Edited, memorised or added to reading queue
on 01-Jun-2022 (Wed)
Do you want BuboFlash to help you learning these things? Click here to log in or create user.
Flashcard 7092440796428
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 7093022756108
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 7093030620428
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itAssumption 3.3 ((Strict) Causal Edges Assumption) In a directed graph, every parent is a direct cause of all its children
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 7093032717580
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itAn estimand is the quantity that we want to estimate.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 7093034814732
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itAssumptions of causal inference: 1. Unconfoundedness (Assumption 2.2) 2. Positivity (Assumption 2.3) 3. No interference (Assumption 2.4) 4. Consistency (Assumption 2.5)
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 7093036649740
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itThe Positivity-Unconfoundedness Tradeoff Although conditioning on more covariates could lead to a higher chance of satisfying unconfoundedness, it can lead to a higher chance of violating positivity.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 7093038484748
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open ite would be, if you were to take treatment 𝑡 . A potential outcome 𝑌(𝑡) is distinct from the observed outcome 𝑌 in that not all potential outcomes are observed. Rather all potential outcomes can <span>potentially be observed. The one that is actually observed depends on the value that the treatment 𝑇 takes on <span>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 7093040581900
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
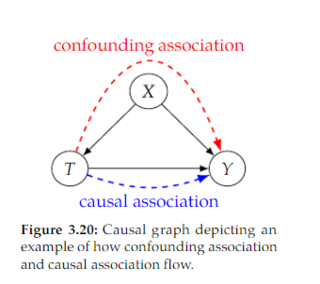
Open itWe refer to the flow of association along directed paths as causal association
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 7093042679052
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itMore generally, the potential outcome 𝑌(𝑡) denotes what your outcome would be, if you were to take treatment 𝑡
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 7093044776204
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itLet's start by considering two extreme examples. In the first causal graph here you see that A and Y have no common causes. And therefore, any association between them will be causation. This is the setting that we expect to find in a randomized experiment.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 7093046611212
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itToday we will focus on confounding in a setting with no selection bias, with no measurement error, and with such a large population that we do not need to worry about chance variability
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itusal graph here you see that A and Y have no common causes. And therefore, any association between them will be causation. This is the setting that we expect to find in a randomized experiment. <span>In the second graph here, you see that A and Y have a common cause, L. But there is no causal effect of A on Y. In this setting, all the association between A and Y is due to confounding. <span>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 7093051067660
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itWhat is the backdoor path criterion? This is a graphical rule that tells us whether we can identify the causal effect of interest if we know the causal DAG. And the rule is the following: we can identify the causal effect
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 7093052902668
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itTwo sources of bias: - common cause (confounding) - conditioning on common effect (selection bias)
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 7093054737676
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itWe have seen that confounding is a systematic bias when we are conducting causal inference research.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 7093056572684
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itWhen there is an association between A and Y, even if A has a null causal effect, a zero causal effect on Y, then we say that there is bias under the null.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 7093058145548
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itWhen there is an association between A and Y, even if A has a null causal effect, a zero causal effect on Y, then we say that there is bias under the null.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 7093059980556
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itOther (wrong definitions of confounder): - change in estimate definition - conventional definition
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 7093061815564
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itSystematic bias is an association between the treatment A and the outcome Y that does not arise from the causal effect of A on Y.