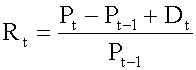Edited, memorised or added to reading queue
on 18-Dec-2018 (Tue)
Do you want BuboFlash to help you learning these things? Click here to log in or create user.
Flashcard 1464617798924
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itChapter 9. How to deflect and roll with the punches.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1480013778188
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1603697511692
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1621034405132
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 3. Cash Flow Statement Analysis
CFO. CFO does not include cash outlays for replacing old equipment. Free Cash Flow (FCF) is intended to measure the cash available to a company for discretionary uses after making all required cash outlays. <span>It accounts for capital expenditures and dividend payments, which are essential to the ongoing nature of the business. The basic definition is cash from operations less the amount of capital expenditures required to maintain the company's present productive capacity. &#
Flashcard 1621041483020
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 3. Cash Flow Statement Analysis
3; The basic definition is cash from operations less the amount of capital expenditures required to maintain the company's present productive capacity. Free cash flow = CFO - capital expenditure <span>Free Cash Flow to the Firm (FCFF): Cash available to shareholders and bondholders after taxes, capital investment, and WC investment. FCFF = NI + NCC + Int (1 - Tax rate) - FCInv - WCInv NI: Net income available to common shareholders. It is the com
Flashcard 1621274529036
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 3. Cash Flow Statement Analysis
; Free cash flow = CFO - capital expenditure Free Cash Flow to the Firm (FCFF): Cash available to shareholders and bondholders after taxes, capital investment, and WC investment. <span>FCFF = NI + NCC + Int (1 - Tax rate) - FCInv - WCInv NI: Net income available to common shareholders. It is the company's earnings after interest, taxes and preferred dividends. NCC: Net non-cash
Flashcard 1621276364044
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 3. Cash Flow Statement Analysis
; Free cash flow = CFO - capital expenditure Free Cash Flow to the Firm (FCFF): Cash available to shareholders and bondholders after taxes, capital investment, and WC investment. <span>FCFF = NI + NCC + Int (1 - Tax rate) - FCInv - WCInv NI: Net income available to common shareholders. It is the company's earnings after interest, taxes and preferred dividends. NCC: Net non-cash
Flashcard 1621291830540
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 1 Time Value of Money and Interest Rates
The time value of money (TVM) refers to the fact that $1 today is worth more than $1 in the future. This is because the $1 today can be invested to earn interest immediately. The TVM reflects the relationship between present value, future value, time, and interest rate. The time value of money underlies rates of return, interest rates, required rates of retu
Flashcard 1621294189836
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 1 Time Value of Money and Interest Rates
The time value of money (TVM) refers to the fact that $1 today is worth more than $1 in the future. This is because the $1 today can be invested to earn interest immediately. The TVM reflects the relationship between present value, future value, time, and interest rate. The time value of money underlies rates of return, interest rates, required rates of return, discount rates, opportunity costs, inflation, and risk. It reflects the relationship between
Flashcard 1621296549132
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 1 Time Value of Money and Interest Rates
interest rate. The time value of money underlies rates of return, interest rates, required rates of return, discount rates, opportunity costs, inflation, and risk. It reflects the relationship between time, cash flow, and interest rate. <span>There are three ways to interpret interest rates: Required rate of return is the return required by investors or lenders to postpone their current consumption. Discount rate is the rate used to discount future cash flows
Flashcard 1621298908428
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 1 Time Value of Money and Interest Rates
n, interest rates, required rates of return, discount rates, opportunity costs, inflation, and risk. It reflects the relationship between time, cash flow, and interest rate. There are three ways to interpret interest rates: <span>Required rate of return is the return required by investors or lenders to postpone their current consumption. Discount rate is the rate used to discount future cash flows to allow for the time value of money (that is, to bring a future value equivalent to present value). Opportunity cost is the
Flashcard 1621303627020
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 1 Time Value of Money and Interest Rates
e return required by investors or lenders to postpone their current consumption. Discount rate is the rate used to discount future cash flows to allow for the time value of money (that is, to bring a future value equivalent to present value). <span>Opportunity cost is the most valuable alternative investors give up when they choose what to do with money. In a certain world, the interest rate is called the risk-free rate. For investors preferring current to future consumption, the risk-free interest rate is the rate of compensation
Flashcard 1621308345612
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 1 Time Value of Money and Interest Rates
licate interest rates: Inflation: When prices are expected to increase, lenders charge not only an opportunity cost for postponing consumption but also an inflation premium that takes into account the expected increase in prices. <span>The nominal cost of money consists of the real rate (a pure rate of interest) and an inflation premium. Risk: Companies exhibit varying degrees of uncertainty concerning their ability to repay lenders. Lenders therefore charge interest rates that incorporate default
Flashcard 1621317782796
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 1 Time Value of Money and Interest Rates
nominal risk-free rate (real rate + an inflation premium) and a default risk premium. Compounding is the process of accumulating interest over a period of time. A compounding period is the number of times per year that interest is paid. <span>Continuous compounding occurs when the number of compounding periods becomes infinite; interest is added continuously. Discounting is the calculation of the present value of some known future value. Discount rate is the rate used to calculate the present value of some future cash flow. Disco
