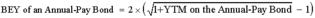Edited, memorised or added to reading queue
on 13-Jul-2017 (Thu)
Do you want BuboFlash to help you learning these things? Click here to log in or create user.
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1626668403980
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 2. Holding Period Return
period t is the capital gain (or loss) plus distributions divided by the beginning-of-period price (dividend yield). Note that for common stocks the distribution is the dividend; for bonds, the distribution is the coupon payment. <span>The holding period return for any asset can be calculated for any time period (day, week, month, or year) simply by changing the interpretation of the time interval. Return can be expressed in decimals (0.05), fractions (5/100), or as a percent (5%). These are all equivalent. &
Flashcard 1632002510092
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 3. Dollar-weighted and Time-weighted Rates of Return
sub-period: HPR = (Dividends + Ending Price)/Beginning Price - 1. For the first year, HPR 1 : (150 + 10)/100 - 1 = 0.60. For the second year, HPR 2 : (280 + 20)/300 - 1 = 0. Calculate the time-weighted rate of return: <span>If the measurement period < 1 year, compound holding period returns to get an annualized rate of return for the year. If the measurement period > 1 year, take the geometric mean of the annual returns. <span><body><html>
Flashcard 1632883051788
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 4. Different Yield Measures of a U.S. Treasury Bill
unt basis D = the dollar discount, which is equal to the difference between the face value of the bill, F, and its purchase price, P t = the number of days remaining to maturity 360 = the bank convention of the number of days in a year. <span>Bank discount yield is not a meaningful measure of the return on investment because: It is based on the face value, not on the purchase price. Instead, return on investment should be measured based on cost of investment. It is annualized using a 360-day year, not a 365-day year. It annualizes with simple interest and ignores the effect of interest on interest (compound interest). Holding period yield (HPY) is the return earned by an investor if the money market instrument is held until maturity: P 0 =
Flashcard 1633376668940
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 4. Different Yield Measures of a U.S. Treasury Bill
990. Bank discount yield: (1000 - 990)/1000 x 360/60 = 6% Holding period yield: (1000 - 990)/990 = 1.0101% Effective annual yield: (1 + 1.0101%) 365/60 - 1 = 6.3047% Money market yield: (360 x 6%)/(360 - 60 x 6%) = 6.0606% <span>If we know HPY, then: EAY = (1 + HPY) 365/t - 1 r MM = HPY x 360/t If we know EAY, then: HPY = ( 1 + EAY) t/365 - 1 r MM = [(1 + EAY) t/365 - 1] x (360/t) If we know r MM , then: HPY = r MM x (t/360) EAY = (1 + r
Flashcard 1633413631244
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 4. Different Yield Measures of a U.S. Treasury Bill
ld: (360 x 6%)/(360 - 60 x 6%) = 6.0606% If we know HPY, then: EAY = (1 + HPY) 365/t - 1 r MM = HPY x 360/t If we know EAY, then: HPY = ( 1 + EAY) t/365 - 1 r MM = [(1 + EAY) t/365 - 1] x (360/t) <span>If we know r MM , then: HPY = r MM x (t/360) EAY = (1 + r MM x t/360) 365/t - 1 <span><body><html>
Flashcard 1633419398412
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 4. Different Yield Measures of a U.S. Treasury Bill
ld: (360 x 6%)/(360 - 60 x 6%) = 6.0606% If we know HPY, then: EAY = (1 + HPY) 365/t - 1 r MM = HPY x 360/t If we know EAY, then: HPY = ( 1 + EAY) t/365 - 1 r MM = [(1 + EAY) t/365 - 1] x (360/t) <span>If we know r MM , then: HPY = r MM x (t/360) EAY = (1 + r MM x t/360) 365/t - 1 <span><body><html>
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Zero-Coupon Bond
What is a 'Zero-Coupon Bond' <span>A zero-coupon bond, also known as an "accrual bond," is a debt security that doesn't pay interest (a coupon) but is traded at a deep discount, rendering profit at maturity when the bond is redeemed for its full face value. Some zero-coupon bonds are issued as such, while others are bonds that have been stripped of their coupons by a financial institution and then repackaged as zero-coupon bonds. Because t
Flashcard 1633769622796
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itA zero-coupon bond, also known as an "accrual bond," is a debt security that doesn't pay interest (a coupon) but is traded at a deep discount, rendering profit at maturity when the bond is redeemed for its full face value.</
Original toplevel document
Zero-Coupon BondWhat is a 'Zero-Coupon Bond' <span>A zero-coupon bond, also known as an "accrual bond," is a debt security that doesn't pay interest (a coupon) but is traded at a deep discount, rendering profit at maturity when the bond is redeemed for its full face value. Some zero-coupon bonds are issued as such, while others are bonds that have been stripped of their coupons by a financial institution and then repackaged as zero-coupon bonds. Because t
Flashcard 1633798982924
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itA zero-coupon bond is a debt security that doesn't pay interest (a coupon) but is traded at a deep discount, rendering profit at maturity when the bond is redeemed for its full face value.
