Edited, memorised or added to reading queue
on 21-Apr-2017 (Fri)
Do you want BuboFlash to help you learning these things? Click here to log in or create user.
Flashcard 1439829200140
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open ity that makes it appear better than similar products from other firms. If a firm is successful in differentiating its product, the differentiation will provide pricing leverage. The more dissimilar the product appears, the more the market will <span>resemble the monopoly market structure. A firm can differentiate its product through aggressive advertising campaigns; frequent styling changes; the linking of its product with other, complementary products; or a host of oth
Original toplevel document
2. ANALYSIS OF MARKET STRUCTURESd monopoly is the local electrical power provider. In most cases, the monopoly power provider is allowed to earn a normal return on its investment and prices are set by the regulatory authority to allow that return. <span>2.2. Factors That Determine Market Structure Five factors determine market structure: The number and relative size of firms supplying the product; The degree of product differentiation; The power of the seller over pricing decisions; The relative strength of the barriers to market entry and exit; and The degree of non-price competition. The number and relative size of firms in a market influence market structure. If there are many firms, the degree of competition increases. With fewer firms supplying a good or service, consumers are limited in their market choices. One extreme case is the monopoly market structure, with only one firm supplying a unique good or service. Another extreme is perfect competition, with many firms supplying a similar product. Finally, an example of relative size is the automobile industry, in which a small number of large international producers (e.g., Ford and Toyota) are the leaders in the global market, and a number of small companies either have market power because they are niche players (e.g., Ferrari) or have little market power because of their narrow range of models or limited geographical presence (e.g., Škoda). In the case of monopolistic competition, there are many firms providing products to the market, as with perfect competition. However, one firm’s product is differentiated in some way that makes it appear better than similar products from other firms. If a firm is successful in differentiating its product, the differentiation will provide pricing leverage. The more dissimilar the product appears, the more the market will resemble the monopoly market structure. A firm can differentiate its product through aggressive advertising campaigns; frequent styling changes; the linking of its product with other, complementary products; or a host of other methods. When the market dictates the price based on aggregate supply and demand conditions, the individual firm has no control over pricing. The typical hog farmer in Nebraska and the milk producer in Bavaria are price takers . That is, they must accept whatever price the market dictates. This is the case under the market structure of perfect competition. In the case of monopolistic competition, the success of product differentiation determines the degree with which the firm can influence price. In the case of oligopoly, there are so few firms in the market that price control becomes possible. However, the small number of firms in an oligopoly market invites complex pricing strategies. Collusion, price leadership by dominant firms, and other pricing strategies can result. The degree to which one market structure can evolve into another and the difference between potential short-run outcomes and long-run equilibrium conditions depend on the strength of the barriers to entry and the possibility that firms fail to recoup their original costs or lose money for an extended period of time and are therefore forced to exit the market. Barriers to entry can result from very large capital investment requirements, as in the case of petroleum refining. Barriers may also result from patents, as in the case of some electronic products and drug formulas. Another entry consideration is the possibility of high exit costs. For example, plants that are specific to a special line of products, such as aluminum smelting plants, are non-redeployable, and exit costs would be high without a liquid market for the firm’s assets. High exit costs deter entry and are therefore also considered barriers to entry. In the case of farming, the barriers to entry are low. Production of corn, soybeans, wheat, tomatoes, and other produce is an easy process to replicate; therefore, those are highly competitive markets. Non-price competition dominates those market structures where product differentiation is critical. Therefore, monopolistic competition relies on competitive strategies that may not include pricing changes. An example of non-price competition is product differentiation through marketing. In other circumstances, non-price competition may occur because the few firms in the market feel dependent on each other. Each firm fears retaliatory price changes that would reduce total revenue for all of the firms in the market. Because oligopoly industries have so few firms, each firm feels dependent on the pricing strategies of the others. Therefore, non-price competition becomes a dominant strategy. Exhibit 1. Characteristics of Market Structure Market Structure Number of Sellers Degree of Product Differentiation Barriers to Entry Pricing Power of Firm Non-price Competition Perfect competition Many Homogeneous/ Standardized Very Low None None Monopolistic competition Many Differentiated Low Some Advertising and Product Differentiation Oligopoly Few Homogeneous/ Standardized High Some or Considerable Advertising and Product Differentiation Monopoly One Unique Product Very High Considerable Advertising From the perspective of the owners of the firm, the most desirable market structure is that with the most control over price, because this control can lead to large profits. Monopoly and oligopoly markets offer the greatest potential control over price; monopolistic competition offers less control. Firms operating under perfectly competitive market conditions have no control over price. From the consumers’ perspective, the most desirable market structure is that with the greatest degree of competition, because prices are generally lower. Thus, consumers would prefer as many goods and services as possible to be offered in competitive