Edited, memorised or added to reading queue
on 17-Dec-2023 (Sun)
Do you want BuboFlash to help you learning these things? Click here to log in or create user.
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
All topics are updated as new evidence becomes available and our peer review process is complete. Literature review current through: Nov 2023. This topic last updated: Sep 25, 2023. ●What's New <span>Pulmonary embolism in patients with severe COPD exacerbation (September 2023) Pulmonary embolism (PE) is an important potential trigger for COPD exacerbation. In a recent multicenter study, 1580 patients with COPD who were admitted to the hospital with acute worsening of respiratory symptoms were all screened for PE with computed tomography pulmonary angiogram within 48 hours of admission [1]. PE was identified in 266 (17 percent), with 166 patients (11 percent) having PE involving the main or lobar pulmonary arteries. Purulent sputum production decreased the odds of PE by 60 percent. We suggest obtaining imaging for PE in patients requiring admission for COPD exacerbation who do not have evidence of other triggers (eg, infection or heart failure). (See "COPD exacerbations: Clinical manifestations and evaluation", section on 'Triggers' and "COPD exacerbations: Clinical manifestations and evaluation", section on 'Additional testing
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
ions: Clinical manifestations and evaluation", section on 'Triggers' and "COPD exacerbations: Clinical manifestations and evaluation", section on 'Additional testing'.) Read more INTRODUCTION — <span>The Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD), a report produced by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) and the World Health Organization (WHO), defines an exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) as "an event characterized by dyspnea and/or cough and sputum that worsens over ≤14 days, which may be accompanied by tachypnea and/or tachycardia, and is often associated with increased local and systemic inflammation caused by airway infection, pollution, or other insult to the airways" [1,2]. This generally includes an acute change in one or more of the following cardinal symptoms: ●Cough increases in frequency and severity ●Sputum production increases in volume and/or changes character ●Dyspnea increases The clinical manifestations and evaluation of patients with exacerbations of COPD are discussed in detail here. A table to assist with emergency management of severe acute exacerbations
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
an acute change in one or more of the following cardinal symptoms: ●Cough increases in frequency and severity ●Sputum production increases in volume and/or changes character ●Dyspnea increases <span>The clinical manifestations and evaluation of patients with exacerbations of COPD are discussed in detail here. A table to assist with emergency management of severe acute exacerbations of COPD is provided (table 1). The diagnosis and treatment of stable COPD and the treatment, risk factors, prognosis, and prevention of exacerbations of COPD are discussed separately. ●(See "Chronic obstructive pulmo
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
are for patients with normal renal function. Some agents require dose adjustment for renal impairment; refer to separate UpToDate algorithms of antibiotic treatment of exacerbations of COPD. ¶ <span>Pseudomonas infection risk factors: Broad spectrum antibiotic use in the past 3 months; chronic colonization or previous isolation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa from sputum (particularly in past 12 months); very severe underlying COPD (FEV1 <30% predicted); chronic systemic glucocorticoid use. Graphic 65420 Version 12.0 © 2023 UpToDate, Inc. and/or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved. Graphics in this topic New diagnosis of COPD Initial emergency management of severe COPD exa
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
and staging".) ●(See "Stable COPD: Overview of management".) ●(See "COPD exacerbations: Management".) ●(See "COPD exacerbations: Prognosis, discharge planning, and prevention".) EPIDEMIOLOGY — <span>Among patients with COPD, the frequency of exacerbation varies with the severity of disease, and some patients have more frequent exacerbations than others independent of other measures of disease severity [1,3]. ●Among almost 100,000 patients with COPD, the number of exacerbations in a baseline year of observation predicted the rate over the subsequent 10 years [4]. Approximately, 25 percent di
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
n [5]. ●In a survey that included over 4000 respondents with COPD, approximately 10 to 25 percent needed an emergency room evaluation for COPD and 5 to 10 percent required hospitalization [6]. ●<span>In a separate survey of more than 1000 patients, 21 percent of those who reported a COPD exacerbation required hospitalization [7]. RISK FACTORS AND TRIGGERS Risk factors — According to observational studies, the risk of developing an exacerbation of COPD correlates with the following features [8-13]: ●Advanced age
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
cent required hospitalization [6]. ●In a separate survey of more than 1000 patients, 21 percent of those who reported a COPD exacerbation required hospitalization [7]. RISK FACTORS AND TRIGGERS <span>Risk factors — According to observational studies, the risk of developing an exacerbation of COPD correlates with the following features [8-13]: ●Advanced age ●Productive cough ●Longer duration of COPD ●History of antibiotic therapy ●COPD-related hospitalization within the previous year ●Chronic mucous hypersecretion ●Peripheral blood eosinophil count >0.34 x 109 cells/L (340 cells/microL) ●Theophylline therapy ●Presence of one or more comorbidities (eg, ischemic heart disease, heart failure, or diabetes mellitus) Women are slightly more likely to experience a COPD exacerbation than men [13,14]. In general, worsening airflow limitation (lower forced expiratory volume in one second [FEV1]) is asso
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
vide a good assessment of exacerbation risk [1]. Other potential contributors to an increased risk of exacerbations include the following: ●Severity of COPD and history of prior exacerbations – <span>The Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD) guidelines suggest using primarily history of exacerbations, history of hospitalization for exacerbation, and symptoms to assess the exacerbation risk [1]. The number of exacerbations in the previous 12 months is stratified: a history of zero or one exacerbation suggests a low future risk of exacerbations, while two or more suggest a high
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
<80 percent predicted) were followed for three years [15]. The single best predictor of exacerbations was a history of prior exacerbations, regardless of severity of airway obstruction [4]. <span>Worsening airflow obstruction remains associated with an increasing prevalence of exacerbations, hospitalization, and death [16]. It is used as a component of the BODE index, a prognostic tool that can also be used to assess therapeutic response to medications, pulmonary rehabilitation therapy, and other interventions [17]. Different COPD staging systems and severity assessments are discussed in more detail separately. (See "Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: Diagnosis and staging", section on 'Assessm
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
onal risk factor for COPD exacerbations [18,19]. In the ECLIPSE study noted above, the occurrence of two or more exacerbations in a year was associated with a history of GERD or heartburn [15]. <span>A similar observation was made in a case-control study that assessed the presence of GERD symptoms and frequency of COPD exacerbations in 80 patients with COPD. The presence of GERD symptoms was associated with an increased risk of COPD exacerbations (RR 6.55, 95% CI 1.86-23.11) [18]. However, in an observational study of 638 patients with stable COPD, therapy with proton pump inhibitors did not decrease the risk for severe exacerbations [20]. Additional studies are needed to determine whether GERD contributes to the development of COPD exacerbations. ●Left ventricular diastolic dysfunction – Left ventricular diastolic dysfun
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
re discussed in more detail separately. (See "Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: Diagnosis and staging", section on 'Assessment of severity and staging'.) ●Gastroesophageal reflux disease – <span>Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) may be an additional risk factor for COPD exacerbations [18,19]. In the ECLIPSE study noted above, the occurrence of two or more exacerbations in a year was associated with a history of GERD or heartburn [15]. A similar observation was made in a case
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
e the risk for severe exacerbations [20]. Additional studies are needed to determine whether GERD contributes to the development of COPD exacerbations. ●Left ventricular diastolic dysfunction – <span>Left ventricular diastolic dysfunction at baseline is associated with a higher frequency of hospitalization for COPD exacerbation [21]. Diastolic dysfunction is common in patients with COPD, likely due to both comorbid vascular mechanisms (eg, hypertension, coronary artery disease, systemic inflammation) as well as metabolic and structural consequences of COPD (eg, lung hyperinflation, chronic hypoxia, and hypercapnia) [22,23]. Many of these contributing factors worsen during an exacerbation and may lead to diastolic decompensation, followed by pulmonary congestion and bronchial hyper-reactivity [24]. High heart rates, whether due to breathlessness, anxiety, or atrial arrhythmias, further exacerbate this pathophysiology. ●Pulmonary hypertension – Secondary pulmonary hypertension may be an additional risk factor for COPD exacerbations, possibly as an indicator of disease severity. In a follow-up to the E
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
ngestion and bronchial hyper-reactivity [24]. High heart rates, whether due to breathlessness, anxiety, or atrial arrhythmias, further exacerbate this pathophysiology. ●Pulmonary hypertension – <span>Secondary pulmonary hypertension may be an additional risk factor for COPD exacerbations, possibly as an indicator of disease severity. In a follow-up to the ECLIPSE study, chest computed tomography scans were used to compute the ratio of the diameter of the pulmonary artery to the diameter of the aorta (PA:A ratio) [25]. In the study, a PA:A ratio greater than 1 was an independent risk factor for a future severe exacerbation (OR 3.44, 95% CI 2.78-4.25). Notably, a PA:A ratio >1 suggests the presence of pulmonary hypertension, although it does not clarify the cause of pulmonary hypertension (eg, hypoxemia due to COPD or other lung disease, left heart failure, sleep apnea). The clinical usefulness of this observation in terms of treatment decisions is unclear. Triggers — Respiratory infections, most commonly viral (eg, rhinovirus) or bacterial, are estimated to trigger approximately 70 percent of COPD exacerbations (table 2) [1,26]; atypical
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
ulmonary hypertension (eg, hypoxemia due to COPD or other lung disease, left heart failure, sleep apnea). The clinical usefulness of this observation in terms of treatment decisions is unclear. <span>Triggers — Respiratory infections, most commonly viral (eg, rhinovirus) or bacterial, are estimated to trigger approximately 70 percent of COPD exacerbations (table 2) [1,26]; atypical bacteria are a relatively uncommon cause [27,28]. The remaining 30 percent are due to environmental pollution, pulmonary embolism, or have an unknown etiology [1,29-31]. (See "Management of infection in exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease".) COPD exacerbations have been associated with exposure to poor outdoor air quality, such as hig
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
percent are due to environmental pollution, pulmonary embolism, or have an unknown etiology [1,29-31]. (See "Management of infection in exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease".) <span>COPD exacerbations have been associated with exposure to poor outdoor air quality, such as higher levels of ozone, carbon monoxide, particulate matter (up to 10 microns), and nitrogen dioxide [32,33]. Increased ambient levels of fine particulate matter (≤2.5 microns, aka PM2.5) are associated with an increase in hospitalization and mortality in COPD [34]. In a trial of 116 patients with COPD and exposure to poor air quality at home (PM2.5 >10 mcg/m3), use of indoor air filters versus sham air filters resulted in a dose-dependent improvement in respiratory symptoms and risk of moderate exacerbations [35]. As dyspnea and cough are nonspecific symptoms, COPD exacerbations of unknown etiology may be triggered or caused by other medical conditions, such as myocardial ischemia, heart failure,
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
uality at home (PM2.5 >10 mcg/m3), use of indoor air filters versus sham air filters resulted in a dose-dependent improvement in respiratory symptoms and risk of moderate exacerbations [35]. <span>As dyspnea and cough are nonspecific symptoms, COPD exacerbations of unknown etiology may be triggered or caused by other medical conditions, such as myocardial ischemia, heart failure, aspiration, or pulmonary embolism [1,36]. The relationship between COPD exacerbation and pulmonary embolism is illustrated by a prospective multicenter study of 1580 patients with COPD who were admitted to the hospital with acu
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