Original toplevel document
Zero-Coupon BondWhat is a 'Zero-Coupon Bond' <span>A zero-coupon bond, also known as an "accrual bond," is a debt security that doesn't pay interest (a coupon) but is traded at a deep discount, rendering profit at maturity when the bond is redeemed for its full face value. Some zero-coupon bonds are issued as such, while others are bonds that have been stripped of their coupons by a financial institution and then repackaged as zero-coupon bonds. Because t
Flashcard 1633823362316
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 5. Bond Equivalent Yield
Periodic bond yields for both straight and zero-coupon bonds are conventionally computed based on semi-annual periods, as U.S. bonds typically make two coupon payments per year. For example, a zero-coupon bond with a maturity of five years will mature in 10 6-month periods. The periodic yield for that
Flashcard 1633877101836
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 5. Bond Equivalent Yield
Periodic bond yields for both straight and zero-coupon bonds are conventionally computed based on semi-annual periods, as U.S. bonds typically make two coupon payments per year. For example, a zero-coupon bond with a maturity of five years will mature in 10 6-month periods. The periodic yield for that bond, r, is indicated by the equation Price = Maturity value x (1 + r) -10 . This yield is an internal rate of return with semi-annual compounding. How do we
Flashcard 1633900432652
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 5. Bond Equivalent Yield
raight and zero-coupon bonds are conventionally computed based on semi-annual periods, as U.S. bonds typically make two coupon payments per year. For example, a zero-coupon bond with a maturity of five years will mature in 10 6-month periods. <span>The periodic yield for that bond, r, is indicated by the equation Price = Maturity value x (1 + r) -10 . This yield is an internal rate of return with semi-annual compounding. How do we annualize it? The convention is to double it and call the result the bond's yield to maturit
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1633971997964
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 5. Bond Equivalent Yield
The convention is to double it and call the result the bond's yield to maturity. This method ignores the effect of compounding semi-annual YTM, and the YTM calculated in this way is called a bond-equivalent yield (BEY). However, <span>yields of a semi-annual-pay and an annual-pay bond cannot be compared directly without conversion. This conversion can be done in one of the two ways: Convert the bond-equivalent yield of a semi-annual-pay bond to an annual-pay bond.
Flashcard 1633989037324
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 5. Bond Equivalent Yield
ted in this way is called a bond-equivalent yield (BEY). However, yields of a semi-annual-pay and an annual-pay bond cannot be compared directly without conversion. This conversion can be done in one of the two ways: <span>Convert the bond-equivalent yield of a semi-annual-pay bond to an annual-pay bond. Convert the equivalent annual yield of an annual-pay bond to a bond-equivalent yield. Example 
Flashcard 1634018135308
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 5. Bond Equivalent Yield
cannot be compared directly without conversion. This conversion can be done in one of the two ways: Convert the bond-equivalent yield of a semi-annual-pay bond to an annual-pay bond. <span>Convert the equivalent annual yield of an annual-pay bond to a bond-equivalent yield. Example A Eurobond pays coupon annually. It has an annual-pay YTM of 8%. A U.S. corporate bond pays coupon semi-annually. It has a bond e
Flashcard 1634082884876
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 5. Bond Equivalent Yield
Periodic bond yields for both straight and zero-coupon bonds are conventionally computed based on semi-annual periods, as U.S. bonds typically make two coupon payments per year. For example, a zero-coupon bond with a maturity of five years will mature in 10 6-month periods. The periodic yield for that bond, r, is indicated by the equation Price = Maturity value
Flashcard 1634085244172
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 5. Bond Equivalent Yield
y. This method ignores the effect of compounding semi-annual YTM, and the YTM calculated in this way is called a bond-equivalent yield (BEY). However, yields of a semi-annual-pay and an annual-pay bond cannot be compared directly <span>without conversion. This conversion can be done in one of the two ways: Convert the bond-equivalent yield of a semi-annual-pay bond to an annual-pay bond.
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1634091273484
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itprehypertension as a systolic blood pressure of 120-139 mm Hg or a diastolic blood pressure of 80-89 mm Hg in the absence of preexisting end-organ disease (for example, diabetes mellitus, chronic kidney disease, or cardiovasc
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1634092846348
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itprehypertension as a systolic blood pressure of 120-139 mm Hg or a diastolic blood pressure of 80-89 mm Hg in the absence of preexisting end-organ disease (for example, diabetes mellitus, chronic kidney disease, or cardiovascular disease)
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1634094419212
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itprehypertension as a systolic blood pressure of 120-139 mm Hg or a diastolic blood pressure of 80-89 mm Hg in the absence of preexisting end-organ disease (for example, diabetes mellitus, chronic kidney disease, or cardiovascular disease)
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1634097564940
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itAppropriate follow-up for those with prehypertension occurs at annual visits.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1634100710668
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itIf blood pressures measuring 140/90 mm Hg or greater were documented, this would require repeat measurements for at least three visits over the period of at least 1 week of more to establish a diagnosis of hypertension
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1634102545676
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itIf blood pressures measuring 140/90 mm Hg or greater were documented, this would require repeat measurements for at least three visits over the period of at least 1 week of more to establish a diagnosis of hypertension
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1634105691404
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itAmbulatory blood pressure monitoring records blood pressures periodically during normal activities. It is indicated primarily for diagnosis of suspected white coat hypertension (persistently elevated blood pressure readings in the office without evidence of end-organ damage) or to confirm a poor response to antihypertensive medication. It may also be useful
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1634107264268
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itpressures periodically during normal activities. It is indicated primarily for diagnosis of suspected white coat hypertension (persistently elevated blood pressure readings in the office without evidence of end-organ damage) or to confirm <span>a poor response to antihypertensive medication. It may also be useful in assessing for masked hypertension (evidence of end-organ damage without apparent elevated blood pressures) or for evaluating episodic or resistant hypertens
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1634108837132