Flashcard 1621322501388
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 1 Time Value of Money and Interest Rates
per year that interest is paid. Continuous compounding occurs when the number of compounding periods becomes infinite; interest is added continuously. Discounting is the calculation of the present value of some known future value. <span>Discount rate is the rate used to calculate the present value of some future cash flow. Discounted cash flow is the present value of some future cash flow. <span><body><html>
Flashcard 1621324860684
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 1 Time Value of Money and Interest Rates
ding periods becomes infinite; interest is added continuously. Discounting is the calculation of the present value of some known future value. Discount rate is the rate used to calculate the present value of some future cash flow. <span>Discounted cash flow is the present value of some future cash flow. <span><body><html>
Flashcard 1621957676300
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 1 Time Value of Money and Interest Rates
licate interest rates: Inflation: When prices are expected to increase, lenders charge not only an opportunity cost for postponing consumption but also an inflation premium that takes into account the expected increase in prices. <span>The nominal cost of money consists of the real rate (a pure rate of interest) and an inflation premium. Risk: Companies exhibit varying degrees of uncertainty concerning their ability to repay lenders. Lenders therefore charge interest rates that incorporate default
Flashcard 1622917909772
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1622919744780
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1622922366220
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1622938619148
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1622941502732
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1622943337740
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1623556754700
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1623560424716
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1623792160012
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1623807888652
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1623815228684
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1623818636556
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1623824403724
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1623830695180
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1623834103052
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1623849307404
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1624281058572
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1624283155724
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1624287350028
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1624656448780
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1624658283788
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1624660380940
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1626637208844
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 1. NPV and IRR
le. Reinvestment The IRR is intended to provide a single number that represents the rate of return generated by a capital investment. As such, it is an easy number to interpret and understand. However, calculation of <span>the IRR assumes that all project cash flows can be reinvested to earn a rate of return exactly equal to the IRR itself. In other words, a project with an IRR of 6% assumes that all cash flows can be reinvested to earn exactly 6%. If the cash flows are invested at a rate lower than 6%, the realized return
Flashcard 1626644286732
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 1. NPV and IRR
usive projects of greatly differing scale: one that requires a relatively small investment and returns relatively small cash flows, and another that requires a much larger investment and returns much larger cash flows. <span>Timing The other situation in which IRR is likely to contradict NPV is when there are two mutually-exclusive projects whose cash flows are timed very differently: one that receives its
Flashcard 1626650053900
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 2. Holding Period Return
When analyzing rates of return, our starting point is the total return, or holding period return (HPR). HPR measures the total return for holding an investment over a certain period of time, and can be calculated using the following formula:
Flashcard 1626652413196
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 2. Holding Period Return
When analyzing rates of return, our starting point is the total return, or holding period return (HPR). HPR measures the total return for holding an investment over a certain period of time, and can be calculated using the following formula:
Flashcard 1626654772492
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 2. Holding Period Return
When analyzing rates of return, our starting point is the total return, or holding period return (HPR). HPR measures the total return for holding an investment over a certain period of time, and can be calculated using the following formula: P t = price per share at the end of time period t P (t-1) = price per share at the
Flashcard 1626657131788
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 2. Holding Period Return
When analyzing rates of return, our starting point is the total return, or holding period return (HPR). HPR measures the total return for holding an investment over a certain period of time, and can be calculated using the following formula: P t = price per share at the end of time period t P (t-1) = price per share at the end of time period t-1, the time period immediately
Flashcard 1631884021004
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 3. Dollar-weighted and Time-weighted Rates of Return
The dollar-weighted rate of return is essentially the internal rate of return (IRR) on a portfolio. This approach considers the timing and amountof cash flows. It is affected by the timing of cash flows. If funds are added to a portfolio when the portfolio is performing well (poorly),
Flashcard 1631928585484
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 3. Dollar-weighted and Time-weighted Rates of Return
rs the timing and amountof cash flows. It is affected by the timing of cash flows. If funds are added to a portfolio when the portfolio is performing well (poorly), the dollar-weighted rate of return will be inflated (depressed). <span>The time-weighted rate of return measures the compound growth rate of $1 initial investment over the measurement period. Time-weightedmeans that returns are averaged over time. This approach is not affected by the timing of cash flows; therefore, it is the preferred method of performance measurement. 
Flashcard 1632046812428
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 3. Dollar-weighted and Time-weighted Rates of Return
For the second year, HPR 2 : (280 + 20)/300 - 1 = 0. Calculate the time-weighted rate of return: If the measurement period < 1 year, compound holding period returns to get an annualized rate of return for the year. <span>If the measurement period > 1 year, take the geometric mean of the annual returns. <span><body><html>
Flashcard 1632835865868
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 4. Different Yield Measures of a U.S. Treasury Bill
unt basis D = the dollar discount, which is equal to the difference between the face value of the bill, F, and its purchase price, P t = the number of days remaining to maturity 360 = the bank convention of the number of days in a year. <span>Bank discount yield is not a meaningful measure of the return on investment because: It is based on the face value, not on the purchase price. Instead, return on investment should be measured based on cost of investment. It is annualized using a 360-day year, not a 365-day year. It annualizes with simple interest and ignores the effect of interest on interest (compound interest). Holding period yield (HPY) is the return earned by an investor if the money market instrument is held until maturity: P 0 =
Flashcard 1632864439564
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 4. Different Yield Measures of a U.S. Treasury Bill
unt basis D = the dollar discount, which is equal to the difference between the face value of the bill, F, and its purchase price, P t = the number of days remaining to maturity 360 = the bank convention of the number of days in a year. <span>Bank discount yield is not a meaningful measure of the return on investment because: It is based on the face value, not on the purchase price. Instead, return on investment should be measured based on cost of investment. It is annualized using a 360-day year, not a 365-day year. It annualizes with simple interest and ignores the effect of interest on interest (compound interest). Holding period yield (HPY) is the return earned by an investor if the money market instrument is held until maturity: P 0 =
Flashcard 1632883051788
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 4. Different Yield Measures of a U.S. Treasury Bill
unt basis D = the dollar discount, which is equal to the difference between the face value of the bill, F, and its purchase price, P t = the number of days remaining to maturity 360 = the bank convention of the number of days in a year. <span>Bank discount yield is not a meaningful measure of the return on investment because: It is based on the face value, not on the purchase price. Instead, return on investment should be measured based on cost of investment. It is annualized using a 360-day year, not a 365-day year. It annualizes with simple interest and ignores the effect of interest on interest (compound interest). Holding period yield (HPY) is the return earned by an investor if the money market instrument is held until maturity: P 0 =
Flashcard 1633376668940
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 4. Different Yield Measures of a U.S. Treasury Bill
990. Bank discount yield: (1000 - 990)/1000 x 360/60 = 6% Holding period yield: (1000 - 990)/990 = 1.0101% Effective annual yield: (1 + 1.0101%) 365/60 - 1 = 6.3047% Money market yield: (360 x 6%)/(360 - 60 x 6%) = 6.0606% <span>If we know HPY, then: EAY = (1 + HPY) 365/t - 1 r MM = HPY x 360/t If we know EAY, then: HPY = ( 1 + EAY) t/365 - 1 r MM = [(1 + EAY) t/365 - 1] x (360/t) If we know r MM , then: HPY = r MM x (t/360) EAY = (1 + r
Flashcard 1633419398412
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 4. Different Yield Measures of a U.S. Treasury Bill
ld: (360 x 6%)/(360 - 60 x 6%) = 6.0606% If we know HPY, then: EAY = (1 + HPY) 365/t - 1 r MM = HPY x 360/t If we know EAY, then: HPY = ( 1 + EAY) t/365 - 1 r MM = [(1 + EAY) t/365 - 1] x (360/t) <span>If we know r MM , then: HPY = r MM x (t/360) EAY = (1 + r MM x t/360) 365/t - 1 <span><body><html>
Flashcard 1634082884876
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 5. Bond Equivalent Yield
Periodic bond yields for both straight and zero-coupon bonds are conventionally computed based on semi-annual periods, as U.S. bonds typically make two coupon payments per year. For example, a zero-coupon bond with a maturity of five years will mature in 10 6-month periods. The periodic yield for that bond, r, is indicated by the equation Price = Maturity value
Flashcard 1634085244172
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 5. Bond Equivalent Yield
y. This method ignores the effect of compounding semi-annual YTM, and the YTM calculated in this way is called a bond-equivalent yield (BEY). However, yields of a semi-annual-pay and an annual-pay bond cannot be compared directly <span>without conversion. This conversion can be done in one of the two ways: Convert the bond-equivalent yield of a semi-annual-pay bond to an annual-pay bond.
