Edited, memorised or added to reading queue
on 24-May-2022 (Tue)
Do you want BuboFlash to help you learning these things? Click here to log in or create user.
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 7088881143052
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
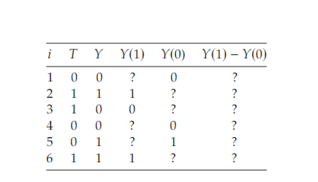
Open ithole population of interest. Because of the fundamental problem of causal inference, this is fundamentally a missing data problem. All of the question marks in the table indicate that we do not <span>observe that cell. <span>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 7088883240204
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itThe simple solution of left-joining the customer table with the order table, consolidating all the information and then synthesising this big table will not work. For two reasons: 1. Each synthesised row will be a new cus
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 7088885075212
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
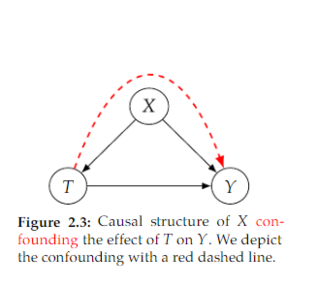
Open itin Figure 2.3. Because 𝑋 is a common cause of 𝑇 and 𝑌 , there is non-causal association between 𝑇 and 𝑌
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 7088887172364
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itIf all the paths between two nodes 𝑋 and 𝑌 are blocked, then we say that 𝑋 and 𝑌 are d-separated.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open ithe intervention do(𝑡) occurs. For example, 𝔼[𝑌 | do(𝑡), 𝑍 = 𝑧] refers to the expected outcome in the subpopulation where 𝑍 = 𝑧 after the whole subpopulation has taken treatment 𝑡 . In contrast, <span>𝔼[𝑌 | 𝑍 = 𝑧] simply refers to the expected value in the (pre-intervention) population where individuals take whatever treatment they would normally take ( 𝑇 ). This distinction will become important when we get to counterfactuals in <span>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 7088933833996
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itBy “flow of association,” we mean whether any two nodes in a graph are associated or not associated. Another way of saying this is whether two nodes are (statistically) dependent or (statistically) independent
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
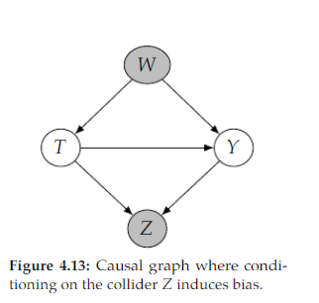
Open itblocked by a collider. For example, this is the case with conditioning on 𝑍 in Figure 4.13. This induces non-causal association between 𝑇 and 𝑌 , which biases the estimate of the causal effect. <span>Consider the following general kind of path, where → · · · → denotes a directed path: 𝑇 → · · · → 𝑍 ← · · · ← 𝑌 . Conditioning on 𝑍 , or any descendant of 𝑍 in a path like this, will induce collider bias. That is, the causal effect estimate will be biased by the non-causal association that we induce when we condition on 𝑍 or any of its descendants (see Section 3.6). <span>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 7088937766156
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itIn observational data, it is unrealistic to assume that the treatment groups are exchangeable. In other words, there is no reason to expect that the groups are the same in all relevant variables other than the treatment.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 7088940387596
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itDefinition 3.3 (blocked path) A path between nodes 𝑋 and 𝑌 is blocked by a (potentially empty) conditioning set 𝑍 if either of the following is true: 1. Along the path, there is a chain · · · → 𝑊 → · · · or a fork · · · ← 𝑊 → · · ·, where 𝑊 is conditioned on (𝑊 ∈ 𝑍). 2. There is a collider 𝑊 on the path that
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 7088942222604
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itIt turns out that much of the work for causal graphical models was done in the field of probabilistic graphical models.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 7088944057612
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itAssumption 3.2 (Minimality Assumption) 1. Given its parents in the DAG, a node 𝑋 is independent of all its non-descendants (Assumption 3.1). 2. Adjacent nodes in the DAG are dependent.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 7088945892620
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itDefinition 3.2 (What is a cause?) A variable 𝑋 is said to be a cause of a variable 𝑌 if 𝑌 can change in response to changes in 𝑋
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 7088950086924
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 7088951135500
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
opics are updated as new evidence becomes available and our peer review process is complete. Literature review current through: Apr 2022. | This topic last updated: May 20, 2022. INTRODUCTION — <span>Monkeypox is a viral zoonotic infection that results in a rash similar to smallpox. However, the person-to-person spread and the mortality from a monkeypox infection are significantly lower than for smallpox. Clinically, these two viral infections are difficult to distinguish, raising concerns that monkeypox could be used for bioterrorism [1]. This topic will review the virology, epidemiology, clinical manifestations, diagnosis, and treatment of monkeypox. Topic reviews that discuss smallpox are presented separately. (See "V
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
atment of monkeypox. Topic reviews that discuss smallpox are presented separately. (See "Variola virus (smallpox)" and "Identifying and managing casualties of biological terrorism".) VIROLOGY — <span>Monkeypox, an orthopoxvirus, was first isolated in the late 1950s from a colony of sick monkeys. The virus is in the same genus as variola (causative agent of smallpox) and vaccinia viruses (the virus used in smallpox vaccine). Electron microscopy of cells infected with monkeypox virus shows a brick-like virion, indistinguishable from the virions of variola or vaccinia viruses (picture 1). Two distinct strain
