Edited, memorised or added to reading queue
on 27-May-2022 (Fri)
Do you want BuboFlash to help you learning these things? Click here to log in or create user.
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 7088695545100
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
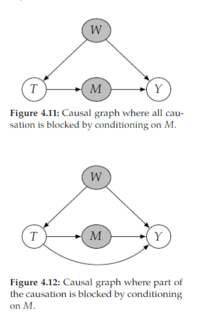
Open itIn contrast, the non-strict causal edges assumption would allow for some parents to not be causes of their children. It would just assume that children are not causes of their parents. This allows us to draw graph
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 7089808346380
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open ition 4.1) for the backdoor adjustment (Theorem 4.2), not only did we specify that the adjustment set 𝑊 blocks all backdoor paths, but we also specified that 𝑊 does not contain any descendants of <span>𝑇 <span>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 7089810443532
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itthe local Markov assumption is, it only gives us information about the independencies in 𝑃 that a DAG implies. It does not even tell us that if 𝑋 and 𝑌 are adjacent in the DAG, then 𝑋 and 𝑌 are <span>dependent. And this additional information is very commonly assumed in causal DAGs. To get this guaranteed dependence between adjacent nodes, we will generally assume a slightly stronger assumpti
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itAn “estimator” is a function that takes a dataset as input and outputs an estimate. We discuss this statistics terminology more in Section 2.4. That’s the math for why we need the positivity assumption, but what’s the intuition? Well, if we have a positivity violation, that means that within some subgroup of the data, everyone always receives treatment or everyone always receives the control. It wouldn’t make sense to be able to estimate a causal effect of treatment vs. control in that subgroup since we see only treatment or only control. We never see the alternative in that subgroup
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itred to as “counterfactual outcomes,” but we will never do that in this book because a potential outcome 𝑌(𝑡) does not become counter to fact until another potential outcome 𝑌(𝑡 0 ) is observed. <span>The potential outcome that is observed is sometimes referred to as a factual. Note that there are no counterfactuals or factuals until the outcome is observed. Before that, there are only potential outcomes <span>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 7089815686412
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itConsistency is the assumption that the outcome we observe 𝑌 is actually the potential outcome under the observed treatment 𝑇
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itThe flow of association is symmetric, whereas the flow of causation is not.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 7089819618572
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itt uses potential outcome notation to one that uses only statistical notation such as 𝑇 , 𝑋 , 𝑌 , expectations, and conditioning. This means that we can calculate the causal effect from just the <span>observational distribution 𝑃(𝑋, 𝑇, 𝑌) <span>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 7089821453580
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itWhen we say “estimation,” we are referring to the process of moving from a statistical estimand to an estimate
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 7089828269324
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itAnswer: conditional association
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 7089830104332
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
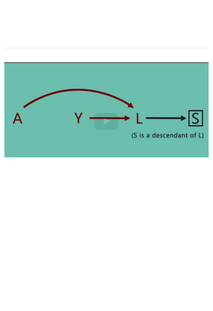
Open itExample of not blocked the path A - Y
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 7089995779340
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itin assumptions that we need for our causal graphical models to tell us how association and causation flow between variables are the following two: 1. Local Markov Assumption (Assumption 3.1) 2. <span>Causal Edges Assumption (Assumption 3.3) <span>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 7089997614348
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itConditional exchangeability is the main assumption necessary for causal inference. Armed with this assumption, we can identify the causal effect within levels of 𝑋
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 7089999449356
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itAn “estimator” is a function that takes a dataset as input and outputs an estimate.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 7090048994572
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itA potential outcome 𝑌(𝑡) is distinct from the observed outcome 𝑌 in that not all potential outcomes are observed
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 7090109549836
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itthe fundamental problem of causal inference It is fundamental because if we cannot observe both 𝑌 𝑖 (1) and 𝑌 𝑖 (0) , then we cannot observe the causal effect 𝑌 𝑖 (1) − 𝑌 𝑖 (0) .
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 7090186095884
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itPositivity is the condition that all subgroups of the data with different covariates have some probability of receiving any value of treatment
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 7090273914124
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
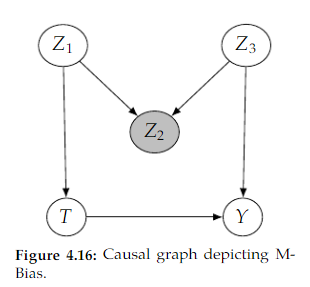
Open itThis is known as M-bias due to the M shape that this non-causal association flows along when the graph is drawn with children below their parents.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 7090618633484
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
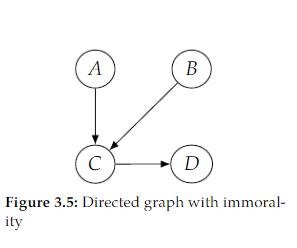
Open itFor example, if we remove the 𝐴 → 𝐵 to get Figure 3.5, then 𝐴 → 𝐶 ← 𝐵 is an immorality