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open its of suspected white coat hypertension (persistently elevated blood pressure readings in the office without evidence of end-organ damage) or to confirm a poor response to antihypertensive medication. It may also be useful in assessing for <span>masked hypertension (evidence of end-organ damage without apparent elevated blood pressures) or for evaluating episodic or resistant hypertension.<span><body><html>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1634110672140
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itd-organ damage) or to confirm a poor response to antihypertensive medication. It may also be useful in assessing for masked hypertension (evidence of end-organ damage without apparent elevated blood pressures) or for evaluating episodic or <span>resistant hypertension.<span><body><html>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1634113817868
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itThis patient has risk factors for CIN (older age, elevated serum creatinine, diabetes mellitus)
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1634114866444
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itThis patient has risk factors for CIN (older age, elevated serum creatinine, diabetes mellitus)
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1634115915020
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itThis patient has risk factors for CIN (older age, elevated serum creatinine, diabetes mellitus)
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1634119060748
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itThe use of gadolinium in MRI studies is relatively contraindicated in patients with an estimated glomerular filtration rate of less than 30 mL/min/1.73 m2due to the increased risk of NSF.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1634120633612
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itThe use of gadolinium in MRI studies is relatively contraindicated in patients with an estimated glomerular filtration rate of less than 30 mL/min/1.73 m2due to the increased risk of NSF.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1634122206476
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itThe use of gadolinium in MRI studies is relatively contraindicated in patients with an estimated glomerular filtration rate of less than 30 mL/min/1.73 m2due to the increased risk of NSF.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1634171751692
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itBalkan endemic nephropathy (BEN) and is at increased risk for transitional cell carcinoma.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1634174897420
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itBEN is a slowly progressive tubulointerstitial disease that has recently been linked to aristolochic acid.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1634178043148
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itFree hemoglobin is partially bound by haptoglobin but may also be filtered into the urine, producing a red color. Heme reacts with peroxidase in the urine dipstick, causing a false-positive result for blood. Hemoglobinuria is
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1634179878156
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itnd by haptoglobin but may also be filtered into the urine, producing a red color. Heme reacts with peroxidase in the urine dipstick, causing a false-positive result for blood. Hemoglobinuria is distinguished from true hematuria by <span>the absence of erythrocytes on urine microscopy. Similar findings on urinalysis will also occur with the release of myoglobin into the circulation, usually from muscle injury (rhabdomyolysis). Myoglobin is a small molecule
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1634181451020
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itd. Hemoglobinuria is distinguished from true hematuria by the absence of erythrocytes on urine microscopy. Similar findings on urinalysis will also occur with the release of myoglobin into the circulation, usually from muscle injury <span>(rhabdomyolysis). Myoglobin is a small molecule relative to hemoglobin, is not bound within the circulation by haptoglobin, and is readily filtered through the kidneys, resulting in red-colored urine
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1634183023884
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itFree hemoglobin is partially bound by haptoglobin but may also be filtered into the urine, producing a red color. Heme reacts with peroxidase in the urine dipstick, causing a false-positive result for blood. Hemoglobinuria is distinguished from true hematuria by the absence of erythrocytes on urine microscopy. Similar find
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1634184596748
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itm muscle injury (rhabdomyolysis). Myoglobin is a small molecule relative to hemoglobin, is not bound within the circulation by haptoglobin, and is readily filtered through the kidneys, resulting in red-colored urine. It also reacts with <span>peroxidase in the urine dipstick indicating blood, although microscopic examination will also be negative for erythrocytes.<span><body><html>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1634186169612
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itbound within the circulation by haptoglobin, and is readily filtered through the kidneys, resulting in red-colored urine. It also reacts with peroxidase in the urine dipstick indicating blood, although microscopic examination will also be <span>negative for erythrocytes.<span><body><html>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1634189577484
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itMKSAP17 MCQ 1646 .Mustafa M. A Bladder cancer is a concern in a patient with a significant smoking history presenting with a finding of red urine. However, the urine color change in bladder cancer is due to bleeding into the urinary tract, and erythrocytes would be seen on urinalysis. </s
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1634191150348
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itA Bladder cancer is a concern in a patient with a significant smoking history presenting with a finding of red urine. However, the urine color change in bladder cancer is due to bleeding into the urinary tract, and erythrocytes would be <span>seen on urinalysis. <span><body><html>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1634197179660
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itGlomerulonephritis may be associated with bleeding into the urine and would be suspected if erythrocytes, particularly acanthocytes (dysmorphic erythrocytes), were found on urine microscopic examination. Proteinuria may also be found in glomerulonephritis,
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1634198752524
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itGlomerulonephritis may be associated with bleeding into the urine and would be suspected if erythrocytes, particularly acanthocytes (dysmorphic erythrocytes), were found on urine microscopic examination. Proteinuria may also be found in glomerulonephritis,
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1634202946828
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itdefinition of resistant hypertension, which is defined by blood pressure readings not at target despite three agents, one of which must be a diuretic.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1634206092556
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itChlorthalidone is often preferred over other thiazide-type diuretics primarily due to its higher potency and longer duration of action.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1634209500428
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itminoxidil promotes sodium retention and is almost always given with a diuretic.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1634211073292