ary arteries (CTPA); 166 patients (11 percent) had pulmonary embolism involving the main or lobar pulmonary arteries. The presence of new purulent sputum reduced the odds of pulmonary embolism. <span>Although the frequency of pulmonary embolism among patients hospitalized with an exacerbation of COPD varies across studies [38-41], a systematic review prior to this multicenter study showed a similar pooled prevalence of 23 percent when all patients were evaluated by CTPA within 48 hours of hospital admission (seven studies, 999 patients) [42]. An important limitation of these studies is their inability to determine whether the pulmonary embolism is the cause of the COPD exacerbation, a result of the COPD exacerbation, or a mere bystander. CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS — The clinical manifestations of exacerbations of COPD range from a mild increase in dyspnea, cough that is productive or nonproductive to respiratory failure wi
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
e studies is their inability to determine whether the pulmonary embolism is the cause of the COPD exacerbation, a result of the COPD exacerbation, or a mere bystander. CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS — <span>The clinical manifestations of exacerbations of COPD range from a mild increase in dyspnea, cough that is productive or nonproductive to respiratory failure with acute respiratory acidosis and/or hypoxemia. Medical history — By definition, patients present with the acute onset or worsening of respiratory symptoms, such as dyspnea, cough, and/or sputum production, over several hours to days
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
manifestations of exacerbations of COPD range from a mild increase in dyspnea, cough that is productive or nonproductive to respiratory failure with acute respiratory acidosis and/or hypoxemia. <span>Medical history — By definition, patients present with the acute onset or worsening of respiratory symptoms, such as dyspnea, cough, and/or sputum production, over several hours to days [1,43]. These symptoms should be characterized further in terms of the following features: ●Time course of the symptoms ●Comparison to baseline level of symptoms ●Severity of respiratory compromise (eg, dyspnea at rest, dyspnea climbing stairs, dyspnea severity using a visual analog [1-10] scale) ●Delineation of sputum characteristics (eg, amount, color, purulence, blood) ●Use of home oxygen now or in the past Associated features that might suggest an alternate diagnosis or comorbidity include: ●Constitutional symptoms (eg, fever, chills, night sweats) ●Chest pain, chest pressure, peripheral
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
dyspnea climbing stairs, dyspnea severity using a visual analog [1-10] scale) ●Delineation of sputum characteristics (eg, amount, color, purulence, blood) ●Use of home oxygen now or in the past <span>Associated features that might suggest an alternate diagnosis or comorbidity include: ●Constitutional symptoms (eg, fever, chills, night sweats) ●Chest pain, chest pressure, peripheral edema, or palpitations ●Risk factors for coronary disease ●Risk factors for thromboembolic disease ●Upper respiratory symptoms that might suggest a viral respiratory infection or exposure to anyone with influenza Patients should be asked if they currently smoke cigarettes or use vaping products. The past history of exacerbations should be ascertained: number of prior exacerbations, courses of sy
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
ons ●Risk factors for coronary disease ●Risk factors for thromboembolic disease ●Upper respiratory symptoms that might suggest a viral respiratory infection or exposure to anyone with influenza <span>Patients should be asked if they currently smoke cigarettes or use vaping products. The past history of exacerbations should be ascertained: number of prior exacerbations, courses of systemic glucocorticoids, antibiotic therapy in the preceding three months, prior exacerbations requiring hospitalization or ventilatory support, and response to therapy of previous exacerbations. Physical examination — Physical findings associated with an exacerbation of COPD often include wheezing and tachypnea and may include features of respiratory compromise such as difficul
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
abdominal motion with respiration). Tachycardia is also frequently present. If present, decreased mental status could reflect hypercapnia or hypoxemia and asterixis could indicate hypercapnia. <span>Attention should also be paid to other physical findings, such as fever, hypotension, bibasilar fine crackles and peripheral edema, which might suggest a comorbidity or alternate diagnosis. EVALUATION AND DIAGNOSIS — The goals of the evaluation of a suspected exacerbation of COPD are to confirm the diagnosis, identify the cause (when possible), assess the severity of respi
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
arbonate (perhaps reflecting compensation for chronic hypercapnia), or the presence of severe airflow obstruction (eg, forced expiratory volume in one second [FEV1] <50 percent of predicted) <span>We do not use procalcitonin or C-reactive protein to determine the need for antibiotics in COPD exacerbations, as study results do not clearly and consistently demonstrate that either assay adds value to clinical judgment alone. (See "Evaluation for infection in exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease", section on 'Procalcitonin and C-reactive protein'.) Additional testing — Additional tests are largely used to exclude processes in the differential diagnosis and are obtained depending on the degree of diagnostic uncertainty following cl
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
gnosis for respiratory symptoms. The frequency of pulmonary embolism in patients with COPD and acute respiratory symptoms in the hospital setting appears to be between 15 to 25 percent [37,42]. <span>In one multicenter study of nearly 1600 patients hospitalized for COPD exacerbation who were assessed with CT pulmonary angiogram, the rates of pulmonary embolism based on low, moderate, or high probability Wells criteria scores were 7, 38, and 74 percent, respectively [37]. Purulent sputum production decreased the odds of venous thromboembolism by approximately 60 percent. Given this prevalence rate, we suggest obtaining imaging for pulmonary embolism (typ
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
n who were assessed with CT pulmonary angiogram, the rates of pulmonary embolism based on low, moderate, or high probability Wells criteria scores were 7, 38, and 74 percent, respectively [37]. <span>Purulent sputum production decreased the odds of venous thromboembolism by approximately 60 percent. Given this prevalence rate, we suggest obtaining imaging for pulmonary embolism (typically CT pulmonary angiogram) in patients with severe symptoms who do not have evidence of other tri
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
te, or high probability Wells criteria scores were 7, 38, and 74 percent, respectively [37]. Purulent sputum production decreased the odds of venous thromboembolism by approximately 60 percent. <span>Given this prevalence rate, we suggest obtaining imaging for pulmonary embolism (typically CT pulmonary angiogram) in patients with severe symptoms who do not have evidence of other triggers (eg, infection or heart failure). (See 'Differential diagnosis' below and "Clinical presentation, evaluation, and diagnosis of the nonpregnant adult with suspected acute pulmonary embolism".) ●Sputum Gram stain and cult
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
ile Access Help & Training Demos Wolters Kluwer Health Emmi® Facts & Comparisons® Lexicomp® Medi-Span® Loading Please wait 5 of 6 Export to Powerpoint Print Share Bookmark Rate Feedback <span>Risk factors for infection with Pseudomonas aeruginosa in patients with acute COPD exacerbations Chronic colonization or previous isolation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa from sputum (particularly in the past 12 months) Very severe COPD (FEV1 <30% predicted) Bronchiectasis on chest imaging Broad-spectrum antibiotic use within the past 3 months Chronic systemic glucocorticoid use COPD: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; FEV1: forced expiratory volume in 1 second. References: Garcia-Vidal C, Almagro P, Romaní V, et al. Pseudomonas aeruginosa in patients hospi
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
(eg, infection or heart failure). (See 'Differential diagnosis' below and "Clinical presentation, evaluation, and diagnosis of the nonpregnant adult with suspected acute pulmonary embolism".) ●<span>Sputum Gram stain and culture are not obtained for most exacerbations of COPD. However, sputum Gram stain and culture can be useful in patients at risk for a poor outcome or increased risk of infection with Pseudomonas (table 3 and table 4). Sputum culture may be helpful in patients who are strongly suspected of having a bacterial infection but fail to respond to initial antibiotic therapy. (See "Evaluation for infection in
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
ction but fail to respond to initial antibiotic therapy. (See "Evaluation for infection in exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease", section on 'When to obtain sputum studies'.) ●<span>Influenza testing is appropriate during influenza season or in patients with features of influenza (eg, acute onset of fever, myalgias, coryza during an influenza outbreak). Rapid antigen testing and direct or indirect immunofluorescence antibody staining tests are useful screening tests for influenza infection but have limited sensitivity; polymerase chain
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
d diagnosis".) ●COVID-19 – Test for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection during the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic. (See "COVID-19: Diagnosis".) ●<span>Respiratory virus panel in selected patients – The majority of COPD exacerbations are caused by viral infections, predominantly adenovirus. While not necessary in most patients, PCR diagnostic panels can detect multiple respiratory viruses simultaneously (eg, influenza, adenovirus, parainfluenza virus, respiratory syncytial virus, human metapneumovirus, coronavirus, and rhinovirus). These studies are more frequently obtained in patients with community-acquired pneumonia, and the exact indications for their use in COPD exacerbations are not clear. Severity of exacerbation — The classification of exacerbation severity proposed by an international commission and adopted by the Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
onavirus, and rhinovirus). These studies are more frequently obtained in patients with community-acquired pneumonia, and the exact indications for their use in COPD exacerbations are not clear. <span>Severity of exacerbation — The classification of exacerbation severity proposed by an international commission and adopted by the Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD) is based on symptoms, vital signs, and arterial blood gas (ABG) and c-reactive protein values (if obtained) (figure 1) [1,17]: ●Mild – Dyspnea <5 on a visual analog (1-10) scale (VAS); respiratory rate <24 breaths per minute; heart rate <95 beats per minute; resting SaO2 ≥92 percent breathing ambient air or the patient's usual oxygen prescription and change in saturation ≤3 percent from baseline (if known); CRP<10 mg/L (if obtained). Treatment with short-acting bronchodilators is often sufficient for mild exacerbations. ●Moderate – Three out of five of the following: Dyspnea ≥5 on VAS; respiratory rate ≥24 breaths per minute, heart rate ≥95 beats per minute; resting SaO2 <92 percent breathing ambient air or the patient's usual oxygen prescription and/or change in saturation >3 percent from baseline (if known); CRP ≥10 mg/L (if obtained). Treatment of moderate exacerbations generally includes short-acting bronchodilators plus antibiotics and/or oral glucocorticoids. ●Severe – Meets moderate criteria combined with hypercapnia and acidosis on ABG (PaCO2 >45 mmHg and pH <7.35). Treatment of severe exacerbations includes short-acting bronchodilators, antibiotics, and oral or intravenous glucocorticoids. Severe exacerbations may be associated with respiratory failure and require noninvasive or invasive ventilation. DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS — Patients with COPD who present to the hospital with acute worsening of dyspnea should be evaluated for potential alternative diagnoses, such as heart failure, c
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
, antibiotics, and oral or intravenous glucocorticoids. Severe exacerbations may be associated with respiratory failure and require noninvasive or invasive ventilation. DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS — <span>Patients with COPD who present to the hospital with acute worsening of dyspnea should be evaluated for potential alternative diagnoses, such as heart failure, cardiac arrhythmia, pneumonia, pulmonary embolism, and pneumothorax [1,44,45]. A chest radiograph will differentiate among several of these possibilities (eg, heart failure, pneumonia, pneumothorax); a clear chest radiograph may be a clue to pulmonary embolism, es
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
al with acute worsening of dyspnea should be evaluated for potential alternative diagnoses, such as heart failure, cardiac arrhythmia, pneumonia, pulmonary embolism, and pneumothorax [1,44,45]. <span>A chest radiograph will differentiate among several of these possibilities (eg, heart failure, pneumonia, pneumothorax); a clear chest radiograph may be a clue to pulmonary embolism, especially when dyspnea and hypoxemia are more prominent than cough or sputum production. The importance of considering these alternate diagnoses was illustrated in an autopsy study of 43 patients with COPD who died within 24 hours of admission for a COPD exacerbation [44].