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
s used in smallpox vaccine). Electron microscopy of cells infected with monkeypox virus shows a brick-like virion, indistinguishable from the virions of variola or vaccinia viruses (picture 1). <span>Two distinct strains of monkeypox exist in different geographic regions of Africa, as suggested by epidemiologic, animal, and molecular evidence [2]. In comparison to strains isolated from Central Africa, monkeypox from Western Africa is less virulent and lacks a number of genes present in the other viral strain [2,3]. EPIDEMIOLOGY History — It is believed that monkeypox virus has infected humans for thousands of years in sub-Saharan Africa [1]. Monkeypox was first identified as a cause of disease in
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
ence [2]. In comparison to strains isolated from Central Africa, monkeypox from Western Africa is less virulent and lacks a number of genes present in the other viral strain [2,3]. EPIDEMIOLOGY <span>History — It is believed that monkeypox virus has infected humans for thousands of years in sub-Saharan Africa [1]. Monkeypox was first identified as a cause of disease in humans in the 1970s in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (formerly the Republic of Zaire) [1,4-7]. Following its recognition
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
of years in sub-Saharan Africa [1]. Monkeypox was first identified as a cause of disease in humans in the 1970s in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (formerly the Republic of Zaire) [1,4-7]. <span>Following its recognition as a human pathogen, 59 cases of human monkeypox were reported between 1970 and 1980, with a mortality rate of 17 percent. All of these cases occurred in the rain forests of Western and Central Africa among individuals exposed to small forest animals (eg, rodents, squirrels, and monkeys). The first outbreak of monkeypox in the Western Hemisphere occurred in the United States in 2003 [8-10]. (See 'United States' below and 'Other countries' below.) Transmission ●Animal-to-
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
tality rate of 17 percent. All of these cases occurred in the rain forests of Western and Central Africa among individuals exposed to small forest animals (eg, rodents, squirrels, and monkeys). <span>The first outbreak of monkeypox in the Western Hemisphere occurred in the United States in 2003 [8-10]. (See 'United States' below and 'Other countries' below.) Transmission ●Animal-to-human transmission – The virus is typically acquired through contact with an infected animal's bodily fluids or through a bite. Monkeys and humans are incidental
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
els, and monkeys). The first outbreak of monkeypox in the Western Hemisphere occurred in the United States in 2003 [8-10]. (See 'United States' below and 'Other countries' below.) Transmission ●<span>Animal-to-human transmission – The virus is typically acquired through contact with an infected animal's bodily fluids or through a bite. Monkeys and humans are incidental hosts; the reservoir remains unknown but is likely to be rodents. Infected rodents from Western Africa were accidentally imported into the United States; this led to the first human monkeypox infections in the Western Hemisphere. Based on findings du
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
but is likely to be rodents. Infected rodents from Western Africa were accidentally imported into the United States; this led to the first human monkeypox infections in the Western Hemisphere. <span>Based on findings during a 2003 United States outbreak, the route of infection and extent of exposure (eg, bite wound versus touching an infected animal) can influence the severity of clinical manifestations of monkeypox infection. For example, one study categorized exposures to a prairie dog as noninvasive (eg, the person touched an infected animal, cleaned an infected animal's cage) or "complex" (eg, invasive bite or scratch from an ill prairie dog) [11]. Patients with complex exposures were more likely than patients with noninvasive exposures to develop signs of systemic illness. (See 'United States' below.) ●Human-to-human transmission – Human-to-human transmission can occur through large respiratory droplets. Transmission can also occur through close contact with infectious skin lesions o
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
atch from an ill prairie dog) [11]. Patients with complex exposures were more likely than patients with noninvasive exposures to develop signs of systemic illness. (See 'United States' below.) ●<span>Human-to-human transmission – Human-to-human transmission can occur through large respiratory droplets. Transmission can also occur through close contact with infectious skin lesions or from contact with lesion material. For droplet transmission, prolonged face-to-face contact may be required for transmission to occur (eg, within a six-foot radius for ≥3 hours in the absence of personal protection equip
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
– Human-to-human transmission can occur through large respiratory droplets. Transmission can also occur through close contact with infectious skin lesions or from contact with lesion material. <span>For droplet transmission, prolonged face-to-face contact may be required for transmission to occur (eg, within a six-foot radius for ≥3 hours in the absence of personal protection equipment [PPE]) [12]. In general, transmissibility from person to person is very low [13]. However, in a cluster of cases seen in May 2022, the risk of person-to-person transmission appears to be high [14].