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itminoxidil promotes sodium retention and is almost always given with a diuretic.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1634215791884
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itIn amyloidosis involving the kidney, glomerular lesions tend to be prominent and present with proteinuria, often in the nephrotic range.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1634219724044
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itamyloid resulting from monoclonal lambda or kappa light chains is termed AL amyloid
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1634222869772
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open it>AL amyloid may present with nonspecific systemic symptoms such as fatigue or weight loss, but most commonly presents with symptoms associated with infiltration of different organ systems. These may include restrictive cardiomyopathy, peripheral neuropathy, hepatosplenomegaly, and, less commonly, cutaneous purpura and macroglossia<html>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1634227588364
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itFindings on biopsy show deposits that stain apple green on Congo red staining under a polarizing microscope; these deposits are also visible on electron microscopy.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1634233093388
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itType 4 (hyperkalemic distal) RTA is caused by aldosterone deficiency or resistance. Primary aldosterone deficiency is seen in primary adrenal deficiency (Addison disease)
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1634234666252
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itType 4 (hyperkalemic distal) RTA is caused by aldosterone deficiency or resistance. Primary aldosterone deficiency is seen in primary adrenal deficiency (Addison disease)
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1634237811980
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itof hyporeninemic hypoaldosteronism in which there is diminished renin release by the kidney.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1634242268428
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itoccurs most commonly in patients with mild to moderate kidney disease due to diabetic nephropathy (such as this patient) or chronic interstitial nephritis (such as in systemic lupus erythematosus or AIDS). It may also be associated with acute glomerulonephritis, specific drugs that impair renin release (NSAIDs and calcineurin inhibitors), tubulointerstitial disease, and drugs that reduce aldosterone production (ACE inhibitors, cyclooxygenase inhibitors, and heparin).
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1634245676300
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open ittype 4 (hyperkalemic distal) RTA typically present with hyperkalemia, a normal anion gap metabolic acidosis, and impaired urine acidification, but with the ability to maintain the urine pH to <5.5. The specific cause can be differentiated by measur
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1634247249164
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open ittype 4 (hyperkalemic distal) RTA typically present with hyperkalemia, a normal anion gap metabolic acidosis, and impaired urine acidification, but with the ability to maintain the urine pH to <5.5. The specific cause can be differentiated by measurement of pl
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1634248822028
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open ittype 4 (hyperkalemic distal) RTA typically present with hyperkalemia, a normal anion gap metabolic acidosis, and impaired urine acidification, but with the ability to maintain the urine pH to <5.5. The specific cause can be differentiated by measurement of plasma renin activity, serum al
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1634250394892
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open ittype 4 (hyperkalemic distal) RTA typically present with hyperkalemia, a normal anion gap metabolic acidosis, and impaired urine acidification, but with the ability to maintain the urine pH to <5.5. The specific cause can be differentiated by measurement of plasma renin activity, serum aldosterone, and serum cortisol. Initial treatment includes correction of the underlying caus
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1634251967756
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itdistal) RTA typically present with hyperkalemia, a normal anion gap metabolic acidosis, and impaired urine acidification, but with the ability to maintain the urine pH to <5.5. The specific cause can be differentiated by measurement of <span>plasma renin activity, serum aldosterone, and serum cortisol. Initial treatment includes correction of the underlying cause if possible, with discontinuation of offending medications. Replacement of mineralocorticoids with fludrocortison
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1634253540620
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itrement of plasma renin activity, serum aldosterone, and serum cortisol. Initial treatment includes correction of the underlying cause if possible, with discontinuation of offending medications. Replacement of mineralocorticoids with <span>fludrocortisone is indicated for patients with documented deficiency and should be considered for those with hyporeninemic hypoaldosteronism unless hypertension or heart failure is present.</s
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1634255113484
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itth discontinuation of offending medications. Replacement of mineralocorticoids with fludrocortisone is indicated for patients with documented deficiency and should be considered for those with hyporeninemic hypoaldosteronism unless <span>hypertension or heart failure is present.<span><body><html>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1634258259212
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itType 1 (hypokalemic distal) RTA results from a defect in urine acidification in the distal tubule with impaired excretion of hydrogen ions and a normal anion gap metabolic acidosis.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1634259832076
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itType 1 (hypokalemic distal) RTA results from a defect in urine acidification in the distal tubule with impaired excretion of hydrogen ions and a normal anion gap metabolic acidosis.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1634262977804
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itType 2 (proximal) RTA involves a defect in regenerating bicarbonate in the proximal tubule and is characterized by hypokalemia, glycosuria (in the setting of normal plasma glucose), low-molecular-weight proteinuria, and renal phosphate wasting
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1634264550668
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itType 2 (proximal) RTA involves a defect in regenerating bicarbonate in the proximal tubule and is characterized by hypokalemia, glycosuria (in the setting of normal plasma glucose), low-molecular-weight proteinuria, and renal phosphate wasting
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1634267958540
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itGlomerular hematuria is typically characterized by brown- or tea- colored urine with dysmorphic erythrocytes (or acanthocytes) and/or erythrocyte casts on urine sediment examination, although some glomerular disorders may cause gross hematuria. Other findings suggestive of a glomerular source in
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1634269531404