markets. As often happens in economics, there is a trade-off. While perfect competition gives the largest quantity of a good at the lowest price, other market forms may spur more innovation. Specifically, there may be high costs in researching a new product, and firms will incur such costs only if they expect to earn an attractive return on their research investment. This is the case often made for medical innovations, for example—the cost of clinical trials and experiments to create new medicines would bankrupt perfectly competitive firms but may be acceptable in an oligopoly market structure. Therefore, consumers can benefit from less-than-perfectly-competitive markets. PORTER’S FIVE FORCES AND MARKET STRUCTURE A financial analyst aiming to establish market conditions and consequent profitability of incumbent firms should start with the questions framed by Exhibit 1: How many sellers are there? Is the product differentiated? and so on. Moreover, in the case of monopolies and quasi monopolies, the analyst should evaluate the legislative and regulatory framework: Can the company set prices freely, or are there governmental controls? Finally, the analyst should consider the threat of competition from potential entrants. This analysis is often summarized by students of corporate strategy as “Porter’s five forces,” named after Harvard Business School professor Michael E. Porter. His book, Competitive Strategy, presented a systematic analysis of the practice of market strategy. Porter (2008) identified the five forces as: Threat of entry; Power of suppliers; Power of buyers (customers); Threat of substitutes; and Rivalry among existing competitors. It is easy to note the parallels between four of these five forces and the columns in Exhibit 1. The only “orphan” is the power of suppliers, which is not at the core of the theoretical economic analysis of competition, but which has substantial weight in the practical analysis of competition and profitability. Some stock analysts (e.g., Dorsey 2004) use the term “economic moat” to suggest that there are factors protecting the profitability of a firm that are similar to the moats (ditches full of water) that used to protect some medieval castles. A deep moat means that there is little or no threat of entry by invaders, i.e. competitors. It also means that customers are locked in because of high switching costs. <span><body><html>
Flashcard 1444552772876
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itAn examination of performance can include an assessment of a company’s profitability (the ability to earn a profit from delivering goods and services) and its ability to generate positive cash flows (cash receipts in excess of cash disbursements)
Original toplevel document
2. SCOPE OF FINANCIAL STATEMENT ANALYSISmance and financial position of a company in order to form expectations about its future performance and financial position. Analysts are also concerned about factors that affect risks to a company’s future performance and financial position. <span>An examination of performance can include an assessment of a company’s profitability (the ability to earn a profit from delivering goods and services) and its ability to generate positive cash flows (cash receipts in excess of cash disbursements). Profit and cash flow are not equivalent. Profit (or loss) represents the difference between the prices at which goods or services are provided to customers and the expenses incurred to
Flashcard 1448312704268
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itThe production function has three distinct regions where both the direction of change and the rate of change in total product (TP or Q, quantity of output) vary as production changes. Regions 1 and 2 have positive changes in TP as labor is added, but the change turns negative in Region 3.
Original toplevel document
Open itThis image illustrates the shape of a typical input–output relationship using labor (L) as the only variable input (all other input factors are held constant). The production function has three distinct regions where both the direction of change and the rate of change in total product (TP or Q, quantity of output) vary as production changes. Regions 1 and 2 have positive changes in TP as labor is added, but the change turns negative in Region 3. Moreover, in Region 1 (L 0 – L 1 ), TP is increasing at an increasing rate, ty
Flashcard 1448570653964
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itFinancial statements communicate financial information gathered and processed in the company's accounting system to parties outside the business.
Original toplevel document
Subject 2. Major Financial StatementsFinancial statements are the most important outcome of the accounting system. They communicate financial information gathered and processed in the company's accounting system to parties outside the business. The four principal financial statements are: Income statement (statement of earnings) Balance sheet (statement of financial position) Cash flow
Flashcard 1450765585676
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
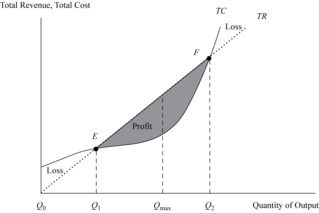
Open itThis shows the breakeven point under perfect competition using the total revenue–total cost approach.
Original toplevel document
Open itExhibit 18 shows the breakeven point under perfect competition using the total revenue–total cost approach. Actually, there are two breakeven points—lower (point E) and upper (point F). Below point E, the firm is losing money (economic losses), and beyond that point is the region of profitabi
Flashcard 1450772663564
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itWithin this profit area, a specific quantity (Q max ) maximizes profit as the largest difference between TR and TC
Original toplevel document
Open itally, there are two breakeven points—lower (point E) and upper (point F). Below point E, the firm is losing money (economic losses), and beyond that point is the region of profitability (shaded area) that extends to the upper breakeven point. <span>Within this profit area, a specific quantity (Q max ) maximizes profit as the largest difference between TR and TC. Point F is where the firm leaves the profit region and incurs economic losses again. This second region of economic losses develops when the firm’s production begins to reach the limit
Flashcard 1450778692876
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itObviously, the firm would not produce beyond Q max because it is the optimal production point that maximizes profit.