Flashcard 1634645445900
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 4. Different Yield Measures of a U.S. Treasury Bill
#13; Since a pure discount instrument (e.g., a T-bill) makes no interest payment, its HPY is (P 1 - P 0 )/P 0 . Note that HPY is computed on the basis of purchase price, not face value. It is not an annualized yield. <span>The effective annual yield is the annualized HPY on the basis of a 365-day year. It incorporates the effect of compounding interest. Money market yield (also known as CD equivalent yield) is the annualized HPY on the basis of
Flashcard 1635073789196
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itThe money-weighted rate of return has a serious drawback. Generally, clients determine when money is given to the investment manager and those decisions may significantly influence the money-weighted rate of return .
Original toplevel document
Open itThe money-weighted rate of return has a serious drawback. Generally, clients determine when money is given to the investment manager and those decisions may significantly influence the money-weighted rate of return . A general principle of evaluation, however, is that a person or entity should be judged only on the basis of their own actions, or actions under their control. An evaluation tool should
Flashcard 1635080604940
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Open it
where the returns are centered (central tendency); how far returns are dispersed from their center (dispersion); whether the distribution of returns is symmetrically shaped or lopsided (skewness); and 
Flashcard 1635085585676
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Open it
where the returns are centered (central tendency); how far returns are dispersed from their center (dispersion); whether the distribution of returns is symmetrically shaped or lopsided (skewness); and whether extreme outcomes are likely (kurtosis).
Flashcard 1635088469260
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1635091352844
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1635094236428
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1635096071436
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1635097906444
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1635101576460
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1635103411468
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1635110751500
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1635112586508
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1635118091532
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1635119926540
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1635128315148
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1635134344460
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1635138014476
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1635139849484
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1635149286668
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1635152956684
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1635156626700
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1635158461708
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1636296166668
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 4. Different Yield Measures of a U.S. Treasury Bill
unt basis D = the dollar discount, which is equal to the difference between the face value of the bill, F, and its purchase price, P t = the number of days remaining to maturity 360 = the bank convention of the number of days in a year. <span>Bank discount yield is not a meaningful measure of the return on investment because: It is based on the face value, not on the purchase price. Instead, return on investment should be measured based on cost of investment. It is annualized using a 360-day year, not a 365-day year. It annualizes with simple interest and ignores the effect of interest on interest (compound interest). Holding period yield (HPY) is the return earned by an investor if the money market instrument is held until maturity: P 0 =
Flashcard 1636857941260
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1636859776268
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1636866067724
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1636869999884
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1636879174924
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1636948905228
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1637148134668
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1637161766156
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1637196893452
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1637206592780
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1637210524940
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1637214457100
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1637258759436
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1637266099468
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1637269769484
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1637564157196
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Odds
y’s EPS for FY2014 beating $0.69 are 1 to 7 means that the speaker believes the probability of the event is 1/(1 + 7) = 1/8 = 0.125. Odds against E = [1 − P(E)]/P(E), the reciprocal of odds for E. <span>Given odds against E of “a to b,” the implied probability of E is b/(a + b). The statement that the odds against the company’s EPS for FY2014 beating $0.69 are 15 to 1 is consistent with a belief that the probability of the event is
Flashcard 1637588798732
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 4. Different Yield Measures of a U.S. Treasury Bill