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
ve been reported in several other countries, mostly related to travel. In the United States, there was an outbreak due to importation of exotic animals from Africa. (See 'United States' below.) <span>Africa — From 1996 to 1998, an outbreak of febrile illness with associated pustular lesions occurred among about 100 persons with reports of secondary attack rates of 80 percent [4,7]. A concurrent chickenpox outbreak may have resulted in misclassification of cases and likely explained the high secondary attack rates. Nevertheless, this outbreak created concern that
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
man cases of monkeypox due to the lack of prior smallpox vaccination; persons with a history of smallpox immunization had a fivefold lower risk of monkeypox infection than unvaccinated persons. <span>Other factors associated with an increased risk of infection included living in forested areas, male sex, and age <15 years. Since 2017, there has been an increase in monkeypox cases in Nigeria; this occurred after almost 40 years with no reported cases [17]. Some of these cases have occurred among returning
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
dy evaluating the 2017 outbreak, a small pool of related isolates was the likely source for the exported infections [18]. (See 'United States' below and 'Other countries' below.) United States ●<span>Outbreak in 2003 – Between May 15 and June 2003, an outbreak of 71 cases of human monkeypox in six states was investigated by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC); 35 cases were laboratory confirmed [8-10]. Prior to this cluster of cases, monkeypox had not been previously found in the Western hemisphere. The investigation demonstrated that the onset of a febrile illness, with subsequent appearance of a pustular rash, had developed in patients who had recently purchased pet prairie dogs.
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
excluded. Of the cases reported in Wisconsin, the veterinary staff who were exposed to an outbreak-associated prairie dog were at particularly high risk, with an attack rate of 23 percent [20]. <span>During this outbreak, monkeypox appeared to have a very low rate of person-to-person transmission. In one study of 57 health care workers who were exposed to patients with monkeypox, none reported signs and symptoms of disease [21]. Only one had laboratory evidence of recent orthopoxvirus infection, which was probably secondary to prior smallpox vaccination. By contrast, secondary attack rates for smallpox can be as high as 70 percent [5,22]. Because of this outbreak, the transportation, sale, or release into the wild of prairie dogs and animals from Africa (including tree squirrels, rope squirrels, dormice, brush-tailed por
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
a [29] and Australia [30]. These cases were not related to travel to endemic areas and appear to be related to the outbreak in Europe, described above. (See 'Europe' above.) INCUBATION PERIOD — <span>The United States outbreak described above allowed estimation of time from exposure to onset of symptoms. Approximately half of the patients reported a scratch, bite, or petting of an infected animal [31]. For 29 patients, the estimated incubation time from exposure to illness was 12 days. Persons with a history of an animal bite or scratch may have a shorter incubation period than those with tactile exposures (13 versus 9 days, respectively) [11]. CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS — Based largely on seroepidemiological studies in Africa, the majority of monkeypox infections are asymptomatic. In symptomatic individuals, monkeypox causes a
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
days. Persons with a history of an animal bite or scratch may have a shorter incubation period than those with tactile exposures (13 versus 9 days, respectively) [11]. CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS — <span>Based largely on seroepidemiological studies in Africa, the majority of monkeypox infections are asymptomatic. In symptomatic individuals, monkeypox causes a systemic illness including fevers, chills, and myalgias, with a characteristic rash that is important to differentiate from that of smallpox. The clinical illness can also differ by viral strain. (See 'Differential diagnosis' below.) Outbreaks in Africa — In Africa, the monkeypox rash starts on the trunk and then spreads peripherally to involve the palms and soles of the feet. L
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
s, and myalgias, with a characteristic rash that is important to differentiate from that of smallpox. The clinical illness can also differ by viral strain. (See 'Differential diagnosis' below.) <span>Outbreaks in Africa — In Africa, the monkeypox rash starts on the trunk and then spreads peripherally to involve the palms and soles of the feet. Lesions can also involve the mucous membranes and usually range from 0.5 to 1 centimeter in size. The rash usually begins as macules and papules; the rash then progresses over a two- to four-week period to vesicles, pustules, followed by umbilication, scabbing, and desquamation. Some patients develop only a localized rash on their hands associated with direct contact with the infected animal. United States outbreaks — Although comprehensive clinical information is limited on monkeypox in Africa, the 2003 United States outbreak allowed further characterization of the illness