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itGlomerular hematuria is typically characterized by brown- or tea- colored urine with dysmorphic erythrocytes (or acanthocytes) and/or erythrocyte casts on urine sediment examination, although some glomerular disorders may cause gross hematuria. Other findings suggestive of a glomerular source include proteinuria. </
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1634272677132
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itDiagnosis of thin glomerular basement membrane disease is usually based on the history of persistent hematuria, normal kidney function, and positive family history of hematuria without kidney failure.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1634275822860
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itthin glomerular basement membrane (GBM) disease, an inherited type IV collagen abnormality that causes thinning of the GBM and results in hematuria. The disorder may affect up to 5% of the population, and 30% to 50% of patients report a family history
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1634277395724
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itlomerular basement membrane (GBM) disease, an inherited type IV collagen abnormality that causes thinning of the GBM and results in hematuria. The disorder may affect up to 5% of the population, and 30% to 50% of patients report a <span>family history of hematuria. The disease is characterized by microscopic or macroscopic hematuria that may be first discovered in young adults. Diagnosis is usually based on the history of persistent hematuria
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1634278968588
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itf patients report a family history of hematuria. The disease is characterized by microscopic or macroscopic hematuria that may be first discovered in young adults. Diagnosis is usually based on the history of persistent hematuria, <span>normal kidney function, and positive family history of hematuria without kidney failure; biopsy is not typically required. Long-term prognosis for kidney function is excellent, with rare pr
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1634280541452
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open ity history of hematuria. The disease is characterized by microscopic or macroscopic hematuria that may be first discovered in young adults. Diagnosis is usually based on the history of persistent hematuria, normal kidney function, and <span>positive family history of hematuria without kidney failure; biopsy is not typically required. Long-term prognosis for kidney function is excellent, with rare progression to chronic kidney disease (CKD).<span><body><html>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1634282114316
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itc or macroscopic hematuria that may be first discovered in young adults. Diagnosis is usually based on the history of persistent hematuria, normal kidney function, and positive family history of hematuria without kidney failure; biopsy is <span>not typically required. Long-term prognosis for kidney function is excellent, with rare progression to chronic kidney disease (CKD).<span><body><html>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1634283687180
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itdults. Diagnosis is usually based on the history of persistent hematuria, normal kidney function, and positive family history of hematuria without kidney failure; biopsy is not typically required. Long-term prognosis for kidney function is <span>excellent, with rare progression to chronic kidney disease (CKD).<span><body><html>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1634286832908
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itFabry disease is a rare X-linked inherited disorder in which there is deficiency of α-galactosidase A (an enzyme in the glycosphingolipid pathway) that leads to progressive deposit of globotriaosylceram
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1634288405772
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itFabry disease is a rare X-linked inherited disorder in which there is deficiency of α-galactosidase A (an enzyme in the glycosphingolipid pathway) that leads to progressive deposit of globotriaosylceramide (Gb3) in lysosomes. This disorder may present as CKD in young ad
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1634289978636
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open it(an enzyme in the glycosphingolipid pathway) that leads to progressive deposit of globotriaosylceramide (Gb3) in lysosomes. This disorder may present as CKD in young adulthood. Other associated clinical features include <span>premature coronary artery disease, severe neuropathic pain, telangiectasias, and angiokeratomas.<span><body><html>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1634293124364
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itHereditary nephritis (also known as Alport syndrome), also a heritable disorder of type IV collagen, is a rare cause of end-stage kidney disease with a prevalence of 0.4% among adult U.S. patients. Most cases are X- linked (80%) and are associated with sensorineural hearing l
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1634294697228
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itd>Hereditary nephritis (also known as Alport syndrome), also a heritable disorder of type IV collagen, is a rare cause of end-stage kidney disease with a prevalence of 0.4% among adult U.S. patients. Most cases are X- linked (80%) and are associated with sensorineural hearing loss and lenticonus (conical deformation of the lens), with proteinuria, hypertension, and kidney failure developing
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1634296270092
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itso known as Alport syndrome), also a heritable disorder of type IV collagen, is a rare cause of end-stage kidney disease with a prevalence of 0.4% among adult U.S. patients. Most cases are X- linked (80%) and are associated with <span>sensorineural hearing loss and lenticonus (conical deformation of the lens), with proteinuria, hypertension, and kidney failure developing over time. The remaining cases are autosomal recessive (15%) or autosomal dominant (5%) and may also be associated with hearing loss. Female carriers variably develop kidney disease
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1634297842956
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open ite X- linked (80%) and are associated with sensorineural hearing loss and lenticonus (conical deformation of the lens), with proteinuria, hypertension, and kidney failure developing over time. The remaining cases are <span>autosomal recessive (15%) or autosomal dominant (5%) and may also be associated with hearing loss. Female carriers variably develop kidney disease depending on activity of the X chromosome in somatic renal cells.</
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1634299415820
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itkidney failure developing over time. The remaining cases are autosomal recessive (15%) or autosomal dominant (5%) and may also be associated with hearing loss. Female carriers variably develop kidney disease depending on <span>activity of the X chromosome in somatic renal cells.<span><body><html>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1634300988684
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itkidney failure developing over time. The remaining cases are autosomal recessive (15%) or autosomal dominant (5%) and may also be associated with hearing loss. Female carriers variably develop kidney disease depending on <span>activity of the X chromosome in somatic renal cells.<span><body><html>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1634304134412
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open its that have a tumor-suppressing effect. Disruption of these gene products allows abnormal cell proliferation in different tissues, including the skin, brain, lung, liver, and kidney. Mild TSC may be detected in adulthood. Renal <span>angiomyolipomas are a characteristic kidney lesion in TSC and occur in 75% of patients on imaging.<span><body><html>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1634307280140
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itstage 1 hypertension (defined as a systolic blood pressure of 140-159 mm Hg and/or a diastolic blood pressure of 90-99 mm Hg)
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1634310425868
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itThere is evidence that in patients with hypertension and CKD, regardless of diabetes status, renin-angiotensin system agents (ACE inhibitor or angiotensin receptor blocker [ARB]) have a protective effect on kidney function
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1634314358028
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itThe most effective lifestyle modification is salt restriction to 1500 mg/d, which lowers blood pressure by an average of 7/3 mm Hg.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1634317503756
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itblood pressure goal of <150/90 mm Hg for those ≥60 years of age. Because his blood pressure measurements have been around 155/85 mm Hg, salt restriction alone as part of lifestyle modifications may be enough to av
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1634320649484
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open ital blood pressure–lowering effect and its effect on urinary frequency, its use as first-line therapy for persistent hypertension following lifestyle modification should be decided while considering its adverse effect profile <span>(such as orthostatic hypotension) and its increased incidence of heart failure<span><body><html>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1634323795212
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itthiazide diuretics such as hydrochlorothiazide, which increases serum urate
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1634327989516
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itThe finding of a nephritic urine sediment (erythrocytes, erythrocyte casts, and proteinuria) in an azotemic patient with an active infection suggests IRGN. IRGN is an immune complex–mediated disease most frequently associated with nonstreptococcal infections, with the antigen in the immune complex derived from the infectious agent. Immune complexes deposit in
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1634329562380
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itnephritic urine sediment (erythrocytes, erythrocyte casts, and proteinuria) in an azotemic patient with an active infection suggests IRGN. IRGN is an immune complex–mediated disease most frequently associated with <span>nonstreptococcal infections, with the antigen in the immune complex derived from the infectious agent. Immune complexes deposit in the subepithelial area and activate complement
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1634331135244
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itcomplex–mediated disease most frequently associated with nonstreptococcal infections, with the antigen in the immune complex derived from the infectious agent. Immune complexes deposit in the subepithelial area and <span>activate complement with recruitment of inflammatory cells, leading to a proliferative GN<span><body><html>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1634334280972
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itDrug-induced tubular toxicity (for example, with vancomycin) typically occurs after 7 to 10 days of antibiotic therapy and the urine sediment does not show cells, unlike in this patient. Antibiotic-induced AIN is typically associated with mild proteinuria, erythrocytes, leuk
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1634335853836
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itd tubular toxicity (for example, with vancomycin) typically occurs after 7 to 10 days of antibiotic therapy and the urine sediment does not show cells, unlike in this patient. Antibiotic-induced AIN is typically associated with mild <span>proteinuria, erythrocytes, leukocytes, and leukocyte casts on urinalysis. Eosinophiluria, recurrence of fevers, rash, and peripheral eosinophilia may also be seen<span><body><html>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1634346863884
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itisolated hematuria with a family history of hematuria may require serial measurements of kidney function and urine protein because kidney failure may occur later in life.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1634350009612
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itfamilial hematuric syndrome, which is typically associated with either X-linked or somatic mutations of type IV collagen. In female carriers of X-linked hereditary nephritis (Alport syndrome), kidney failure may occur later in life. Thus, annual measurements of blood pressure, kidney function, and urin
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1634351582476
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itdrome, which is typically associated with either X-linked or somatic mutations of type IV collagen. In female carriers of X-linked hereditary nephritis (Alport syndrome), kidney failure may occur later in life. Thus, annual measurements of <span>blood pressure, kidney function, and urine protein are reasonable<span><body><html>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1634354728204
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itBlood pressure averages ≥135/85 mm Hg by ambulatory blood pressure monitoring or home monitoring meet most consensus panels' definition of hypertension and should be treated with pharmacologic therapy<
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1634358136076
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itnighttime hypertension is defined by average values >125/75 mm Hg
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1634360757516
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open ithead><head> the typical blood pressure drop from daytime to nighttime (during sleep) of approximately 15%, noted in both normotensive and hypertensive patients. A lack of blood pressure drop of at least 10% (“non-dipping”) is independently associated with left ventricular hypertrophy, cardiovascular events, moderately increased albuminuria (formerly known as microalbuminuria), a
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1634362330380
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open iture drop from daytime to nighttime (during sleep) of approximately 15%, noted in both normotensive and hypertensive patients. A lack of blood pressure drop of at least 10% (“non-dipping”) is independently associated with <span>left ventricular hypertrophy, cardiovascular events, moderately increased albuminuria (formerly known as microalbuminuria), and a more rapid rate of decline in glomerular filtration rate<span><body><html>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1634366000396
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itManagement of uric acid nephrolithiasis includes adequate urine output, urine alkalinization, and xanthine oxidase inhibitors if needed to decrease uric acid production.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1634369932556
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itlow urine pH, markedly increase the risk of uric acid stones by favoring the development of insoluble uric acid from the relatively soluble urate salt.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1634373078284