se price, not face value. It is not an annualized yield. The effective annual yield is the annualized HPY on the basis of a 365-day year. It incorporates the effect of compounding interest. <span>Money market yield (also known as CD equivalent yield) is the annualized HPY on the basis of a 360-day year using simple interest. Example An investor buys a $1,000 face-value T-bill due in 60 days at a price of $990. Bank discount yield: (1000 - 990
Flashcard 1637678451980
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1640988544268
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1641040448780
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1644831837452
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1644833672460
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1644835769612
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1644840488204
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1644842585356
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1644844682508
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1644847041804
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1644849401100
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1644851236108
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1644853071116
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1644864605452
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1644869061900
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1644872731916
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1644876664076
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1644878761228
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1644886363404
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1644888198412
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1644892130572
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1644904975628
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1644908907788
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1644920442124
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1644922277132
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1644924898572
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1644926733580
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1644928830732
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1644932500748
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1644934860044
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1644936695052
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1644938530060
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1645005114636
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1645231082764
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
https://www.google.com.mx/search?q=sample%2Bspace%2Bprobability&rlz=1C5CHFA_enMX588MX588&oq=sample%2Bspace%2Bproba&aqs=chrome.0.0j69i57j0l4.4172j0j1&sourceid=chrome&ie=UTF-8
t":"Math Goodies","th":98,"tu":"https://encrypted-tbn0.gstatic.com/images?q\u003dtbn:ANd9GcQcW8yGVex34TZK0u33zmGPrJUYi4Sw9vz1DI4e1YYbbQn3bEVPNVAGcXN2","tw":216} In probability theory, <span>the sample space of an experiment or random trial is the set of all possible outcomes or results of that experiment. A sample space is usually denoted using set notation, and the possible ordered outcomes are listed as elements in the set. Sample space - Wikipedia https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sam
t":"Math Goodies","th":98,"tu":"https://encrypted-tbn0.gstatic.com/images?q\u003dtbn:ANd9GcQcW8yGVex34TZK0u33zmGPrJUYi4Sw9vz1DI4e1YYbbQn3bEVPNVAGcXN2","tw":216} In probability theory, <span>the sample space of an experiment or random trial is the set of all possible outcomes or results of that experiment. A sample space is usually denoted using set notation, and the possible ordered outcomes are listed as elements in the set. Sample space - Wikipedia https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sam
Flashcard 1645290851596
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 2. Unconditional, Conditional, and Joint Probabilities
The complement of event A is the event that A does not occur. It is expressed as A c . The probabilities of an event and its complement must have a sum of 1: P(A) + P(A c ) = 1. Note that event A and its complement, A c , are mutually exclusive (t
The complement of event A is the event that A does not occur. It is expressed as A c . The probabilities of an event and its complement must have a sum of 1: P(A) + P(A c ) = 1. Note that event A and its complement, A c , are mutually exclusive (t
Flashcard 1645293210892
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 2. Unconditional, Conditional, and Joint Probabilities
The complement of event A is the event that A does not occur. It is expressed as A c . The probabilities of an event and its complement must have a sum of 1: P(A) + P(A c ) = 1. Note that event A and its complement, A c , are mutually exclusive (there is no overlapping
The complement of event A is the event that A does not occur. It is expressed as A c . The probabilities of an event and its complement must have a sum of 1: P(A) + P(A c ) = 1. Note that event A and its complement, A c , are mutually exclusive (there is no overlapping
Flashcard 1645890637068
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 3. Addition Rule for Probabilities: the Probability that at Least One of Two Events Will Occur
P(A or B) = P(A) + P(B) - P(AB) The logic behind this formula is that when P(A) and P(B) are added, the occasions on which A and B both occur are counted twice. To adjust for this, P(AB) is subtracted. <span>If events A and B are mutually exclusive, the joint probability of A and B is 0. Consequently, the probability that either A or B occurs is simply the sum of the unconditional probabilities of A and B: P (A or B) = P(A) + P(B). What is the probability t