Original toplevel document
Open itthe profit region and incurs economic losses again. This second region of economic losses develops when the firm’s production begins to reach the limits of physical capacity, resulting in diminished productivity and an acceleration of costs. <span>Obviously, the firm would not produce beyond Q max because it is the optimal production point that maximizes profit. Breakeven points, profit regions, and economic loss ranges are influenced by demand and supply conditions, which change frequently according to the market behavior of consume
Flashcard 1450814606604
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itLa estrategia corporativa conlleva tomar decisiones que se hacen con respecto a la dirección de la organización en su conjunto. Esta estrategia se refiere a los asuntos que afectan a la empresa en general, tales
Original toplevel document
Estrategia de negocios y corporativaEstrategia corporativa La estrategia corporativa conlleva tomar decisiones que se hacen con respecto a la dirección de la organización en su conjunto. Esta estrategia se refiere a los asuntos que afectan a la empresa en general, tales como decidir el tamaño y la composición del portafolio de negocios. Estrategia de negocios La estrategia de negocios es la forma en que un negocio compite en un sector particular. Las decisiones estratégicas adop
Flashcard 1450818800908
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itLa estrategia de negocios es la forma en que un negocio compite en un sector particular. Las decisiones estratégicas adoptadas a nivel negocio tienen que ver con asuntos tales como la fijación de precios y la ef
Original toplevel document
Estrategia de negocios y corporativarespecto a la dirección de la organización en su conjunto. Esta estrategia se refiere a los asuntos que afectan a la empresa en general, tales como decidir el tamaño y la composición del portafolio de negocios. <span>Estrategia de negocios La estrategia de negocios es la forma en que un negocio compite en un sector particular. Las decisiones estratégicas adoptadas a nivel negocio tienen que ver con asuntos tales como la fijación de precios y la eficacia en la fabricación y la publicidad. La estrategia de negocios se basa principalmente en la obtención de una ventaja competitiva en el mercado . <span><body><html>
Flashcard 1450832956684
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itLas finanzas se relacionan con tres grandes áreas: a) Mercados de dinero y capital (Mercados Financieros) b) Inversiones. c) Administración financiera.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1450845015308
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itEn términos generales, en el Mercado de Dinero se llevan a cabo las transacciones en instrumentos de deuda a corto plazo o valores comerciables; en éste se obtienen créditos a corto plazo y se invierten los e
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1450932309260
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itLa Reestructuración Financiera es algo más complicada que la negociación con los acreedores sobre los nuevos plazos y tasas a considerar para los adeudos insolutos, o la solución a problemas de liquidez. Es necesario
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1450946202892
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open ituna reestructuración financiera es el convenio acordado, entre el deudor y el acreedor, bajo un esquema que propicie el beneficio conjunto, para ambas partes, una vez adecuado el perfil financiero de la empresa obj
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1450959047948
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open iteestructuración financiera •Disminuir los costos financieros. •Reducir el nivel de endeudamiento. •Elevar la productividad. •Mejorar la mezcla entre recursos internos y externos. •Mejorar <span>la posición de flujos.<span><body><html>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1450969795852
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itPrimera fase: Marco de referencia. Es el momento actual que está viviendo la empresa sin llevar a cabo una reestructuración financiera. Es necesario conocer, entre otros, los niveles de ventas, costos, utilidades, flujos de efectivo, rentabilidad, productividad, apalancamiento y valor de la empresa.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1451198909708
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Open it
response was probably one of the following: - False modesty – Oh, my muscles? I just started going to the gym and apparently it’s working! - Awkward stuttering – Um… you mean my biceps? Thanks… I guess… Um… - <span>Flat-out denial – What are you talking about? I’m fat, ugly and out of shape. You’re blind. - Evocation of a deep insecurity – I’m fit? I don’t know, I used to be the fat kid and I never rea
Flashcard 1451206774028
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Open it
re you talking about? I’m fat, ugly and out of shape. You’re blind. - Evocation of a deep insecurity – I’m fit? I don’t know, I used to be the fat kid and I never really see myself as attractive or deserving of anyone… - <span>Direct gratitude – Hey, thanks! Now how about the weather? … Each with its varying negative implications. Only the last example doesn’t derail a conversation and make both parties feel
Flashcard 1451365109004
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Open it
ssociated with fixed cost at zero production. By terminating business operations through market exit, investors escape the erosion in their equity capital from economic losses. When total revenue is enough to cover total <span>variable cost but not all of total fixed cost, the firm can survive in the short run but will be unable to maintain financial solvency in the long run. Exhibit 21 Revenu