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
heart failure, pneumonia, pneumothorax); a clear chest radiograph may be a clue to pulmonary embolism, especially when dyspnea and hypoxemia are more prominent than cough or sputum production. <span>The importance of considering these alternate diagnoses was illustrated in an autopsy study of 43 patients with COPD who died within 24 hours of admission for a COPD exacerbation [44]. The primary causes of death were heart failure, pneumonia, pulmonary thromboembolism, and COPD in 37, 28, 21, and 14 percent, respectively. ●Heart failure – Acute decompensated heart failure (ADHF) is characterized by the development of acute dyspnea associated with elevated intracardiac filling pressures with or without pu
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
t radiograph, echocardiogram) are often supportive, the diagnosis cannot be based on a single test. (See "Approach to diagnosis and evaluation of acute decompensated heart failure in adults".) ●<span>Cardiac arrhythmias – Cardiac arrhythmias, such as atrial fibrillation, are frequent in patients with COPD, and may be a trigger or consequence of COPD exacerbation [1]. A bedside electrocardiogram can be diagnostic. (See "Atrial fibrillation: Overview and management of new-onset atrial fibrillation".) ●Pneumonia – Pneumonia can present with acute shortness of breath, hypoxemia, and an inconclusive
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
ribution is not present with pneumonia. Fever and leukocytosis may suggest an infectious process. (See "Clinical evaluation and diagnostic testing for community-acquired pneumonia in adults".) ●<span>Pneumothorax – COPD is a risk factor for pneumothorax. Worsening dyspnea can be due to either a COPD exacerbation or pneumothorax, but acute pleuritic chest pain would be more suggestive of pneumothorax while increased volume of sputum and sputum purulence would suggest a COPD exacerbation. A pneumothorax is usually apparent on conventional chest radiograph or thoracic ultrasound, although bullous emphysema can mimic a pneumothorax and necessitate a chest computed tomograp
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
und, although bullous emphysema can mimic a pneumothorax and necessitate a chest computed tomography (CT) scan for differentiation. (See "Clinical presentation and diagnosis of pneumothorax".) ●<span>Pulmonary embolism – The sudden onset of symptoms such as dyspnea, pleuritic chest pain, tachypnea, and cough may be caused by a pulmonary embolism. The suspicion for pulmonary embolism rises in the absence of purulent sputum production, history of an upper respiratory infection, or pneumothorax [36-42,46,47]. (See 'Triggers' above and 'Additional testing' above.) Testing may include a blood D-dimer test, lower extremity compression ultrasonography with Doppler, and CT pulmonary angiogram. (S
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
illions of patients with pulmonary disease and may be the primary manifestation of lung disease, myocardial ischemia or dysfunction, anemia, neuromuscular disorders, obesity, or deconditioning. <span>Examination of the language of dyspnea suggests that this symptom represents a number of qualitatively distinct sensations, and that the words utilized by patients to describe their breathing discomfort may provide insight into the underlying pathophysiology of the disease. The key elements in the evaluation of the patient with dyspnea will be reviewed here. The basic physiology of dyspnea, the evaluation of acute dyspnea, and dyspnea in pregnancy are disc
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
ions to pregnancy: Dyspnea and other physiologic respiratory changes".) DEFINITION OF DYSPNEA — A consensus statement of the American Thoracic Society defines dyspnea in the following way [1]: "<span>Dyspnea is a term used to characterize a subjective experience of breathing discomfort that is comprised of qualitatively distinct sensations that vary in intensity. The experience derives from interactions among multiple physiological, psychological, social, and environmental factors, and may induce secondary physiological and behavioral responses." Dyspnea is considered acute when it develops over hours to days and chronic when it occurs for more than four to eight weeks. Some patients present with acute worsening of chronic brea
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
nsity. The experience derives from interactions among multiple physiological, psychological, social, and environmental factors, and may induce secondary physiological and behavioral responses." <span>Dyspnea is considered acute when it develops over hours to days and chronic when it occurs for more than four to eight weeks. Some patients present with acute worsening of chronic breathlessness that may be caused by a new problem or a worsening of the underlying disease (eg, asthma, chronic obstructive pulmo
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
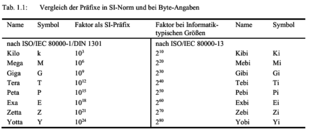
Open itProzessoren besitzen eine gewisse Wortbreite. Die Wortbreite ist die maximale Zahl von Bits, die sie auf einmal verarbeiten können.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itProzessoren besitzen eine gewisse Wortbreite. Die Wortbreite ist die maximale Zahl von Bits, die sie auf einmal verarbeiten können.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
at www.thoracic.org/statements. PATHOPHYSIOLOGY — Most patients with breathing discomfort can be categorized into one of two groups: respiratory system dyspnea or cardiovascular system dyspnea. <span>Respiratory system dyspnea includes discomfort related to disorders of the central controller, the ventilatory pump, and the gas exchanger (table 1), while cardiovascular system dyspnea includes cardiac diseases (eg, acute ischemia, systolic dysfunction, valvular disorders, pericardial diseases), as well as anemia and deconditioning; the latter two lead to dyspnea via altered delivery and/or utilization of oxygen (figure 1). More than one process may be active in a given patient, and the basic physiology of dyspnea does not always adhere to this structure; for example, stimulation of pulmonary receptors can
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
he lungs by bulk transport to the atmosphere. Several components must be functioning smoothly for this process to occur; derangements in any of these elements can lead to dyspnea. ●Controller – <span>The "respiratory controller" determines the rate and depth of breathing via efferent signals sent to the ventilatory muscles. Factors that stimulate the respiratory centers in the brainstem lead to increased ventilation and breathing discomfort in a variety of settings; these often are secondary to derangements in other parts of the system, such as hypoxia or hypercapnia due to ventilation/perfusion mismatching in the gas exchanger, or stimulation of pulmonary receptors as occurs with interstitial inflammation or edema. In addition, drugs such as aspirin (at a toxic dose) or progesterone and conditions such as pregnancy or diabetic ketoacidosis can produce dyspnea through central effects independent of
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
he system, such as hypoxia or hypercapnia due to ventilation/perfusion mismatching in the gas exchanger, or stimulation of pulmonary receptors as occurs with interstitial inflammation or edema. <span>In addition, drugs such as aspirin (at a toxic dose) or progesterone and conditions such as pregnancy or diabetic ketoacidosis can produce dyspnea through central effects independent of problems in the ventilatory pump or gas exchanger. Typically, dyspnea associated with stimulation of the respiratory controller is described as a sensation of "air hunger" or an "urge or need to breathe" [2-4]. (See "Control of ventilation" and "Physiology of dyspnea".) To some degree, the breathing pattern may also reflect what are presumed to be attempts by the controller to reduce breathing
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
ted with stimulation of the respiratory controller is described as a sensation of "air hunger" or an "urge or need to breathe" [2-4]. (See "Control of ventilation" and "Physiology of dyspnea".) <span>To some degree, the breathing pattern may also reflect what are presumed to be attempts by the controller to reduce breathing discomfort. Thus, patients with severe airflow obstruction generally adapt a relatively slow, deep breathing pattern to minimize the pleural pressures needed to overcome airways resistance to generate adequate flow. Alternatively, patients with interstitial fibrosis or kyphoscoliosis and reduced lung or chest wall compliance have a characteristic rapid, shallow breathing pattern which minimizes the work needed to expand the thorax. When the respiratory controller is stimulated (eg, by exercise), airflow obstruction may heighten the sensation of air hunger. The increase in respiratory rate during exercise in the se
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
th interstitial fibrosis or kyphoscoliosis and reduced lung or chest wall compliance have a characteristic rapid, shallow breathing pattern which minimizes the work needed to expand the thorax. <span>When the respiratory controller is stimulated (eg, by exercise), airflow obstruction may heighten the sensation of air hunger. The increase in respiratory rate during exercise in the setting of expiratory flow limitation can lead to exercise-induced air-trapping, a process known as dynamic hyperinflation. Dynamic hyperinflation is associated with a reduced inspiratory reserve and increased dyspnea. For those in whom hyperinflation is substantial, such that inspiratory capacity at rest or
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
ise is limited by total lung capacity, dyspnea is further exacerbated, and patients may also complain of an inability to get a deep breath. (See "Dynamic hyperinflation in patients with COPD".) <span>For patients with restrictive lung disease, the adoption of breathing patterns with either an increase or decrease in tidal volume from their average resting tidal volume results in increased dyspnea [5]. Breathing with a rapid, shallow pattern, the patient experiences an increase in the ratio of dead space to tidal volume (since anatomic dead space is relatively fixed), which leads to a need for greater total ventilation (hence, the increase in respiratory rate); this adds to respiratory work-load and may contribute to the development of hypercapnia. In contrast, an increase in tidal volume requires a significant increase in respiratory work due to the stiffness of the lung. Since most patients with restrictive lung disease tend to use a rapid, shallow breathing pattern, we conclude that this pattern, relative to alternatives, must produce less dyspnea. ●Ventilatory pump – The "ventilatory pump" comprises the ventilatory muscles, the peripheral nerves which transmit signals to them from the controller, the bones of the chest wall which
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
hich transforms movement of the chest wall to negative pressure inside the thorax, and the airways that serve as a conduit for the flow of gas from the atmosphere to the alveoli and back again. <span>The most common derangements of the ventilatory pump result in a sense of increased "work of breathing" [6-10]. Neuromuscular weakness (eg, myasthenia gravis, Guillain-Barré syndrome) leads to a condition in which the patient must exert near maximal inspiratory effort to produce a normal negative
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
a conduit for the flow of gas from the atmosphere to the alveoli and back again. The most common derangements of the ventilatory pump result in a sense of increased "work of breathing" [6-10]. <span>Neuromuscular weakness (eg, myasthenia gravis, Guillain-Barré syndrome) leads to a condition in which the patient must exert near maximal inspiratory effort to produce a normal negative pleural pressure [11]. Patients with reduced compliance of the chest wall (eg, kyphoscoliosis) or lungs (eg, interstitial fibrosis) must perform more work than normal to move air into the lungs. Obstructive l
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
ncreased resistance to flow and, in patients with significant hyperinflation, reduced compliance as breathing occurs on the stiff portion of the pressure-volume curve of the respiratory system. <span>When hyperinflation results in an end-inspiratory volume that approximates total lung capacity, patients often complain of an inability to get a deeper satisfying breath [9]. A sensation of chest tightness may also be present in patients in whom acute bronchoconstriction is the cause of airflow obstruction [6,7,12,13]. ●Gas exchanger – The "gas exchanger" consists of the alveoli and the pulmonary capillaries across which oxygen and carbon dioxide diffuse. Most of the common cardiopulmonary disorders l