P(A or B) = P(A) + P(B) - P(AB) The logic behind this formula is that when P(A) and P(B) are added, the occasions on which A and B both occur are counted twice. To adjust for this, P(AB) is subtracted. <span>If events A and B are mutually exclusive, the joint probability of A and B is 0. Consequently, the probability that either A or B occurs is simply the sum of the unconditional probabilities of A and B: P (A or B) = P(A) + P(B). What is the probability t
Flashcard 1645902433548
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 4. Multiplication Rule for Independent Events
Two events, A and B, are independent if and only if P(A|B) = P(A), or equivalently, P(B|A) = P(B). That is, the occurrence of one event has no influence on the probability of the occurrence of the other event. In more detail, whether or not B occurs will have no effect on
Two events, A and B, are independent if and only if P(A|B) = P(A), or equivalently, P(B|A) = P(B). That is, the occurrence of one event has no influence on the probability of the occurrence of the other event. In more detail, whether or not B occurs will have no effect on
Flashcard 1645915016460
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 4. Multiplication Rule for Independent Events
nd B both occur is: P(A and B) = P(A) x P(B) In other words, the probability of A and B both occurring is the product of the probability of A and the probability of B. This relationship is known as the <span>multiplication rule for independent events. What is the probability that a fair coin will come up with heads twice in a row? Two events must occur: heads on the first toss and heads on the second toss. Since the prob
nd B both occur is: P(A and B) = P(A) x P(B) In other words, the probability of A and B both occurring is the product of the probability of A and the probability of B. This relationship is known as the <span>multiplication rule for independent events. What is the probability that a fair coin will come up with heads twice in a row? Two events must occur: heads on the first toss and heads on the second toss. Since the prob
Flashcard 1645917375756
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 4. Multiplication Rule for Independent Events
in the deck, the probability of the first event is 1/52. Since 13/52 = 1/4 of the deck is composed of clubs, the probability of the second event is 1/4. Therefore, the probability of both events is: 1/52 x 1/4 = 1/208. Similarly, <span>for any number of independent events E 1 , E 2 .....E n , the probability that all of them occur is: P(E 1 and E 2 ..... and E n ) = P(E 1 ) x P(E 2 ) x ..... x P(E n ) Example In a bullish market, three shares, chosen from different sectors of the market, have probabilities of 0.6, 0.5 and 0.8 that their share prices will ris
in the deck, the probability of the first event is 1/52. Since 13/52 = 1/4 of the deck is composed of clubs, the probability of the second event is 1/4. Therefore, the probability of both events is: 1/52 x 1/4 = 1/208. Similarly, <span>for any number of independent events E 1 , E 2 .....E n , the probability that all of them occur is: P(E 1 and E 2 ..... and E n ) = P(E 1 ) x P(E 2 ) x ..... x P(E n ) Example In a bullish market, three shares, chosen from different sectors of the market, have probabilities of 0.6, 0.5 and 0.8 that their share prices will ris
Flashcard 1645930220812
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 5. The Total Probability Rule
If we have an event or scenario S, the event not-S, called the complement of S, is written S C . Note that P(S) + P(S C ) = 1, as either S or not-S must occur. The total probability rule explains the unconditional probability of an event in terms of probabilities conditional on the scenarios. P(A) = P(A|S)P(S) + P(A|S C )P(S C ) P(A) = P(A|S 1 )P(S 1 ) + P(A|S 2 )P(S 2 ) + ... + P(A|S n )P(S n ) The first equation is just a special case of the secon
If we have an event or scenario S, the event not-S, called the complement of S, is written S C . Note that P(S) + P(S C ) = 1, as either S or not-S must occur. The total probability rule explains the unconditional probability of an event in terms of probabilities conditional on the scenarios. P(A) = P(A|S)P(S) + P(A|S C )P(S C ) P(A) = P(A|S 1 )P(S 1 ) + P(A|S 2 )P(S 2 ) + ... + P(A|S n )P(S n ) The first equation is just a special case of the secon
Flashcard 1646448479500
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 6. Expected Value, Variance, and Standard Deviation of a Random Variable
40,000 + 24,000 + 0 = $64,000 Thus, the organizers can expect to take in $64,000. Since it costs $50,000 to stage the event, this translates to a profit of $14,000, so they should certainly go ahead with the venture. <span>It's important to realize that none of the outcomes actually produces an amount of $64,000. This is simply the weighted average of all possible outcomes. Although there is a 50% chance of a loss the big profit that will be made the remaining 50% of the time more than offsets t
40,000 + 24,000 + 0 = $64,000 Thus, the organizers can expect to take in $64,000. Since it costs $50,000 to stage the event, this translates to a profit of $14,000, so they should certainly go ahead with the venture. <span>It's important to realize that none of the outcomes actually produces an amount of $64,000. This is simply the weighted average of all possible outcomes. Although there is a 50% chance of a loss the big profit that will be made the remaining 50% of the time more than offsets t
Flashcard 1646652427532
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itIf we have two events, A and B, that we are interested in, we often want to know the probability that either A or B occurs. Note the use of the word "or," the key to this rule. The "or" is what we call an "inclusive or." In other words, either one event can occur or both events can occur.