ssociated with fixed cost at zero production. By terminating business operations through market exit, investors escape the erosion in their equity capital from economic losses. When total revenue is enough to cover total <span>variable cost but not all of total fixed cost, the firm can survive in the short run but will be unable to maintain financial solvency in the long run. Exhibit 21 Revenu
Flashcard 1451379264780
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Shutdown Analysis
For the most recent financial reporting period, a business domiciled in Ecuador (which recognizes the US dollar as an official currency) has revenue of $2 million and total costs of $2.5 million, which are or can be broken down into total fixed cost of $1 million and total variable cost of $1.5 million. The net loss on the firm’s income statement is reported as $500,000 (ignoring tax implications). In prior periods, the firm had reported profits on its operations. What decision should the firm make regarding operations over the short term? What decision should the firm make regarding operations over the long term? Assume the same business scenario except that revenue is now $1.3 million, wh
For the most recent financial reporting period, a business domiciled in Ecuador (which recognizes the US dollar as an official currency) has revenue of $2 million and total costs of $2.5 million, which are or can be broken down into total fixed cost of $1 million and total variable cost of $1.5 million. The net loss on the firm’s income statement is reported as $500,000 (ignoring tax implications). In prior periods, the firm had reported profits on its operations. What decision should the firm make regarding operations over the short term? What decision should the firm make regarding operations over the long term? Assume the same business scenario except that revenue is now $1.3 million, wh
Flashcard 1451593436428
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itto waste. Take note of it and put it in your pocket for use in the very near future. Don’t let it go old like some month-old milk that you’re afraid to throw away because of the smell. You are going to callback to it. What do I mean by this? <span>It’s simple, and it’s also a tactic used by just about every standup comedian. You are just going to refer to it in the context of your current topic. For example, you talked about your favorite kind of dog earlier in the conversation. There was a high
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1452507794700
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open it>Cuarta fase: Análisis derivado de la reestructura financiera Deben considerarse los impactos de corto, mediano y largo plazo en diferentes renglones, como: v Costos financieros. v Utilidades. v Flujos de efectivo. v Estructura de activos y pasivos. v Niveles de apalancamiento financiero y operativo. v Tasas de productivida
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Japanese IME hiragana toggle keys? - Microsoft Community
010 Hey moronicus_lithog, <span>Please check these keyboard shortcuts for Japanese IME. Keyboard shortcuts ALT-~ (tilde): Cycles between kana and direct input mode ALT-SHIFT: Cycles through available languages ALT-CAPS_LOCK: Switches to katakana input mode CTRL-CAPS_LOCK: Switches to hiragana input mode SHIFT-ALT: Switches between English mode and Japanese mode. Control - ~: Switches between the current input mode and the English mode within the Japanese IME. TIP: Switching between Hiragana input mode and Direct Input mode through the language bar is tedious. Instead you can switch by pressing Alt-Tilde (the key below ESC on your keyboard). So, if you need to type Japanese, press Alt-Tilde and start typing. When you are done press Alt-Tilde again to switch back to English. To achieve the same result when in Japanese mode, press Control - ~. Hope this answers your question. Regards, Shinmila H - Microsoft Support Visit our Microsoft Answers Feedback Forum and let us know what you think. Be the first person to
Flashcard 1533057568012
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Shutdown Analysis
For the most recent financial reporting period, a business domiciled in Ecuador (which recognizes the US dollar as an official currency) has revenue of $2 million and total costs of $2.5 million, which are or can be broken down into total fixed cost of $1 million and total variable cost of $1.5 million. The net loss on the firm’s income statement is reported as $500,000 (ignoring tax implications). In prior periods, the firm had reported profits on its operations. What decision should the firm make regarding operations over the short term? What decision should the firm make regarding operations over the long term? Assume the same business scenario except that revenue is now $1.3 million, wh
For the most recent financial reporting period, a business domiciled in Ecuador (which recognizes the US dollar as an official currency) has revenue of $2 million and total costs of $2.5 million, which are or can be broken down into total fixed cost of $1 million and total variable cost of $1.5 million. The net loss on the firm’s income statement is reported as $500,000 (ignoring tax implications). In prior periods, the firm had reported profits on its operations. What decision should the firm make regarding operations over the short term? What decision should the firm make regarding operations over the long term? Assume the same business scenario except that revenue is now $1.3 million, wh