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
ction is the cause of airflow obstruction [6,7,12,13]. ●Gas exchanger – The "gas exchanger" consists of the alveoli and the pulmonary capillaries across which oxygen and carbon dioxide diffuse. <span>Most of the common cardiopulmonary disorders leading to dyspnea are associated with some derangement of the gas exchanger due either to destruction of the diffusing membrane (eg, emphysema, pulmonary fibrosis) or the addition of fluid or inflammatory material into the lungs such that ventilation to alveoli is reduced regionally. To a lesser degree, the distance for diffusion may also contribute in these conditions or in the greatly dilated pulmonary capillaries seen in some patients with hepatopulmonary syndrome. Diseases affecting the gas exchanger are typically characterized by hypoxemia, either at rest or with exercise, and by chronic hypercapnia in more severe cases. These gas exchange abnor
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
ally. To a lesser degree, the distance for diffusion may also contribute in these conditions or in the greatly dilated pulmonary capillaries seen in some patients with hepatopulmonary syndrome. <span>Diseases affecting the gas exchanger are typically characterized by hypoxemia, either at rest or with exercise, and by chronic hypercapnia in more severe cases. These gas exchange abnormalities stimulate the respiratory centers in the brainstem and lead to a sensation of "air hunger" or an increased urge to breathe. Cardiovascular — The cardiovascular system is designed to move oxygenated blood from the lungs to metabolically active tissues, and then transport carbon dioxide from the tissues back t
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
eakness, and dyspnea on exertion) and those due to increased pulmonary or systemic venous pressure and fluid accumulation (dyspnea at rest and exertion, edema, hepatic congestion, and ascites). <span>When heart failure causes an increase in pulmonary venous pressure, it can lead to dyspnea either by producing hypoxemia or by stimulating pulmonary vascular and/or interstitial receptors (eg, unmyelinated J-receptors, also called C-fibers). Causes of heart failure include ventricular systolic dysfunction, ventricular diastolic dysfunction, and valvular disease. Cardiac tamponade may also lead to dyspnea by increasing pulmo
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
ac output, which may necessitate elevated left ventricular volume and pulmonary vascular pressures. However, the quality of dyspnea is usually quite different in these two clinical situations. ●<span>Deconditioning – Individuals usually complain of respiratory discomfort when they engage in vigorous physical activity, even in the presence of a normal cardiovascular and respiratory system and normal hematocrit. More fit individuals experience less discomfort for any given workload; cardiovascular fitness is determined by the ability of the heart to increase maximal cardiac output and by the ability of the peripheral muscles to utilize oxygen efficiently for aerobic metabolism. In contrast, a sedentary existence reduces fitness and leads to dyspnea, often with seemingly trivial tasks. It is common for patients with chronic cardiopulmonary disease to assume a s
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
density in the muscles, and reduced mitochondrial capacity to sustain aerobic metabolism) and ultimately may be limited more by poor cardiovascular fitness than by the underlying disease [16]. <span>Dyspnea due to deconditioning is typically described as "heavy breathing" or a sense of "breathing more" [8], and with careful questioning, one can determine that the patient is actually limited by fatigue or leg discomfort rather than breathing discomfort. A pathologic variant of this phenomenon has been reported in a subset of patients with post-COVID-19 infections and persistent dyspnea. Cardiopulmonary exercise testing has demonstrated
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
oxygen to support aerobic metabolism [17,18]. (See "Cardiopulmonary exercise testing in the evaluation of unexplained dyspnea", section on 'Peripheral causes of dyspnea'.) CLINICAL ASSESSMENT — <span>While clinical history is often insufficient to make a secure diagnosis, it provides guidance in narrowing the diagnostic possibilities and selecting diagnostic tests. In one study of 85 patients presenting to a pulmonary unit with a complaint of chronic dyspnea, the initial impression of the etiology of dyspnea based upon the patient history alone was correct in 66 percent of cases [19]. Thus, a systematic diagnostic approach to history-taking can be extremely helpful. Temporal pattern and triggers — The temporal pattern of breathlessness and association with certain tr
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
based upon the patient history alone was correct in 66 percent of cases [19]. Thus, a systematic diagnostic approach to history-taking can be extremely helpful. Temporal pattern and triggers — <span>The temporal pattern of breathlessness and association with certain triggers can provide important clues. Breathing discomfort arising over the course of minutes to hours is due to a relatively limited number of conditions (table 2). These entities typically have associated symptoms and signs that provide clues to the appropriate diagnosis, eg, substernal chest pain with cardiac ischemia; fever, cough, and sputum wi
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
Mobile Access Help & Training Demos Wolters Kluwer Health Emmi® Facts & Comparisons® Lexicomp® Medi-Span® Loading Please wait 2 of 13 Export to Powerpoint Print Share Bookmark Feedback <span>Causes of acute dyspnea Cardiovascular system Acute myocardial ischemia Heart failure Cardiac tamponade Respiratory system Bronchospasm Pulmonary embolism Pneumothorax Pulmonary infection - bronchitis, pneumonia Upper airway obstruction - aspiration, anaphylaxis Causes_of_acute_dyspnea.htm Graphic 82700 Version 1.0 © 2023 UpToDate, Inc. and/or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved. Cardiovascular system Acute myocardial ischemia Heart failure Car
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
is are important. The approach to acute dyspnea is described separately. (See "Approach to the adult with dyspnea in the emergency department".) ●Exertional, positional, and nocturnal dyspnea – <span>Chronic exertional dyspnea and paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea (PND) are both associated with heart failure, although nocturnal dyspnea is more specific to heart failure. Asthma is also associated with exertional and nocturnal dyspnea, but unlike PND does not usually improve with sitting or standing. Orthopnea, the development of or worsening of dyspnea in the supine position, is also associated with heart failure and increased pulmonary capillary pressure due to the increased veno
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
although nocturnal dyspnea is more specific to heart failure. Asthma is also associated with exertional and nocturnal dyspnea, but unlike PND does not usually improve with sitting or standing. <span>Orthopnea, the development of or worsening of dyspnea in the supine position, is also associated with heart failure and increased pulmonary capillary pressure due to the increased venous return to the heart in this position. Central obesity, however, with a large protuberant abdomen, may also lead to orthopnea; increased intra-abdominal pressure associated with large abdominal girth impairs movement of the diaphragm during inhalation; in addition, intrapleural pressure increases, which may lead to narrowing or closure of small airways at the bases of the lungs, and can worsen gas exchange and hypoxemia. Finally, patients with inspiratory muscle weakness may also complain of orthopnea due to the increased work of breathing associated with moving the diaphragm against high intra-abdominal pressure. Bendopnea, the worsening of dyspnea when leaning forward, is described in patients with decompensated heart failure [20] but may also be seen in patients with central obesity, particula
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
ally, patients with inspiratory muscle weakness may also complain of orthopnea due to the increased work of breathing associated with moving the diaphragm against high intra-abdominal pressure. <span>Bendopnea, the worsening of dyspnea when leaning forward, is described in patients with decompensated heart failure [20] but may also be seen in patients with central obesity, particularly when the patient attempts to tie their shoes from the sitting position. Dyspnea that is not exacerbated by exertion is more often due to a functional or perceptual problem than to cardiopulmonary disease. ●Intermittent dyspnea – Intermittent dyspnea associa
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
bed in patients with decompensated heart failure [20] but may also be seen in patients with central obesity, particularly when the patient attempts to tie their shoes from the sitting position. <span>Dyspnea that is not exacerbated by exertion is more often due to a functional or perceptual problem than to cardiopulmonary disease. ●Intermittent dyspnea – Intermittent dyspnea associated with cold air or animal dander exposure suggests asthma; work-related dyspnea may suggest occupational asthma; and dyspnea follow
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
ient attempts to tie their shoes from the sitting position. Dyspnea that is not exacerbated by exertion is more often due to a functional or perceptual problem than to cardiopulmonary disease. ●<span>Intermittent dyspnea – Intermittent dyspnea associated with cold air or animal dander exposure suggests asthma; work-related dyspnea may suggest occupational asthma; and dyspnea following upper respiratory infections may be due to asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). In addition to asthma, intermittent symptoms that resolve completely between episodes can be seen with recurrent aspiration; recurrent pulmonary emboli and heart failure can also wax an
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
e suggests asthma; work-related dyspnea may suggest occupational asthma; and dyspnea following upper respiratory infections may be due to asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). <span>In addition to asthma, intermittent symptoms that resolve completely between episodes can be seen with recurrent aspiration; recurrent pulmonary emboli and heart failure can also wax and wane, but generally are characterized by a baseline level of dysfunction. The presence of specific, reproducible inciting events such as exercise or cold air exposure is common with airways hyperreactivity. ●Rapidity of symptom onset and progression – The rapidity with which symptoms develop during exercise can also provide useful diagnostic information. For example, patients who develop s
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
of dysfunction. The presence of specific, reproducible inciting events such as exercise or cold air exposure is common with airways hyperreactivity. ●Rapidity of symptom onset and progression – <span>The rapidity with which symptoms develop during exercise can also provide useful diagnostic information. For example, patients who develop shortness of breath and wheezing after walking 50 to 100 feet often have acute elevations in pulmonary capillary wedge pressure (usually due to cardiac diastolic dysfunction) or pulmonary hypertension. In contrast, symptoms of exercise-induced asthma usually are precipitated by more intense activity, beginning three minutes into exercise, peaking within 10 to 15 minutes, and resolving by 60 minutes. (See "Exercise-induced bronchoconstriction".) Respiratory muscle weakness generally leads to gradually progressive dyspnea, sometimes with an acute worsening at a time of illness, particularly a respiratory infection. Severity of d
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
lly are precipitated by more intense activity, beginning three minutes into exercise, peaking within 10 to 15 minutes, and resolving by 60 minutes. (See "Exercise-induced bronchoconstriction".) <span>Respiratory muscle weakness generally leads to gradually progressive dyspnea, sometimes with an acute worsening at a time of illness, particularly a respiratory infection. Severity of dyspnea — For patients with chronic dyspnea, formal assessment of the severity of dyspnea can help create a baseline for future comparisons [21]. A number of instruments are
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
lp assess the severity of dyspnea, such as the Baseline Dyspnea Index, the Modified Medical Research Council (mMRC) dyspnea scale (calculator 1) (table 3), and the Borg scale (table 4) [22-26]. <span>It is important to note that scales like the mMRC do not measure dyspnea directly; rather, they assess the intensity of exercise that provokes dyspnea and, indirectly, the degree of disability resulting from dyspnea. Routine assessment of dyspnea in hospitalized patients is feasible [27] and severity of dyspnea on admission to the hospital predicts increased mortality [28]. The Edmonton Dyspnea Inventory (EDI), a clinical instrument to measure dyspnea severity with activities of daily living, exercise, and rest using a numeric rating scale (0 through 10),
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
0 through 10), has been proposed as a measurement of dyspnea severity in the context of daily activities, particularly in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis [29]. Associated symptoms — <span>Associated symptoms such as cough, sputum production, nasal congestion, chest pain, peripheral edema, Raynaud phenomenon, joint swelling, and muscle weakness can help identify areas for further investigation. As examples, asymmetric lower extremity edema might suggest venous thromboembolic disease; Raynaud phenomenon is seen in a number of rheumatic diseases that are associated with intersti
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
eathing discomfort from a variety of cardiopulmonary disorders [6-8,31]. Subjects were asked to select the phrases that best described their breathing discomfort, and distinct clusters emerged. <span>While some clusters of phrases were common to a number of disease categories (eg, increased work or effort of breathing was found with COPD, asthma, and neuromuscular disease), each disease had a relatively unique set of clusters associated with it. The combined data from studies that were performed in patients with known cardiopulmonary disorders or in normal subjects made breathless under experimental conditions indicate the foll
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
studies that were performed in patients with known cardiopulmonary disorders or in normal subjects made breathless under experimental conditions indicate the following (table 6) [2,6-8,30,31]: ●<span>The sensation of "air hunger" has been associated with acute bronchoconstriction and hyperinflation in asthma and COPD, heart failure, pulmonary embolism, and restricted thoracic motion, as well as acute hypercapnia from any cause [3,4,32]. ●Acute bronchoconstriction leads to a series of sensations as the degree of obstruction worsens, from "chest tightness" to an increased "effort to breathe" to a sensation of "air hunger
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
d with acute bronchoconstriction and hyperinflation in asthma and COPD, heart failure, pulmonary embolism, and restricted thoracic motion, as well as acute hypercapnia from any cause [3,4,32]. ●<span>Acute bronchoconstriction leads to a series of sensations as the degree of obstruction worsens, from "chest tightness" to an increased "effort to breathe" to a sensation of "air hunger" [6-9,12,13]. The sensation of "tightness" appears to be independent of the work of breathing [33]. Attention to the use of verbal descriptors of dyspnea may help the clinician avoid underestimation of the severity of airflow limitation when objective measurements of lung function are not possible. ●Report of "increased work of breathing" is associated with COPD, moderate to severe asthma, myopathy, and pulmonary fibrosis. ●Patients with COPD and dynamic hyperinflation sometimes c
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
on to the use of verbal descriptors of dyspnea may help the clinician avoid underestimation of the severity of airflow limitation when objective measurements of lung function are not possible. ●<span>Report of "increased work of breathing" is associated with COPD, moderate to severe asthma, myopathy, and pulmonary fibrosis. ●Patients with COPD and dynamic hyperinflation sometimes complain of a sensation of "unsatisfying breaths" or a sense that they "cannot get a deep breath" [9]. ●A sensation of rapid, sh
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
on when objective measurements of lung function are not possible. ●Report of "increased work of breathing" is associated with COPD, moderate to severe asthma, myopathy, and pulmonary fibrosis. ●<span>Patients with COPD and dynamic hyperinflation sometimes complain of a sensation of "unsatisfying breaths" or a sense that they "cannot get a deep breath" [9]. ●A sensation of rapid, shallow breathing may correspond to interstitial lung disease or reduced chest wall compliance. ●Heart failure is also associated with a sensation of "suffocation
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
yopathy, and pulmonary fibrosis. ●Patients with COPD and dynamic hyperinflation sometimes complain of a sensation of "unsatisfying breaths" or a sense that they "cannot get a deep breath" [9]. ●<span>A sensation of rapid, shallow breathing may correspond to interstitial lung disease or reduced chest wall compliance. ●Heart failure is also associated with a sensation of "suffocation" [6]. ●A sense of heavy breathing is typical of deconditioning. Patient questionnaires have been developed for use in
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
nsatisfying breaths" or a sense that they "cannot get a deep breath" [9]. ●A sensation of rapid, shallow breathing may correspond to interstitial lung disease or reduced chest wall compliance. ●<span>Heart failure is also associated with a sensation of "suffocation" [6]. ●A sense of heavy breathing is typical of deconditioning. Patient questionnaires have been developed for use in research and clinical settings, and allow the doctor to assess symptom in
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
●A sensation of rapid, shallow breathing may correspond to interstitial lung disease or reduced chest wall compliance. ●Heart failure is also associated with a sensation of "suffocation" [6]. ●<span>A sense of heavy breathing is typical of deconditioning. Patient questionnaires have been developed for use in research and clinical settings, and allow the doctor to assess symptom intensity, quality, and associated affective responses as pa
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
the wording used to describe dyspnea [36-41]. Further research in this area is underway. (See 'Perceptual and psychological factors' below.) Cigarette smoking and exposures to dusts and fumes — <span>The absence of cigarette smoking argues strongly against a diagnosis of COPD, unless the patient has a history of tuberculosis or use of biomass cooking fuels. In one study, a history of smoking cigarettes had a positive predictive value for COPD of 0.4; COPD is uncommon among patients who have never smoked or have smoked less than 10 pack years [42]. Exposure to particulates in the air, particularly for individuals living in proximity to highways, may contribute to airway disease and dyspnea [43]. The occupational history may lead t
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
nal and environmental exposures' and "Overview of bronchiolar disorders in adults" and "Asbestos-related pleuropulmonary disease" and "Chronic beryllium disease (berylliosis)" and "Silicosis".) <span>Physical examination — A complete physical examination is essential. In particular, the focus should be directed at the presence or absence of stridor, wheezing, crackles, tachycardia, arrhythmia, heart murmurs, gallop, peripheral edema, muscle weakness, dysphonia, and evidence of rheumatic disease. However, the absence of physical findings tends to have a greater negative predictive value, than the positive predictive value of any identified signs [19]. ●Clubbing is associated with several causes of dyspnea, including bronchiectasis, idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, lung cancer, and pediatric cyanotic heart disease, but not asthma, COPD,
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
and evidence of rheumatic disease. However, the absence of physical findings tends to have a greater negative predictive value, than the positive predictive value of any identified signs [19]. ●<span>Clubbing is associated with several causes of dyspnea, including bronchiectasis, idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, lung cancer, and pediatric cyanotic heart disease, but not asthma, COPD, or adult-onset hypoxemia. ●Jugular venous distention indicates elevated R-sided filling pressures that suggest heart failure, valvular disease, or pulmonary hypertension. ●Decreased or distant heart sounds may s
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
ated with several causes of dyspnea, including bronchiectasis, idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, lung cancer, and pediatric cyanotic heart disease, but not asthma, COPD, or adult-onset hypoxemia. ●<span>Jugular venous distention indicates elevated R-sided filling pressures that suggest heart failure, valvular disease, or pulmonary hypertension. ●Decreased or distant heart sounds may suggest a pericardial effusion but may also be due to obesity or hyperinflation from emphysema. ●Abdominal rounding, the protruding of the central
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
but not asthma, COPD, or adult-onset hypoxemia. ●Jugular venous distention indicates elevated R-sided filling pressures that suggest heart failure, valvular disease, or pulmonary hypertension. ●<span>Decreased or distant heart sounds may suggest a pericardial effusion but may also be due to obesity or hyperinflation from emphysema. ●Abdominal rounding, the protruding of the central abdomen with diminished transverse diameter during exhalation, has been associated with acute heart failure [47]. EVALUATION OF ACUTE
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
art failure, valvular disease, or pulmonary hypertension. ●Decreased or distant heart sounds may suggest a pericardial effusion but may also be due to obesity or hyperinflation from emphysema. ●<span>Abdominal rounding, the protruding of the central abdomen with diminished transverse diameter during exhalation, has been associated with acute heart failure [47]. EVALUATION OF ACUTE DYSPNEA — Breathing discomfort arising over the course of minutes to hours is generally due to a limited number of conditions (table 2) and generally involves proces
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
iscomfort arising over the course of minutes to hours is generally due to a limited number of conditions (table 2) and generally involves processes that require prompt evaluation and treatment. <span>Clues to the need for an urgent evaluation include heart rate >120 beats/minute, respiratory rate >30 breaths/minute, pulse oxygen saturation (SpO2) <90 percent, use of accessory respiratory muscles, difficulty speaking in full sentences (which may be a sign of reduced vital capacity or very high drive to breathe), stridor, asymmetric breath sounds or percussion, diffuse crackles, diaphoresis, and cyanosis. The evaluation of dyspnea in the emergency department is described separately. (See "Approach to the adult with dyspnea in the emergency department".) INITIAL TESTING IN CHRONIC DYSPNEA
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
iopulmonary disease does not guarantee that the patient's symptoms or the etiology of their exercise limitation are due to that condition, particularly in patients with coexisting disease [16]. <span>The five most common causes of chronic dyspnea are the following: ●Asthma (see 'Respiratory' above) ●Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) (see 'Respiratory' above) ●Interstitial lung disease (see 'Respiratory' above) ●Myocardial dysfunction (see 'Cardiovascular' above) ●Obesity/deconditioning (see 'Cardiovascular' above) Pace of testing — For patients with chronic dyspnea, the severity of dyspnea and rate of worsening are important determinants of the pace and location of diagnostic testing [21]. The op
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
may evolve through as many as four stages with highly variable temporal evolution of ECG changes. The four typical stages of ECG changes (figure 1) in patients with acute pericarditis include: <span>Typical ECG findings ●Stage 1, seen in the first hours to days, is characterized by widespread ST elevation (typically concave up) with reciprocal ST depression in leads aVR and V1 (waveform 1). There is also frequently an atrial current of injury, reflected by elevation of the PR segment in lead aVR and depression of the PR segment in other limb leads and in the left chest leads, primarily V5 and V6. Thus, the PR and ST segments typically change in opposite directions. PR segment deviation, which is highly specific, though less sensitive, is frequently overlooked. The TP segment is recommended as the baseline for comparison when measuring both PR and ST segment changes in acute pericarditis. ●Stage 2, typically seen in the first week, is characterized by normalization of the ST and PR segments. ●Stage 3 is characterized by the development of diffuse T-wave inversions, generally after the ST segments have become isoelectric. It is typically seen in the subacute phase, and its duration is not well documented and likely highly variable. ●Stage 4 is represented by normalization of the ECG. It can occur directly from stage 1 in self-limited cases or with prompt response to medical therapy. Atypical ECG findings — Pericarditis does not always result in the typical ECG changes described above. In many patients, the ECG returns to normal without going through the above stage
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
erized by fever, respiratory distress, and sepsis. Because of the wide spectrum of associated clinical features, CAP is a part of the differential diagnosis of most acute respiratory illnesses. <span>In patients with a clinically compatible syndrome, the demonstration of an infiltrate on chest imaging is generally sufficient to establish an initial working diagnosis and start empiric therapy. However, this combination of findings is ultimately nonspecific and is shared among many cardiopulmonary disorders. Thus, it is important to remain attentive to the possibility of an alternate diagnosis as a patient's course evolves. The clinical manifestations, diagnosis, and microbiologic evaluation of CAP in immunocompetent adults are reviewed here. An general overview of CAP in adults is provided separately (see
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
diagnosis of CAP generally requires the demonstration of an opacity on chest imaging in a patient with a clinically compatible syndrome (eg, fever, dyspnea, cough, and sputum production) [1]. ●<span>For most patients with suspected CAP, we obtain posteroanterior and lateral chest radiographs. Radiographic findings consistent with the diagnosis of CAP include lobar consolidations (image 1A-B), interstitial infiltrates (image 2A-C), and/or cavitations (image 3). Although certain radiographic features suggest specific causes of pneumonia (eg, lobar consolidations suggest infection with typical bacterial pathogens), radiographic appearance alone cannot reliably differentiate among etiologies. ●In selected cases, it is reasonable to make a clinical diagnosis without chest imaging in otherwise healthy patients with highly compatible syndromes (eg, acute onset, fever, cough, an
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
uggest specific causes of pneumonia (eg, lobar consolidations suggest infection with typical bacterial pathogens), radiographic appearance alone cannot reliably differentiate among etiologies. ●<span>In selected cases, it is reasonable to make a clinical diagnosis without chest imaging in otherwise healthy patients with highly compatible syndromes (eg, acute onset, fever, cough, and signs of consolidation on physical examination) and lack of concern for other causes. However, clinical features alone have limited diagnostic accuracy, thus, we typically reserve this option for circumstances in which chest radiography cannot be easily obtained and the patient can be closely followed. ●When CAP is suspected based on clinical features despite a negative chest radiograph, we obtain computed tomography (CT) of the chest in selected patients. These patients include immun
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
s alone have limited diagnostic accuracy, thus, we typically reserve this option for circumstances in which chest radiography cannot be easily obtained and the patient can be closely followed. ●<span>When CAP is suspected based on clinical features despite a negative chest radiograph, we obtain computed tomography (CT) of the chest in selected patients. These patients include immunocompromised patients, who may not mount strong inflammatory responses and thus have negative chest radiographs, as well as patients with known exposures to epidemic pathogens that cause pneumonia (eg, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2, Legionella spp). ●Obtaining a CT scan is also reasonable when CAP is suspected but the clinical presentation is atypical or the patient has possible alternative explanations for their syndrome (eg, chro
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
thus have negative chest radiographs, as well as patients with known exposures to epidemic pathogens that cause pneumonia (eg, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2, Legionella spp). ●<span>Obtaining a CT scan is also reasonable when CAP is suspected but the clinical presentation is atypical or the patient has possible alternative explanations for their syndrome (eg, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease exacerbation, pulmonary edema, atelectasis, etc). In such cases, CT scanning can help confirm or exclude the diagnosis of pneumonia [2]. Because there is no direct evidence to suggest that CT scanning improves outcomes for most patient
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
heir syndrome (eg, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease exacerbation, pulmonary edema, atelectasis, etc). In such cases, CT scanning can help confirm or exclude the diagnosis of pneumonia [2]. <span>Because there is no direct evidence to suggest that CT scanning improves outcomes for most patients and cost is high, we do not routinely obtain CT scans when evaluating patients for CAP. (See 'Chest imaging findings' below.) All patients with possible CAP should be tested for coronavirus disease 2019 during the pandemic. Microbiologic testing is otherwise generally rese
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
racy, availability, and affordability of rapid microbiologic diagnostics tests is growing, and we expect that indications for testing will broaden soon [3]. (See 'Microbiologic testing' below.) <span>In all cases, the initial diagnosis of CAP should be considered a working diagnosis. A substantial portion of patients initially diagnosed with CAP are ultimately found to have alternate diagnoses [4], therefore, findings that further support or refute the initial diagnoses should continue to be sought as the patient’s course progresses. CLINICAL EVALUATION History and physical — The history and physical examination should be directed at recognizing the clinical syndrome of CAP, evaluating its severity, assessing for co
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
s severity, assessing for complications, identifying important exposures that may indicate the cause of infection, and assessing for comorbidities that may contribute to the patient’s symptoms. <span>Classically, CAP is characterized by acute onset fever, cough (with or without sputum production), and shortness of breath [5-7]. In some cases, pleuritic chest pain may also be present. Less common symptoms include gastrointestinal complaints (eg, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain), loss of appetite, and mental status changes. In patients with advanced age or
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
ptoms. Classically, CAP is characterized by acute onset fever, cough (with or without sputum production), and shortness of breath [5-7]. In some cases, pleuritic chest pain may also be present. <span>Less common symptoms include gastrointestinal complaints (eg, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain), loss of appetite, and mental status changes. In patients with advanced age or impaired immune systems, presenting symptoms can be subtle. For example, fever may be absent in older patients and mental status changes may be the sole
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
dvanced age or impaired immune systems, presenting symptoms can be subtle. For example, fever may be absent in older patients and mental status changes may be the sole presenting symptom [8,9]. <span>Tachycardia, tachypnea, hypoxemia, or increased work of breathing may be present on physical examination. Crackles (rales) and rhonchi may be heard on chest auscultation, along with other signs of consolidation (eg, tactile fremitus, egophony, dullness to percussion). As infection progresses, the dominant clinical picture may be of sepsis and/or respiratory distress. While the clinical features described above support the diagnosis of pneumonia, no c
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
esent on physical examination. Crackles (rales) and rhonchi may be heard on chest auscultation, along with other signs of consolidation (eg, tactile fremitus, egophony, dullness to percussion). <span>As infection progresses, the dominant clinical picture may be of sepsis and/or respiratory distress. While the clinical features described above support the diagnosis of pneumonia, no combination of symptoms and signs has been found to accurately predict the presence or absence of pneu
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
pleuritic chest pain may also be present. Less common symptoms include gastrointestinal complaints (eg, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain), loss of appetite, and mental status changes. <span>In patients with advanced age or impaired immune systems, presenting symptoms can be subtle. For example, fever may be absent in older patients and mental status changes may be the sole presenting symptom [8,9]. Tachycardia, tachypnea, hypoxemia, or increased work of breathing may be present on physical examination. Crackles (rales) and rhonchi may be heard on chest auscultation, along with oth
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
e, the sensitivity of the combination of fever, cough, tachycardia, and crackles was less than 50 percent when chest radiograph was used as a reference standard in one retrospective review [6]. <span>In another study evaluating >28,000 adults presenting to primary care with an acute cough attributed to a lower respiratory tract infection, independent predictors of radiographic-confirmed pneumonia included fever, tachycardia, crackles on chest auscultation, and oxygen saturation <95 percent [7]. However, the positive predictive value (PPV) of all four variables combined was estimated to be only 67 percent. Concordantly, studies comparing clinical judgement with chest radiography for the diagnosis of pneumonia have similar findings [6,11]. One cohort study of >2800 adults with acute cou
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
ur variables combined was estimated to be only 67 percent. Concordantly, studies comparing clinical judgement with chest radiography for the diagnosis of pneumonia have similar findings [6,11]. <span>One cohort study of >2800 adults with acute cough estimates the PPV of clinical judgement at 57 percent [11]. Similarly, there are no signs or symptoms that reliably distinguish among the many infectious causes of pneumonia (eg, viral versus bacterial or between different bacterial causes) [12]
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
h chest radiography for the diagnosis of pneumonia have similar findings [6,11]. One cohort study of >2800 adults with acute cough estimates the PPV of clinical judgement at 57 percent [11]. <span>Similarly, there are no signs or symptoms that reliably distinguish among the many infectious causes of pneumonia (eg, viral versus bacterial or between different bacterial causes) [12]. However, the presence of certain features may raise the index of suspicion for particular pathogens (table 2). This concept is particularly important during outbreaks, family clusters, and other known/potential exposures, where knowledge of a particular exposure may change the need for testing,
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
with established diagnoses of CAP. (See "Procalcitonin use in lower respiratory tract infections", section on 'Community-acquired pneumonia in hospitalized patients'.) DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS — <span>CAP is a common working diagnosis and is on the differential diagnosis of patients presenting with respiratory tract infections, patients with cough and abnormal chest imaging, and patients with sepsis. Because CAP is common and its symptoms overlap with many other cardiopulmonary disorders, it is frequently overdiagnosed [4]. In one cohort study, approximately 17 percent of patients hospitalized with CAP were ultimately found to have a different diagnosis. The most common alternate diagnoses included heart failure, malignancy, and pulmonary infarct or fibrosis [4]. Other respiratory tract infections that present similarly to CAP include, but are not limited, to influenza, coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), acute bronchitis, chronic obstructive p
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
, and other respiratory tract infections. Generally, signs of consolidation on chest auscultation and the presence of an opacity on chest imaging distinguish CAP from the latter two disorders. ●<span>Acute bronchitis – Acute bronchitis is an infection that primarily involves the large airways (bronchi) but not the alveoli or pulmonary parenchyma. Prolonged cough, typically following an upper respiratory tract infection, is the most common symptom of acute bronchitis. In contrast to pneumonia, acute bronchitis is less likely to present with abnormal vital signs (pulse >100/minute, respiratory rate >24 breaths/minute, temperature >38°C [100.4°F], or oxygen saturation <95 percent) (figure 1). Mental status changes and/or other signs of systemic infection are typically absent. Signs of consolidation (rales, egophony, or tactile fremitus) should be absent on chest auscultation. (See "Acute bronchitis in adults".) ●Influenza – Influenza is characterized by acute onset fever and cough, often accompanied by pronounced systemic symptoms including chills, rigors, m
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
ther signs of systemic infection are typically absent. Signs of consolidation (rales, egophony, or tactile fremitus) should be absent on chest auscultation. (See "Acute bronchitis in adults".) ●<span>Influenza – Influenza is characterized by acute onset fever and cough, often accompanied by pronounced systemic symptoms including chills, rigors, myalgias, and/or arthralgias. Pneumonia complicates a minority of cases and may be primary (caused by influenza virus itself) or secondary, caused by bacterial respiratory pathogens (most often streptococci or Staphylococcus aureus). (See "Seasonal influenza in adults: Clinical manifestations and diagnosis".) ●Upper respiratory tract infection (URI) – URIs are commonly characterized by fever and cough, but in contra
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
itself) or secondary, caused by bacterial respiratory pathogens (most often streptococci or Staphylococcus aureus). (See "Seasonal influenza in adults: Clinical manifestations and diagnosis".) ●<span>Upper respiratory tract infection (URI) – URIs are commonly characterized by fever and cough, but in contrast to pneumonia lack signs of consolidation on chest auscultation. While the presence of rhinorrhea and pharyngitis favor the diagnosis URI over pneumonia, URIs sometimes precede or co-occur with CAP [11]. (See "The common cold in adults: Diagnosis and clinical features".) ●Coronavirus disease 2019 – The range of presenting symptoms for COVID-19 is wide, ranging from asymptomatic infecti
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
us disease 2019 – The range of presenting symptoms for COVID-19 is wide, ranging from asymptomatic infection to CAP with profound acute respiratory failure. (See "COVID-19: Clinical features".) <span>Exacerbations of chronic pulmonary diseases are frequently triggered by viral or bacterial infection or colonization of the respiratory tract mucosa. In most cases, infection does not extend beyond the mucosa, however, pneumonia can complicate these disorders. Higher fever, adventitious breath sounds on chest auscultation (eg, focal rales/crackles or rhonchi), and impaired oxygenation suggest pneumonia and generally indicate need for chest imaging. ●Acute exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (AECOPD) – AECOPD is defined as an acute increase in COPD symptoms that go beyond day-to-day variation, typically character
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
s (eg, granulomatosis with polyangiitis, rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, dermatomyositis). (See "Approach to the adult with interstitial lung disease: Clinical evaluation".) <span>Febrile illness and/or sepsis can also be the presenting syndrome in patients with CAP; other common causes of these syndromes include urinary tract infections, intra-abdominal infections, and endocarditis. In all cases, monitoring the patient’s progress over time helps confirm or refute the initial diagnosis. For example, the rapid resolution of pulmonary opacities on chest imaging sugges
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
ss and/or sepsis can also be the presenting syndrome in patients with CAP; other common causes of these syndromes include urinary tract infections, intra-abdominal infections, and endocarditis. <span>In all cases, monitoring the patient’s progress over time helps confirm or refute the initial diagnosis. For example, the rapid resolution of pulmonary opacities on chest imaging suggests a noninfectious process such as pulmonary edema or atelectasis. Conversely, lack of response to empiric treatment in 48 to 72 hours suggest that initial antibiotic selection was inadequate, there are complications, or that there is an alternate diagnosis. (See 'Follow-up care' below.) CHEST IMAGING FINDINGS Imaging techniques — Chest imaging is indicated for the majority of patients with suspected CAP to confirm the diagnosis, assess for complications (eg, parapneumo
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
UpToDate
rtion of patients initially diagnosed with CAP will ultimately be found to have an alternate diagnosis, close follow-up is important for both outpatient and hospitalized patients (algorithm 3). <span>Most patients will show some signs of improvement within 48 to 72 hours of starting treatment. Subjectively, we look for improvement in cough, sputum production, dyspnea, and chest pain. Objectively, we assess for resolution of fever and normalization of heart rate, respiratory rate, oxygenation, and white blood cell count. Generally, patients demonstrate some clinical improvement within 48 to 72 hours. Both failure to improve and very rapid response should raise suspicion for diagnoses other than CAP. Reasons for clinical failure can generally be categorized as either progression of i
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Built-in React APIs – React
Built-in React APIs In addition to Hooks and Components, the react package exports a few other APIs that are useful for defining components. This page lists all the remaining modern React APIs. <span>createContext lets you define and provide context to the child components. Used with useContext. forwardRef lets your component expose a DOM node as a ref to the parent. Used with useRef. lazy lets you defer loading a component’s code until it’s rendered for the first time. memo le
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Built-in React APIs – React
Is that are useful for defining components. This page lists all the remaining modern React APIs. createContext lets you define and provide context to the child components. Used with useContext. <span>forwardRef lets your component expose a DOM node as a ref to the parent. Used with useRef. lazy lets you defer loading a component’s code until it’s rendered for the first time. memo lets your component skip re-renders with same props. Used with useMemo and useCallback. start
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Built-in React APIs – React
APIs. createContext lets you define and provide context to the child components. Used with useContext. forwardRef lets your component expose a DOM node as a ref to the parent. Used with useRef. <span>lazy lets you defer loading a component’s code until it’s rendered for the first time. memo lets your component skip re-renders with same props. Used with useMemo and useCallback. startTransition lets you mark a state update as non-urgent. Similar to useTransition. How do
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Built-in React APIs – React
ith useContext. forwardRef lets your component expose a DOM node as a ref to the parent. Used with useRef. lazy lets you defer loading a component’s code until it’s rendered for the first time. <span>memo lets your component skip re-renders with same props. Used with useMemo and useCallback. startTransition lets you mark a state update as non-urgent. Similar to useTransition. How do you like these docs? Take our survey! ©2023 Learn React Quick Start Installation Describing
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Built-in React APIs – React
with useRef. lazy lets you defer loading a component’s code until it’s rendered for the first time. memo lets your component skip re-renders with same props. Used with useMemo and useCallback. <span>startTransition lets you mark a state update as non-urgent. Similar to useTransition. How do you like these docs? Take our survey! ©2023 Learn React Quick Start Installation Describing the UI Adding Interactivity Managing State Escape Hatches API Reference React APIs Rea
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Client React DOM APIs – React
hese APIs are typically used at the top level of your app to initialize your React tree. A framework may call them for you. Most of your components don’t need to import or use them. Client APIs <span>createRoot lets you create a root to display React components inside a browser DOM node. hydrateRoot lets you display React components inside a browser DOM node whose HTML content was previously generated by react-dom/server. Browser support React supports all popular brows
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Client React DOM APIs – React
A framework may call them for you. Most of your components don’t need to import or use them. Client APIs createRoot lets you create a root to display React components inside a browser DOM node. <span>hydrateRoot lets you display React components inside a browser DOM node whose HTML content was previously generated by react-dom/server. Browser support React supports all popular browsers, including Internet Explorer 9 and above. Some polyfills are required for older browsers such as IE 9 and IE 10. How do you like thes
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Client React DOM APIs – React
ct components inside a browser DOM node. hydrateRoot lets you display React components inside a browser DOM node whose HTML content was previously generated by react-dom/server. Browser support <span>React supports all popular browsers, including Internet Explorer 9 and above. Some polyfills are required for older browsers such as IE 9 and IE 10. How do you like these docs? Take our survey! ©2023 Learn React Quick Start Installation Describing the UI Adding Interactivity Managing State Escape Hatches API Reference React APIs Rea
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Client React DOM APIs – React
e Hatches REACT API Hooks Components APIs Legacy APIs REACT DOM API Components APIs Client APIs Server APIs GET INVOLVED React Community STAY INFORMED React Blog Is this page useful? React Docs <span>Client React DOM APIs The react-dom/client APIs let you render React components on the client (in the browser). These APIs are typically used at the top level of your app to initialize your React tree. A framework may call them for you. Most of your components don’t need to import or use them. Client APIs createRoot lets you create a root to display React components inside a browser DOM node. hydrateRoot lets you display React components inside a browser DOM node whose HTML c
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Built-in React Hooks – React
eact Hooks Hooks let you use different React features from your components. You can either use the built-in Hooks or combine them to build your own. This page lists all built-in Hooks in React. <span>State Hooks State lets a component “remember” information like user input. For example, a form component can use state to store the input value, while an image gallery component can use state to store the selected image index. To add state to a component, use one of these Hooks: useState declares a state variable that you can update directly. useReducer declares a state variable with the update logic inside a reducer function. function ImageGallery() { const [index, setIndex] = useState(0); // ... Context Hooks Context lets a component receive information from distant parents without passing it as props. For example, your app’s top-level component can pass the current UI theme to
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Built-in React Hooks – React
iable that you can update directly. useReducer declares a state variable with the update logic inside a reducer function. function ImageGallery() { const [index, setIndex] = useState(0); // ... <span>Context Hooks Context lets a component receive information from distant parents without passing it as props. For example, your app’s top-level component can pass the current UI theme to all components below, no matter how deep. useContext reads and subscribes to a context. function Button() { const theme = useContext(ThemeContext); // ... Ref Hooks Refs let a component hold some information that isn’t used for rendering, like a DOM node or a timeout ID. Unlike with state, updating a ref does not re-render your component.