Original toplevel document
Subject 3. Addition Rule for Probabilities: the Probability that at Least One of Two Events Will OccurIf we have two events, A and B, that we are interested in, we often want to know the probability that either A or B occurs. Note the use of the word "or," the key to this rule. The "or" is what we call an "inclusive or." In other words, either one event can occur or both events can occur. Such probabilities are calculated using the addition rule for probabilities. P(A or B) = P(A) + P(B) - P(AB) The logic behind this f
Flashcard 1646894386444
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 7. Covariance and Correlation
Facts about covariance: Covariance of returns is negative if, when the return on one asset is above its expected value, the return on the other asset is below its expected value (an average inverse relationship between returns). <span>Covariance of returns is 0 if returns on the assets are unrelated. Covariance of returns is positive if, when the return on one asset is above its expected value, the return on the other asset is above its expected value (an average positive relationsh
Facts about covariance: Covariance of returns is negative if, when the return on one asset is above its expected value, the return on the other asset is below its expected value (an average inverse relationship between returns). <span>Covariance of returns is 0 if returns on the assets are unrelated. Covariance of returns is positive if, when the return on one asset is above its expected value, the return on the other asset is above its expected value (an average positive relationsh
Flashcard 1646896745740
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 7. Covariance and Correlation
tive if, when the return on one asset is above its expected value, the return on the other asset is below its expected value (an average inverse relationship between returns). Covariance of returns is 0 if returns on the assets are unrelated. <span>Covariance of returns is positive if, when the return on one asset is above its expected value, the return on the other asset is above its expected value (an average positive relationship between returns). The covariance of a random variable with itself (own covariance) is its own variance. Example Suppose that the future short-term outlook for the economy is favorable w
tive if, when the return on one asset is above its expected value, the return on the other asset is below its expected value (an average inverse relationship between returns). Covariance of returns is 0 if returns on the assets are unrelated. <span>Covariance of returns is positive if, when the return on one asset is above its expected value, the return on the other asset is above its expected value (an average positive relationship between returns). The covariance of a random variable with itself (own covariance) is its own variance. Example Suppose that the future short-term outlook for the economy is favorable w
Flashcard 1646899105036
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 7. Covariance and Correlation
returns on the assets are unrelated. Covariance of returns is positive if, when the return on one asset is above its expected value, the return on the other asset is above its expected value (an average positive relationship between returns). <span>The covariance of a random variable with itself (own covariance) is its own variance. Example Suppose that the future short-term outlook for the economy is favorable with a probability 0.6 and unfavorable with a probability of 0.4. For two stocks, F and
returns on the assets are unrelated. Covariance of returns is positive if, when the return on one asset is above its expected value, the return on the other asset is above its expected value (an average positive relationship between returns). <span>The covariance of a random variable with itself (own covariance) is its own variance. Example Suppose that the future short-term outlook for the economy is favorable with a probability 0.6 and unfavorable with a probability of 0.4. For two stocks, F and
Flashcard 1646905396492
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 7. Covariance and Correlation
where. The correlation between two random variables, R i and R j , is defined as: Alternative notations are corr(R i , R j ) and ρ ij . Properties of correlation: <span>Correlation is a number between -1 and +1. A correlation of 0 indicates an absence of any linear (straight-line) relationship between the variables. Increasingly positive correlation indicates an increasingly strong positive lin
where. The correlation between two random variables, R i and R j , is defined as: Alternative notations are corr(R i , R j ) and ρ ij . Properties of correlation: <span>Correlation is a number between -1 and +1. A correlation of 0 indicates an absence of any linear (straight-line) relationship between the variables. Increasingly positive correlation indicates an increasingly strong positive lin
Flashcard 1646907755788
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 7. Covariance and Correlation
two random variables, R i and R j , is defined as: Alternative notations are corr(R i , R j ) and ρ ij . Properties of correlation: Correlation is a number between -1 and +1. <span>A correlation of 0 indicates an absence of any linear (straight-line) relationship between the variables. Increasingly positive correlation indicates an increasingly strong positive linear relationship (up to 1, which indicates a perfect linear relationship). Increasingly negative correlati
two random variables, R i and R j , is defined as: Alternative notations are corr(R i , R j ) and ρ ij . Properties of correlation: Correlation is a number between -1 and +1. <span>A correlation of 0 indicates an absence of any linear (straight-line) relationship between the variables. Increasingly positive correlation indicates an increasingly strong positive linear relationship (up to 1, which indicates a perfect linear relationship). Increasingly negative correlati
Flashcard 1646910115084
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 7. Covariance and Correlation
otations are corr(R i , R j ) and ρ ij . Properties of correlation: Correlation is a number between -1 and +1. A correlation of 0 indicates an absence of any linear (straight-line) relationship between the variables. <span>Increasingly positive correlation indicates an increasingly strong positive linear relationship (up to 1, which indicates a perfect linear relationship). Increasingly negative correlation indicates an increasingly strong negative linear relationship (down to -1, which indicates a perfect inverse linear relationship). The correlati
otations are corr(R i , R j ) and ρ ij . Properties of correlation: Correlation is a number between -1 and +1. A correlation of 0 indicates an absence of any linear (straight-line) relationship between the variables. <span>Increasingly positive correlation indicates an increasingly strong positive linear relationship (up to 1, which indicates a perfect linear relationship). Increasingly negative correlation indicates an increasingly strong negative linear relationship (down to -1, which indicates a perfect inverse linear relationship). The correlati
Flashcard 1646945766668
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1647708343564
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1647713848588
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1647723810060
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1647743470860
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1647772044556
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1647782792460
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1647821851916
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1647829191948
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1647852522764
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1648670936332
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1648900574476
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1648906341644
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1648995994892
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1652129402124
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 10. Principles of Counting
(The combination formula, or the binomial formula): For example, if you select two of the ten stocks you are analyzing, how many ways can you select the stocks? 10! / [(10 - 2)! x 2!] = 45. <span>An ordered listing is known as a permutation, and the formula that counts the number of permutations is known as the permutation formula. The number of ways that we can choose r objects from a total of n objects, where the order i
(The combination formula, or the binomial formula): For example, if you select two of the ten stocks you are analyzing, how many ways can you select the stocks? 10! / [(10 - 2)! x 2!] = 45. <span>An ordered listing is known as a permutation, and the formula that counts the number of permutations is known as the permutation formula. The number of ways that we can choose r objects from a total of n objects, where the order i
Flashcard 1652316048652
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itRegarding counting, there can never be more combinations than permutations for the same problem, because permutations take into account all possible orderings of items, whereas combinations do not.
Original toplevel document
Subject 10. Principles of Countinghe ten stocks you are analyzing and invest $10,000 in one stock and $20,000 in another stock, how many ways can you select the stocks? Note that the order of your selection is important in this case. 10 P 2 = 10!/(10 - 2)! = 90 <span>Note that there can never be more combinations than permutations for the same problem, because permutations take into account all possible orderings of items, whereas combinations do not. <span><body><html>
Flashcard 1652332039436
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Open it
the covariance between two random variables is the probability-weighted average of the cross-products of each random variable’s deviation from its own expected value.
Flashcard 1652360350988
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Open it
l>In analyses of probabilities presented in tables, unconditional probabilities usually appear at the ends or margins of the table, hence the term marginal probability. Because of possible confusion with the way marginal is used in economics (roughly meaning incremental), we use the term unconditional probability throughout this discussion.<html>
Flashcard 1652366642444
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Open it
If we know both the set of all the distinct possible outcomes of a random variable and the assignment of probabilities to those outcomes—the probability distribution of the random variable—we have a complete description of the random variable, and we can assign a probability to any event that we might describe
Flashcard 1652376866060
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Multinominal formula
A mutual fund guide ranked 18 bond mutual funds by total returns for the year 2014. The guide also assigned each fund one of five risk labels: high risk (four funds), above-average risk (four funds), average risk (t
Flashcard 3663972142348
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |