Edited, memorised or added to reading queue
on 26-Apr-2022 (Tue)
Do you want BuboFlash to help you learning these things? Click here to log in or create user.
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 7074625752332
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
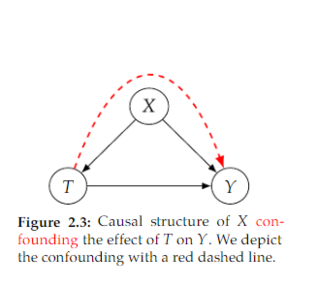
Open itHowever, we do have conditional exchangeability in the data. This is because, when we condition on 𝑋 , there is no longer any non-causal association between 𝑇 and 𝑌 . The non-causal association is now “blocked” at 𝑋 by conditioning o
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 7074628373772
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
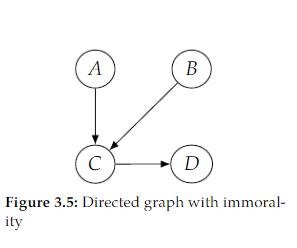
Open itIn contrast, the non-strict causal edges assumption would allow for some parents to not be causes of their children. It would just assume that children are not causes of their parents. This allows us to draw graphs with extra edges to make fewer assumptions, just like we would in Bayesian networks, where more edges means fewer independence assumptions. Causal graphs are sometimes drawn with this kind of non-minimal meaning, but the vast majority of the time, when someone draws a causal graph, they mean that parents are causes of their
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 7074632830220
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itProbabilistic graphical models are statistical models while causal graphical models are causal models.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 7074636762380
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itDefinition 3.2 (What is a cause?) A variable 𝑋 is said to be a cause of a variable 𝑌 if 𝑌 can change in response to changes in 𝑋
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 7074638597388
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itWhen we say “identification” in this book, we are referring to the process of moving from a causal estimand to an equivalent statistical estimand
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 7074640432396
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itA graph is a collection of nodes (also called “vertices”) and edges that connect the nodes.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 7074642267404
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itAssumption 3.3 ((Strict) Causal Edges Assumption) In a directed graph, every parent is a direct cause of all its children
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itIf there is a directed path that starts at node 𝑋 and ends at node 𝑌 , then 𝑋 is an ancestor of 𝑌 , and 𝑌 is a descendant of 𝑋
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 7074648034572
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itIf there is a directed path that starts at node 𝑋 and ends at node 𝑌 , then 𝑋 is an ancestor of 𝑌 , and 𝑌 is a descendant of 𝑋
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itThe causal graph for interventional distributions is simply the same graph that was used for the observational joint distribution, but with all of the edges to the intervened node(s) removed. This is because the probability for the intervened factor has been set to 1, so we can just ignore that factor (this is the focus of the next section). Another way to see that the inter
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itAssociation flows along all unblocked paths. In causal graphs, causation flows along directed paths. Recall from Section 1.3.2 that not only is association not causation, but causation is a sub-category of association. That’s why association and causation both flow along directed paths