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
to vesicles, pustules, followed by umbilication, scabbing, and desquamation. Some patients develop only a localized rash on their hands associated with direct contact with the infected animal. <span>United States outbreaks — Although comprehensive clinical information is limited on monkeypox in Africa, the 2003 United States outbreak allowed further characterization of the illness in 34 of 37 subjects for whom medical records were available [31]. The predominant signs and symptoms were: ●Rash (97 percent) ●Fever (85 percent) ●Chills (71 percent) ●Lymphadenopathy (71 percent) ●Headache (65 percent) ●Myalgias (56 percent) The onset of fever preceded the rash by approximately two days, but the median duration of fever was shorter than the rash (8 and 12 days, respectively). The following clinical pictures
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
available [31]. The predominant signs and symptoms were: ●Rash (97 percent) ●Fever (85 percent) ●Chills (71 percent) ●Lymphadenopathy (71 percent) ●Headache (65 percent) ●Myalgias (56 percent) <span>The onset of fever preceded the rash by approximately two days, but the median duration of fever was shorter than the rash (8 and 12 days, respectively). The following clinical pictures of the initial case identified in the United States were taken at the Marshfield Clinic in Wisconsin (picture 2A-D). The rash in this United States outbr
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
che (65 percent) ●Myalgias (56 percent) The onset of fever preceded the rash by approximately two days, but the median duration of fever was shorter than the rash (8 and 12 days, respectively). <span>The following clinical pictures of the initial case identified in the United States were taken at the Marshfield Clinic in Wisconsin (picture 2A-D). The rash in this United States outbreak was described as maculopapular in nature on initial presentation; the rash subsequently evolved into vesicles, then pustules, which eventually crusted within a two- to three-week period [31]. Nine of the 34 patients were hospitalized for a variety of reasons, including nausea, vomiting, and dysphagia. The discharge diagnoses of two of the most seriously ill patients were enc
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
k was described as maculopapular in nature on initial presentation; the rash subsequently evolved into vesicles, then pustules, which eventually crusted within a two- to three-week period [31]. <span>Nine of the 34 patients were hospitalized for a variety of reasons, including nausea, vomiting, and dysphagia. The discharge diagnoses of two of the most seriously ill patients were encephalopathy and a retropharyngeal abscess. All of the patients in this case series survived with supportive therapy; no antiviral therapy was administered. Multiple nonspecific laboratory findings were also noted including abnormal aminotransferases, leukocytosis, mild thrombocytopenia, and hypoalbuminemia. In the cluster of cases reported
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
e most seriously ill patients were encephalopathy and a retropharyngeal abscess. All of the patients in this case series survived with supportive therapy; no antiviral therapy was administered. <span>Multiple nonspecific laboratory findings were also noted including abnormal aminotransferases, leukocytosis, mild thrombocytopenia, and hypoalbuminemia. In the cluster of cases reported in May 2022, it was noted that some patients may present with proctitis or with lesions located on the genital or perianal area alone [23,32]. DIAGNOSIS
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
; no antiviral therapy was administered. Multiple nonspecific laboratory findings were also noted including abnormal aminotransferases, leukocytosis, mild thrombocytopenia, and hypoalbuminemia. <span>In the cluster of cases reported in May 2022, it was noted that some patients may present with proctitis or with lesions located on the genital or perianal area alone [23,32]. DIAGNOSIS — Although clinical features are helpful in making the diagnosis, laboratory confirmation of monkeypox virus is necessary to differentiate this disease from those caused by ot
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
the 2003 United States outbreak, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) developed an immunoglobulin M-capture and an IgG ELISA that demonstrated recent monkeypox virus infection. <span>Serum IgM and IgG antibodies were detected five and eight days after onset of rash, respectively [35]. Other experimental antibody and cellular based assays are under development, which may be useful for the prospective and retrospective diagnosis of monkeypox [22]. If the diagnosis of m
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
idered, local and state public health officials, along with the CDC, should be notified so that the samples are quickly processed. (See 'Differential diagnosis' below.) DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS — <span>Several infections need to be considered in the differential diagnosis of monkeypox; these include varicella, herpes simplex virus, smallpox, and other poxviruses. Given the worldwide eradication of smallpox, the most likely diagnostic consideration is varicella (chickenpox). Unlike varicella where vesicular lesions are characteristically in diffe