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itOral hydration to maintain a urine output of at least 2 L/d is the mainstay of therapy. If this is inadequate, the next treatment is urine alkalinization (usually with potassium citrate or potassium bicarbonate) to increase the solubility of uric acid.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1634377010444
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itCholestyramine binds bile salts and oxalate in the gut and is sometimes used as a treatment for kidney stones related to hyperoxaluria but would likely not benefit this patient with uric acid stones.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1634380156172
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itThiazide diuretics, such as hydrochlorothiazide, decrease hypercalciuria by increasing proximal sodium reabsorption and passive calcium reabsorption in the kidney. However, this is a strategy for treating calcium-based nephrolithiasis and is not effective for uric acid stones.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1634381729036
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open it><head>Thiazide diuretics, such as hydrochlorothiazide, decrease hypercalciuria by increasing proximal sodium reabsorption and passive calcium reabsorption in the kidney. However, this is a strategy for treating calcium-based nephrolithiasis and is not effective for uric acid stones.<html>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1634384874764
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itchronic kidney disease stage 4 and greater (glomerular filtration rate <30 mL/min/1.73 m 2 ), thiazide diuretics lose potency, and loop diuretics may often be required.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1634388282636
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itetimes used in cases of resistant hypertension if maximal doses of more conventional agents are unsuccessful. However, this patient is not currently on optimal triple therapy, and both agents also increase the risk of <span>orthostatic hypotension in those with autonomic neuropathy, such as this patient. Moreover, the use of minoxidil without adequate diuresis will worsen salt and water retention and should be avoided
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1634391428364
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itl>Combination therapy with the ACE inhibitor lisinopril and the calcium channel blocker (CCB) amlodipine is appropriate for this patient with stage 2 hypertension, which is defined as a systolic blood pressure ≥160 mm Hg and/or a diastolic blood pressure ≥100 mm Hg<html>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1634393001228
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itherapy with the ACE inhibitor lisinopril and the calcium channel blocker (CCB) amlodipine is appropriate for this patient with stage 2 hypertension, which is defined as a systolic blood pressure ≥160 mm Hg and/or a diastolic blood pressure <span>≥100 mm Hg<span><body><html>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1634396146956
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itDiagnose white coat hypertension using ambulatory blood pressure monitoring
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1634399292684
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itWhite coat hypertension is defined as blood pressure readings in the office ≥140/90 mm Hg and out-of-office readings that average <135/85 mm Hg.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1634402438412
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itUrine testing for fractionated metanephrines is used to evaluate for pheochromocytoma as a secondary cause of hypertension.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1634405584140
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itPheochromocytoma is generally suspected in patients with the symptom triad of episodic headache, sweating, and tachycardia associated with coincident increases in blood pressure
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1634408729868
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itAminoglycoside-induced acute kidney injury typically presents as nonoliguric acute tubular necrosis with granular casts in the urine sediment and a fractional excretion of sodium >1%, and the serum creatinine characteristically rises 5 to 10 days after starting therapy
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1634410302732
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itAminoglycoside-induced acute kidney injury typically presents as nonoliguric acute tubular necrosis with granular casts in the urine sediment and a fractional excretion of sodium >1%, and the serum creatinine characteristically rises 5 to 10 days after starting therapy
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1634411875596
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itan>Aminoglycoside-induced acute kidney injury typically presents as nonoliguric acute tubular necrosis with granular casts in the urine sediment and a fractional excretion of sodium >1%, and the serum creatinine characteristically rises <span>5 to 10 days after starting therapy<span><body><html>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1634415021324
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itHypokalemia and hypomagnesemia can also occur with aminoglycoside toxicity due to kidney potassium and magnesium wasting.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1634418167052
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itCephalosporins, such as cefazolin, can cause AKI from acute interstitial nephritis. Urine findings include leukocytes, erythrocytes, and leukocyte casts. Fever, maculopapular rash, peripheral eosinophilia, and eosinophiluria can also occur. Onset of AKI after d
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1634419739916
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itCephalosporins, such as cefazolin, can cause AKI from acute interstitial nephritis. Urine findings include leukocytes, erythrocytes, and leukocyte casts. Fever, maculopapular rash, peripheral eosinophilia, and eosinophiluria can also occur. Onset of AKI after drug exposure ranges from 3 to 5 days with a second exposure, t
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1634421312780
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itCephalosporins, such as cefazolin, can cause AKI from acute interstitial nephritis. Urine findings include leukocytes, erythrocytes, and leukocyte casts. Fever, maculopapular rash, peripheral eosinophilia, and eosinophiluria can also occur. Onset of AKI after drug exposure ranges from 3 to 5 days with a second exposure, to as long as several weeks to months with a first exposure. </s
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1634422885644
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open it/head>Cephalosporins, such as cefazolin, can cause AKI from acute interstitial nephritis. Urine findings include leukocytes, erythrocytes, and leukocyte casts. Fever, maculopapular rash, peripheral eosinophilia, and eosinophiluria can also occur. Onset of AKI after drug exposure ranges from 3 to 5 days with a second exposure, to as long as several weeks to months with a first exposure. </ht
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1634424458508
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itacute interstitial nephritis. Urine findings include leukocytes, erythrocytes, and leukocyte casts. Fever, maculopapular rash, peripheral eosinophilia, and eosinophiluria can also occur. Onset of AKI after drug exposure ranges from <span>3 to 5 days with a second exposure, to as long as several weeks to months with a first exposure. <span><body><html>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1634427604236