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 7074656947468
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itDefinition 3.4 (d-separation) Two (sets of) nodes 𝑋 and 𝑌 are d-separated by a set of nodes 𝑍 if all of the paths between (any node in) 𝑋 and (any node in) 𝑌 are blocked by 𝑍 Source: Pearl (1988), Probabilistic Rea
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 7074659306764
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 7074661141772
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itThe Positivity-Unconfoundedness Tradeoff
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 7074662976780
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itnditional exchangeability (Assumption 2.2) was that it seemed like a more realistic assumption. However, we often cannot know for certain if conditional exchangeability holds. There may be some <span>unobserved confounders that are not part of 𝑋 , meaning conditional exchangeability is violated. Fortunately, that is not a problem in randomized experiments <span>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 7074664811788
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itMore generally, the potential outcome 𝑌(𝑡) denotes what your outcome would be, if you were to take treatment 𝑡
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 7074666908940
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itWe do not have exchangeability in the data because 𝑋 is a common cause of 𝑇 and 𝑌
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsArticle 7074675559692
实验诊断
#Diagnosis
常见的重要的血象指标和正常值 PLT 100-300*10^9/L 血小板计数 WBC 4-10*10^9/L 白细胞计数RBC 3.5-5.5*10^12/L 红细胞计数NEUT 1.2-6.8*10^9/L 中性粒细胞计数HGB 120-160g/L 血红蛋白浓度 网织红细胞是什么,正常值以及在疾病诊断中的意义? 未成熟红细胞,反映骨髓红系造血,正常值0.5%-2% 新生儿2%-6% 正常骨髓象 https://www.yixue.com/正常骨髓象 溶血性贫血的原因、表现和鉴别诊断 破坏大于代偿。 贫血、黄疸、脾大。血红蛋白尿强烈提示(但不是溶血就一定有,比如脾导致的) 鉴别原位性mds伴有网织红细胞增加 外周血细胞的分类 红白(有无粒)板 肾功能检查 检查肾功能采用什么体液,以及常用指标? 血清和尿。 肌酐、胱抑素C、二氧化碳结合力,β2微球蛋白、尿酸、尿素。 肾小球滤过率是什么,一般通过清除率来近似,清除率是什么? 单位时间内(min)经肾小球滤过的血浆量(ml) XXX清除率指的是针对某种几乎不被人体吸收(如菊粉)且经单一(肾小球)排泄的物质,单位时间内被全部清除的血浆量。 血中可以判定肾小球功能的几个指标和特点? 肌酐Cr(晚至1/3,特异)、胱抑素C(敏感,特异,最)、尿素BUN(较早)、尿酸UA(很早)、两种微球蛋白(敏感) 敏感的指标适合已确诊可损害肾功能的全身疾病患者 远近肾小管的功能 近端重吸收、远端稀释、集合浓缩 判断肾小管功能的几个指标及特点 尿比密(浓缩稀释实验,昼夜),尿渗量血渗量(浓缩稀释),尿β2(重吸收) 血浆二氧化碳结合力是干嘛的 判断肾脏平衡酸碱功能
Flashcard 7074677656844
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
实验诊断
常见的重要的血象指标和正常值 PLT 100-300*10^9/L 血小板计数 WBC 4-10*10^9/L 白细胞计数RBC 3.5-5.5*10^12/L 红细胞计数NEUT 1.2-6.8*10^9/L 中性粒细胞计数HGB 120-160g/L 血红蛋白浓度 网织红细胞是什么,正常值以及在疾病诊断中的意义? 未成熟红细胞,反映骨髓红系造血,正常值0.5%-2% 新生儿2%-6% 正常骨髓象 https://www.yixue.com/正常骨髓象 溶血性贫血的原因、表现和鉴别诊断 破坏大于代偿。 贫血、黄疸、脾大。血红蛋白尿强烈提示(但不是溶血就一定有,比如脾导致的) 鉴别原位性mds伴有网织红细胞增加 外周血细胞的分类 红
常见的重要的血象指标和正常值 PLT 100-300*10^9/L 血小板计数 WBC 4-10*10^9/L 白细胞计数RBC 3.5-5.5*10^12/L 红细胞计数NEUT 1.2-6.8*10^9/L 中性粒细胞计数HGB 120-160g/L 血红蛋白浓度 网织红细胞是什么,正常值以及在疾病诊断中的意义? 未成熟红细胞,反映骨髓红系造血,正常值0.5%-2% 新生儿2%-6% 正常骨髓象 https://www.yixue.com/正常骨髓象 溶血性贫血的原因、表现和鉴别诊断 破坏大于代偿。 贫血、黄疸、脾大。血红蛋白尿强烈提示(但不是溶血就一定有,比如脾导致的) 鉴别原位性mds伴有网织红细胞增加 外周血细胞的分类 红
Flashcard 7074679229708
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
实验诊断
常见的重要的血象指标和正常值 PLT 100-300*10^9/L 血小板计数 WBC 4-10*10^9/L 白细胞计数RBC 3.5-5.5*10^12/L 红细胞计数NEUT 1.2-6.8*10^9/L 中性粒细胞计数HGB 120-160g/L 血红蛋白浓度 网织红细胞是什么,正常值以及在疾病诊断中的意义? 未成熟红细胞,反映骨髓红系造血,正常值0.5%-2% 新生儿2%-6% 正常骨髓
常见的重要的血象指标和正常值 PLT 100-300*10^9/L 血小板计数 WBC 4-10*10^9/L 白细胞计数RBC 3.5-5.5*10^12/L 红细胞计数NEUT 1.2-6.8*10^9/L 中性粒细胞计数HGB 120-160g/L 血红蛋白浓度 网织红细胞是什么,正常值以及在疾病诊断中的意义? 未成熟红细胞,反映骨髓红系造血,正常值0.5%-2% 新生儿2%-6% 正常骨髓
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |