodes 𝑋 and 𝑌 are d-separated by a set of nodes 𝑍 if all of the paths between (any node in) 𝑋 and (any node in) 𝑌 are blocked by 𝑍 Source: Pearl (1988), Probabilistic Reasoning in Intelligent Systems: Networks of Plausible Inference
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 7088161557772
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itWe assumed 𝑋 is discrete when we summed over its values, but we can simply replace the sum with an integral if 𝑋 is continuous. Throughout this book, that will be the case, so we usually won’t point it out To jest kluczowe równanie.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itsfying unconfoundedness, it can lead to a higher chance of violating positivity. As we increase the dimension of the covariates, we make the subgroups for any level 𝑥 of the covariates smaller. <span>The Positivity-Unconfoundedness Tradeoff This is related to the curse of dimensionality. As each subgroup gets smaller, there is a higher and higher chance that either the whole subgroup will have treatment or the whole subgroup will have control. For example, once the size of any subgroup has decreased to one, positivity is guaranteed to not hold. <span>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 7088166276364
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itExchangeability means that the treatment groups are exchangeable in the sense that if they were swapped, the new treatment group would observe the same outcomes as the old treatment group