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open ithrombolytic agent within the past several months. Emboli from ruptured atheromatous plaques occlude small and medium arterioles, causing ischemia and inflammation with organ dysfunction. Clinical features include rash <span>(livedo reticularis), AKI, purple discoloration of the toes, bowel ischemia, neurologic manifestations, and eosinophilia.<span><body><html>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1634429177100
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itthe past several months. Emboli from ruptured atheromatous plaques occlude small and medium arterioles, causing ischemia and inflammation with organ dysfunction. Clinical features include rash (livedo reticularis), AKI, <span>purple discoloration of the toes, bowel ischemia, neurologic manifestations, and eosinophilia.<span><body><html>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1634430749964
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open iti from ruptured atheromatous plaques occlude small and medium arterioles, causing ischemia and inflammation with organ dysfunction. Clinical features include rash (livedo reticularis), AKI, purple discoloration of the toes, <span>bowel ischemia, neurologic manifestations, and eosinophilia.<span><body><html>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1634433895692
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itIodinated contrast can induce vasospasm and cause ischemic injury or direct damage to the kidneys. Low osmolar contrast is thought to be safer than high osmolar contrast
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1634435468556
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itIodinated contrast can induce vasospasm and cause ischemic injury or direct damage to the kidneys. Low osmolar contrast is thought to be safer than high osmolar contrast
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1634438614284
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itContrast-induced nephropathy (CIN) is defined as either an increase in serum creatinine of 0.5 mg/dL (44.2 µmol/L) or an increase in serum creatinine of 25% from baseline at 48 hours after contrast administration.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1634442022156
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itKidney transplant recipients are predisposed to new-onset diabetes after transplantation (often referred to as NODAT). Medications that promote development of NODAT include glucocorticoids, tacrolimus, and the mammalian target of rapamyci
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1634443595020
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itKidney transplant recipients are predisposed to new-onset diabetes after transplantation (often referred to as NODAT). Medications that promote development of NODAT include glucocorticoids, tacrolimus, and the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) inhibitors sirolimus and everolimus.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1634446740748
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itDyslipidemia is also a common complication posttransplantation, and commonly used immunosuppressive medications that promote dyslipidemia include cyclosporine and mTOR inhibitors.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1634449886476
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itcardiovascular disease is the leading cause of death among kidney transplant recipients
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1634453032204
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itMany patients have residual hyperparathyroidism after transplant that can be slow to resolve; hypercalcemia is relatively commonly observed posttransplant but hypocalcemia is uncommon.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1634454605068
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itMany patients have residual hyperparathyroidism after transplant that can be slow to resolve; hypercalcemia is relatively commonly observed posttransplant but hypocalcemia is uncommon.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1634457750796
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itMechanical stone removal is appropriate for patients with large (>10 mm) kidney stones or those with smaller stones who have failed medical management or have complicated nephrolithiasis (urosepsis, acute kidney injury, anuria, refractory pain). </
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1634461158668
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itney stones <10 mm in size may usually be treated with conservative management (including hydration, analgesia, observation, and periodic re-evaluation) and medical expulsive therapy, which usually consists of either an α-blocker <span>(such as tamsulosin) or calcium channel blocker (such as nifedipine). <span><body><html>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1634462731532
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open ited with conservative management (including hydration, analgesia, observation, and periodic re-evaluation) and medical expulsive therapy, which usually consists of either an α-blocker (such as tamsulosin) or calcium channel blocker <span>(such as nifedipine). <span><body><html>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1634465877260
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itml>The most likely diagnosis is IgG4-related interstitial nephritis. This patient has a history of autoimmune pancreatitis and now presents with acute kidney injury. Her urinalysis is most consistent with a tubulointerstitial pattern, with mild proteinuria and the presence of inflammatory cells.<html>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1634467450124
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itThe most likely diagnosis is IgG4-related interstitial nephritis. This patient has a history of autoimmune pancreatitis and now presents with acute kidney injury. Her urinalysis is most consistent with a tubulointerstitial pattern, with mild proteinuria and the presence of inflammatory cells.</s
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1634470595852
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itSystemic IgG4-related disease is an uncommon disorder characterized by infiltration of different organs by lymphoplasmacytic infiltrates of IgG4-positive plasma cells with resultant fibrosis associated with elevated serum IgG4 levels
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1634473741580
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itThe first step when assessing a patient with metabolic alkalosis is to clinically assess the patient's volume status.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1634476887308
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open iturine electrolytes show increased excretion of sodium and chloride despite the evident hypovolemia. These findings suggest the presence of active diuretic use or a renal tubular defect that impairs handling of sodium and chloride, such as <span>Bartter and Gitelman syndromes.<span><body><html>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1634480033036
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itMeasurement of 24-hour urine free cortisol excretion is a standard test for diagnosing Cushing syndrome, which is characterized by proximal muscle weakness, hypokalemia, hypertension, and diabetes mellitus.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1634483178764
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itPlasma aldosterone-plasma renin ratio is unlikely to be helpful in this situation. Although primary hyperaldosteronism is characterized by hypokalemia and metabolic alkalosis, the absence of hypertension makes this diagnosis unlikely