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
; these include varicella, herpes simplex virus, smallpox, and other poxviruses. Given the worldwide eradication of smallpox, the most likely diagnostic consideration is varicella (chickenpox). <span>Unlike varicella where vesicular lesions are characteristically in different stages of development and healing when the patient is examined, monkeypox lesions are all generally at the same stage. (See "Clinical features of varicella-zoster virus infection: Chickenpox".) Because of concerns regarding bioterrorism, it is also important to consider the possibility of smallpox in t
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
also important to consider the possibility of smallpox in the differential diagnosis of a patient who has not been in the rain forests of Africa or exposed to potentially infected animals [6]. <span>Lymphadenopathy, which has been observed in the majority of unvaccinated patients, is a key distinguishing feature of monkeypox [10]. Lymphadenopathy can occur in the submandibular, cervical, or inguinal regions. (See "Identifying and managing casualties of biological terrorism" and "Variola virus (smallpox)".) Also in the differential diagnosis is tanapox, another African poxvirus that causes a
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
sea, vomiting, dysphagia) may require a short hospital stay for intravenous hydration. For the seriously ill patient, supportive care is necessary until the patient recovers from the infection. <span>Antivirals — Several antivirals may be useful for the treatment of monkeypox. These drugs were approved for treatment of smallpox based on animal models and dose studies in healthy humans but are expected to have the same activity against human monkeypox. (See "Variola virus (smallpox)", section on 'Antiviral therapy'.) In general, tecovirimat is the treatment of choice, though some experts may use dual therapy with tecovirimat and brinc
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
x based on animal models and dose studies in healthy humans but are expected to have the same activity against human monkeypox. (See "Variola virus (smallpox)", section on 'Antiviral therapy'.) <span>In general, tecovirimat is the treatment of choice, though some experts may use dual therapy with tecovirimat and brincidofovir in patients with severe disease. Treatment decisions should be made in consultation with local departments of health and/or the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). In the United States, tecovirimat and br
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
available through the United States government's Strategic National Stockpile. Additional information regarding management of monkeypox during an outbreak can be also found on the CDC website. <span>Tecovirimat — In July 2018, tecovirimat was approved for use in the United States for treatment of smallpox [37]. This drug protects nonhuman primates from lethal monkeypox virus infections [37-39] and will likely be efficacious against this infection in humans as well. Tecovirimat is a potent inhibitor of an orthopoxvirus protein required for the formation of an infectious virus particle that is essential for dissemination within an infected host. The recommended dose of tecovirimat depends upon the patient's weight, as described in manufacturer labeling and the Lexicomp drug information topic within UpToDate. The duration of tre
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
ns as well. Tecovirimat is a potent inhibitor of an orthopoxvirus protein required for the formation of an infectious virus particle that is essential for dissemination within an infected host. <span>The recommended dose of tecovirimat depends upon the patient's weight, as described in manufacturer labeling and the Lexicomp drug information topic within UpToDate. The duration of treatment is 14 days. The most frequently reported side effects are headache, nausea, and abdominal pain. A more detailed discussion of this agent is found elsewhere. (See "Variola virus (smallpox)", section on 'Tecovirimat'.) Brincidofovir — In June 2021, brincidofovir was approved for use
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
regarding its efficacy against monkeypox infection in humans and its use can be associated with significant adverse events, including nephrotoxicity. (See "Cidofovir: An overview".) MORTALITY — <span>In Central Africa, the fatality rate is approximately 10 percent and deaths generally occur in the second week of illness [1,47]. In contrast, there were no deaths in the outbreak in the United States. These more favorable outcomes in the United States may be related to a healthier patient population, greater availability of supportive medical care, and a less virulent strain of monkeypox, which was imported from the West African nation of Ghana [31]. PREVENTION — Data suggest that prior immunization with smallpox vaccine prevents infection and ameliorates symptoms. The role of postexposure prophylaxis with smallpox vaccine or vaccin
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
althier patient population, greater availability of supportive medical care, and a less virulent strain of monkeypox, which was imported from the West African nation of Ghana [31]. PREVENTION — <span>Data suggest that prior immunization with smallpox vaccine prevents infection and ameliorates symptoms. The role of postexposure prophylaxis with smallpox vaccine or vaccinia immunoglobulin is unclear, as discussed below. Smallpox immunization — Prior smallpox vaccination with vaccinia virus has a significant protective effect against acquisition of monkeypox virus and may ameliorate the clinical manifes
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
ed with unvaccinated persons (0.78 versus 4.05 per 10,000). In that study, vaccine efficacy was estimated to be approximately 81 percent in those with a distant history of smallpox vaccination. <span>In the United States outbreak, further investigation using experimental techniques identified three additional monkeypox exposures in individuals who had previously received smallpox vaccination 13, 29, and 48 years prior to exposure to monkeypox [22]. These individuals were unaware that they had been infected because they did not have any recognizable disease symptoms. These findings suggested that the United States monkeypox outbreak was larger than previously realized. Furthermore, cross-protective antiviral immunity against West African monkeypox can potentially be maintained for decades after smallpox vaccination. Postexposure prophylaxis Postexposure vaccination — In addition to monitoring and isolating close contacts, postexposure vaccination with MVA vaccine may be considered for certain patie
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
ypox (eg, direct contact with patient or materials from patient’s room without personal protection equipment (PPE) [26]). This decision must be made in conjunction with public health authorities<span>. Public Health England developed risk assessment and public health recommendations for persons potentially exposed that are summarized in the table (table 1) [26]. Since prior vaccination with vaccinia virus protects against monkeypox infection, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommended vaccination with vaccinia virus for th
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
revention (CDC) recommended vaccination with vaccinia virus for the limited number of individuals exposed to monkeypox in the 2003 United States outbreak, including children and pregnant women. <span>The CDC also recommended pre-exposure vaccination for those involved in the investigation of the outbreak and for health care workers caring for patients with monkeypox [8,10]. Twenty-eight adults and two children received the smallpox vaccine for this purpose and no cases of monkeypox were identified among these recipients [10]. Furthermore, no cases of monkeypox were identified during pregnancy during the 2003 outbreak; it is not known if the infection carries a different prognosis in pregnant women [49]. Base
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
pients [10]. Furthermore, no cases of monkeypox were identified during pregnancy during the 2003 outbreak; it is not known if the infection carries a different prognosis in pregnant women [49]. <span>Based on historical data on postexposure vaccination for smallpox with vaccinia vaccine, the optimal time for monkeypox postexposure vaccination is within four days; however, vaccination can be considered for up to 14 days of a close contact exposure, according to the CDC [50]. Close contact is defined as direct exposure within six feet of a probable or confirmed monkeypox case in an animal with respiratory symptoms such as nasal discharge, cough, or conjuncti
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
ne, the optimal time for monkeypox postexposure vaccination is within four days; however, vaccination can be considered for up to 14 days of a close contact exposure, according to the CDC [50]. <span>Close contact is defined as direct exposure within six feet of a probable or confirmed monkeypox case in an animal with respiratory symptoms such as nasal discharge, cough, or conjunctivitis in a setting where the animal has been manipulated (eg, an exam room) [50]. (See "Vaccinia virus as the smallpox vaccine" and "Immunizations during pregnancy", section on 'Smallpox'.) Vaccinia immune globulin — The use of vaccinia immune globulin may be conside
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
nctivitis in a setting where the animal has been manipulated (eg, an exam room) [50]. (See "Vaccinia virus as the smallpox vaccine" and "Immunizations during pregnancy", section on 'Smallpox'.) <span>Vaccinia immune globulin — The use of vaccinia immune globulin may be considered in immunosuppressed patients with an exposure history, since immunization with vaccinia virus vaccine is contraindicated [1]. Infection control precautions — Use of both contact and airborne precautions are recommended for any generalized vesicular rash of unknown etiology in which monkeypox and smallpox are i
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
of both contact and airborne precautions are recommended for any generalized vesicular rash of unknown etiology in which monkeypox and smallpox are included in the differential diagnosis [21]. <span>During the first week of the rash, persons with suspected monkeypox should be considered infectious and be isolated until all scabs separate and results of throat swab polymerase chain reaction (PCR) are negative [1]. Additional information on infection control precautions to prevent monkeypox transmission can be found on the CDC website. SUMMARY AND RECOMMENDATIONS ●Virology – Monkeypox, an orthopox