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Built-in React Hooks – React
onent can pass the current UI theme to all components below, no matter how deep. useContext reads and subscribes to a context. function Button() { const theme = useContext(ThemeContext); // ... <span>Ref Hooks Refs let a component hold some information that isn’t used for rendering, like a DOM node or a timeout ID. Unlike with state, updating a ref does not re-render your component. Refs are an “escape hatch” from the React paradigm. They are useful when you need to work with non-React systems, such as the built-in browser APIs. useRef declares a ref. You can hold any value in it, but most often it’s used to hold a DOM node. useImperativeHandle lets you customize the ref exposed by your component. This is rarely used. function Form() { const inputRef = useRef(null); // ... Effect Hooks Effects let a component connect to and synchronize with external systems. This includes dealing with network, browser DOM, animations, widgets written using a different UI
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Built-in React Hooks – React
t most often it’s used to hold a DOM node. useImperativeHandle lets you customize the ref exposed by your component. This is rarely used. function Form() { const inputRef = useRef(null); // ... <span>Effect Hooks Effects let a component connect to and synchronize with external systems. This includes dealing with network, browser DOM, animations, widgets written using a different UI library, and other non-React code. useEffect connects a component to an external system. function ChatRoom({ roomId }) { useEffect(() => { const connection = createConnection(roomId); connection.connect(); return () => connection.disconnect(); }, [roomId]); // ... Effects are an “escape hatch” from the React paradigm. Don’t use Effects to orchestrate the data flow of your application. If you’re not interacting with an external system, you might not need an Effect. There are two rarely used variations of useEffect with differences in timing: useLayoutEffect fires before the browser repaints the screen. You can measure layout here. useInsertionEffect fires before React makes changes to the DOM. Libraries can insert dynamic CSS here. Performance Hooks A common way to optimize re-rendering performance is to skip unnecessary work. For example, you can tell React to reuse a cached calculation or to skip a re-render if
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Built-in React Hooks – React
useLayoutEffect fires before the browser repaints the screen. You can measure layout here. useInsertionEffect fires before React makes changes to the DOM. Libraries can insert dynamic CSS here. <span>Performance Hooks A common way to optimize re-rendering performance is to skip unnecessary work. For example, you can tell React to reuse a cached calculation or to skip a re-render if the data has not changed since the previous render. To skip calculations and unnecessary re-rendering, use one of these Hooks: useMemo lets you cache the result of an expensive calculation. useCallback lets you cache a function definition before passing it down to an optimized component. function TodoList({ todos, tab, theme }) { const visibleTodos = useMemo(() => filterTodos(todos, tab), [todos, tab]); // ... } Sometimes, you can’t skip re-rendering because the screen actually needs to update. In that case, you can improve performance by separating blocking updates that must be synchronous (like typing into an input) from non-blocking updates which don’t need to block the user interface (like updating a chart). To prioritize rendering, use one of these Hooks: useTransition lets you mark a state transition as non-blocking and allow other updates to interrupt it. useDeferredValue lets you defer updating a non-critical part of the UI and let other parts update first. Resource Hooks Resources can be accessed by a component without having them as part of their state. For example, a component can read a message from a Promise or read styling informatio
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Built-in React Hooks – React
ets you mark a state transition as non-blocking and allow other updates to interrupt it. useDeferredValue lets you defer updating a non-critical part of the UI and let other parts update first. <span>Resource Hooks Resources can be accessed by a component without having them as part of their state. For example, a component can read a message from a Promise or read styling information from a context. To read a value from a resource, use this Hook: use lets you read the value of a resource like a Promise or context. function MessageComponent({ messagePromise }) { const message = use(messagePromise); const theme = use(ThemeContext); // ... } Other Hooks These Hooks are mostly useful to library authors and aren’t commonly used in the application code. useDebugValue lets you customize the label React DevTools displays for you
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Built-in React Hooks – React
e lets you read the value of a resource like a Promise or context. function MessageComponent({ messagePromise }) { const message = use(messagePromise); const theme = use(ThemeContext); // ... } <span>Other Hooks These Hooks are mostly useful to library authors and aren’t commonly used in the application code. useDebugValue lets you customize the label React DevTools displays for your custom Hook. useId lets a component associate a unique ID with itself. Typically used with accessibility APIs. useSyncExternalStore lets a component subscribe to an external store. Your own Hooks You can also define your own custom Hooks as JavaScript functions. PreviousOverview Nextuse How do you like these docs? Take our survey! © 2023 Learn React Quick Start In
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Built-in React Hooks – React
ays for your custom Hook. useId lets a component associate a unique ID with itself. Typically used with accessibility APIs. useSyncExternalStore lets a component subscribe to an external store. <span>Your own Hooks You can also define your own custom Hooks as JavaScript functions. PreviousOverview Nextuse How do you like these docs? Take our survey! © 2023 Learn React Quick Start Installation Describing the UI Adding Interactivity Managing State Escape Hatches AP
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Built-in React Components – React
LVED React Community STAY INFORMED React Blog Is this page useful? React Docs Built-in React Components React exposes a few built-in components that you can use in your JSX. Built-in components <span><Fragment>, alternatively written as <>...</>, lets you group multiple JSX nodes together. <Profiler> lets you measure rendering performance of a React tree programmatically. <Suspense> lets you display a fallback while the child components are loading. <Strict
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Built-in React Components – React
exposes a few built-in components that you can use in your JSX. Built-in components <Fragment>, alternatively written as <>...</>, lets you group multiple JSX nodes together. <span><Profiler> lets you measure rendering performance of a React tree programmatically. <Suspense> lets you display a fallback while the child components are loading. <StrictMode> enables extra development-only checks that help you find bugs early. Your own com
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Built-in React Components – React
ragment>, alternatively written as <>...</>, lets you group multiple JSX nodes together. <Profiler> lets you measure rendering performance of a React tree programmatically. <span><Suspense> lets you display a fallback while the child components are loading. <StrictMode> enables extra development-only checks that help you find bugs early. Your own components You can also define your own components as JavaScript functions. How do you l
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Built-in React Components – React
SX nodes together. <Profiler> lets you measure rendering performance of a React tree programmatically. <Suspense> lets you display a fallback while the child components are loading. <span><StrictMode> enables extra development-only checks that help you find bugs early. Your own components You can also define your own components as JavaScript functions. How do you like these docs? Take our survey! ©2023 Learn React Quick Start Installation Describing t
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Built-in React Components – React
<Suspense> lets you display a fallback while the child components are loading. <StrictMode> enables extra development-only checks that help you find bugs early. Your own components <span>You can also define your own components as JavaScript functions. How do you like these docs? Take our survey! ©2023 Learn React Quick Start Installation Describing the UI Adding Interactivity Managing State Escape Hatches API Reference React APIs Rea
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Tutorial: Get started with Go - The Go Programming Language
For example, the module path might be github.com/mymodule. If you plan to publish your module for others to use, the module path must be a location from which Go tools can download your module. <span>For more about naming a module with a module path, see Managing dependencies. For the purposes of this tutorial, just use example/hello. $ go mod init example/hello go: creating new go.mod: module example/hello In your text editor, create a file hello.go in which
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Tutorial: Get started with Go - The Go Programming Language
rite some simple "Hello, world" code. Use the go command to run your code. Use the Go package discovery tool to find packages you can use in your own code. Call functions of an external module. <span>Note: For other tutorials, see Tutorials. Prerequisites Some programming experience. The code here is pretty simple, but it helps to know something about functions. A tool to edit your code. Any text editor you have will work f
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Tutorial: Get started with Go - The Go Programming Language
, World!") } This is your Go code. In this code, you: Declare a main package (a package is a way to group functions, and it's made up of all the files in the same directory). Import the popular <span>fmt package, which contains functions for formatting text, including printing to the console. This package is one of the standard library packages you got when you installed Go. Implement a main fu
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Tutorial: Get started with Go - The Go Programming Language
it's made up of all the files in the same directory). Import the popular fmt package, which contains functions for formatting text, including printing to the console. This package is one of the <span>standard library packages you got when you installed Go. Implement a main function to print a message to the console. A main function executes by default when you run the main package. Run your code to see the g
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Tutorial: Get started with Go - The Go Programming Language
. Implement a main function to print a message to the console. A main function executes by default when you run the main package. Run your code to see the greeting. $ go run . Hello, World! The <span>go run command is one of many go commands you'll use to get things done with Go. Use the following command to get a list of the others: $ go help Call code in an external package When you need your co
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Tutorial: Get started with Go - The Go Programming Language
ecutes by default when you run the main package. Run your code to see the greeting. $ go run . Hello, World! The go run command is one of many go commands you'll use to get things done with Go. <span>Use the following command to get a list of the others: $ go help Call code in an external package When you need your code to do something that might have been implemented by someone else, you can look for a package that has functions you can use in y
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Introduction - Anki Manual
iles 19. Statistics 20. Media 21. Math & Symbols 22. Leeches 23. Add-ons 24. Troubleshooting 25. Sync Server 26. Miscellaneous Contributing FAQs Resources Light (default) Rust Coal Navy Ayu <span>Anki Manual Introduction Quickstart In a hurry? Jump straight to Getting Started. Getting Help Looking for help? Please see Getting Help. Translations Volunteers have contributed translations of th
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |