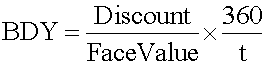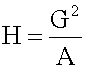Edited, memorised or added to reading queue
on 07-Aug-2017 (Mon)
Do you want BuboFlash to help you learning these things? Click here to log in or create user.
Flashcard 1438338125068
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open it#13; Future cash flows represented by negative externalities occur regardless of the project, so they are non-incremental. Such cash flows represent a transfer from existing projects to new projects, and thus should be <span>subtracted from the new projects' cash flows.<span><body><html>
Original toplevel document
Subject 2. Basic Principles of Capital Budgetingd in the estimated cash flows since the effects of debt financing are reflected in the cost of capital used to discount the cash flows. The existence of a project depends on business factors, not financing. <span>Important capital budgeting concepts: A sunk cost is a cash outlay that has already been incurred and which cannot be recovered regardless of whether a project is accepted or rejected. Since sunk costs are not increment costs, they should not be included in the capital budgeting analysis. For example, a small bookstore is considering opening a coffee shop within its store, which will generate an annual net cash outflow of $10,000 from selling coffee. That is, the coffee shop will always be losing money. In the previous year, the bookstore spent $5,000 to hire a consultant to perform an analysis. This $5,000 consulting fee is a sunk cost; whether the coffee shop is opened or not, the $5,000 is spent. Incremental cash flow is the net cash flow attributable to an investment project. It represents the change in the firm's total cash flow that occurs as a direct result of accepting the project. Forget sunk costs. Subtract opportunity costs. Consider side effects on other parts of the firm: externalities and cannibalization. Recognize the investment and recovery of net working capital. Opportunity cost is the return on the best alternative use of an asset or the highest return that will not be earned if funds are invested in a particular project. For example, to continue with the bookstore example, the space to be occupied by the coffee shop is an opportunity cost - it could be used to sell books and generate a $5,000 annual net cash inflow. Externalities are the effects of a project on cash flows in other parts of a firm. Although they are difficult to quantify, they should be considered. Externalities can be either positive or negative: Positive externalities create benefits for other parts of the firm. For example, the coffee shop may generate some additional customers for the bookstore (who otherwise may not buy books there). Future cash flows generated by positive externalities occur with the project and do not occur without the project, so they are incremental. Negative externalities create costs for other parts of the firm. For example, if the bookstore is considering opening a branch two blocks away, some customers who buy books at the old store will switch to the new branch. The customers lost by the old store are a negative externality. The primary type of negative externality is cannibalization, which occurs when the introduction of a new product causes sales of existing products to decline. Future cash flows represented by negative externalities occur regardless of the project, so they are non-incremental. Such cash flows represent a transfer from existing projects to new projects, and thus should be subtracted from the new projects' cash flows. Conventional versus non-conventional cash flows. A conventional cash flow pattern is one with an initial outflow followed by a series of inflows. In a non-conventional cash flow pattern, the initial outflow can be followed by inflows and/or outflows. Some project interactions: Indepe
Flashcard 1439321427212
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itdy>NPV measures the dollar benefit of the project to shareholders. However, it does not measure the rate of return of the project, and thus cannot provide "safety margin" information. Safety margin refers to how much the project return could fall in percentage terms before the invested capital is at risk.<body><html>
Original toplevel document
Subject 3. Investment Decision Criteriaon that capital. If a firm takes on a project with a positive NPV, the position of the stockholders is improved. Decision rules: The higher the NPV, the better. Reject if NPV is less than or equal to 0. <span>NPV measures the dollar benefit of the project to shareholders. However, it does not measure the rate of return of the project, and thus cannot provide "safety margin" information. Safety margin refers to how much the project return could fall in percentage terms before the invested capital is at risk. Assuming the cost of capital for the firm is 10%, calculate each cash flow by dividing the cash flow by (1 + k) t where k is the cost of capital and t is the year number.
Flashcard 1442507001100
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itNon-price competition dominates those market structures where product differentiation is critical. Therefore, monopolistic competition relies on competitive strategies that may not include pricing changes.
Original toplevel document
2. ANALYSIS OF MARKET STRUCTURESd monopoly is the local electrical power provider. In most cases, the monopoly power provider is allowed to earn a normal return on its investment and prices are set by the regulatory authority to allow that return. <span>2.2. Factors That Determine Market Structure Five factors determine market structure: The number and relative size of firms supplying the product; The degree of product differentiation; The power of the seller over pricing decisions; The relative strength of the barriers to market entry and exit; and The degree of non-price competition. The number and relative size of firms in a market influence market structure. If there are many firms, the degree of competition increases. With fewer firms supplying a good or service, consumers are limited in their market choices. One extreme case is the monopoly market structure, with only one firm supplying a unique good or service. Another extreme is perfect competition, with many firms supplying a similar product. Finally, an example of relative size is the automobile industry, in which a small number of large international producers (e.g., Ford and Toyota) are the leaders in the global market, and a number of small companies either have market power because they are niche players (e.g., Ferrari) or have little market power because of their narrow range of models or limited geographical presence (e.g., Škoda). In the case of monopolistic competition, there are many firms providing products to the market, as with perfect competition. However, one firm’s product is differentiated in some way that makes it appear better than similar products from other firms. If a firm is successful in differentiating its product, the differentiation will provide pricing leverage. The more dissimilar the product appears, the more the market will resemble the monopoly market structure. A firm can differentiate its product through aggressive advertising campaigns; frequent styling changes; the linking of its product with other, complementary products; or a host of other methods. When the market dictates the price based on aggregate supply and demand conditions, the individual firm has no control over pricing. The typical hog farmer in Nebraska and the milk producer in Bavaria are price takers . That is, they must accept whatever price the market dictates. This is the case under the market structure of perfect competition. In the case of monopolistic competition, the success of product differentiation determines the degree with which the firm can influence price. In the case of oligopoly, there are so few firms in the market that price control becomes possible. However, the small number of firms in an oligopoly market invites complex pricing strategies. Collusion, price leadership by dominant firms, and other pricing strategies can result. The degree to which one market structure can evolve into another and the difference between potential short-run outcomes and long-run equilibrium conditions depend on the strength of the barriers to entry and the possibility that firms fail to recoup their original costs or lose money for an extended period of time and are therefore forced to exit the market. Barriers to entry can result from very large capital investment requirements, as in the case of petroleum refining. Barriers may also result from patents, as in the case of some electronic products and drug formulas. Another entry consideration is the possibility of high exit costs. For example, plants that are specific to a special line of products, such as aluminum smelting plants, are non-redeployable, and exit costs would be high without a liquid market for the firm’s assets. High exit costs deter entry and are therefore also considered barriers to entry. In the case of farming, the barriers to entry are low. Production of corn, soybeans, wheat, tomatoes, and other produce is an easy process to replicate; therefore, those are highly competitive markets. Non-price competition dominates those market structures where product differentiation is critical. Therefore, monopolistic competition relies on competitive strategies that may not include pricing changes. An example of non-price competition is product differentiation through marketing. In other circumstances, non-price competition may occur because the few firms in the market feel dependent on each other. Each firm fears retaliatory price changes that would reduce total revenue for all of the firms in the market. Because oligopoly industries have so few firms, each firm feels dependent on the pricing strategies of the others. Therefore, non-price competition becomes a dominant strategy. Exhibit 1. Characteristics of Market Structure Market Structure Number of Sellers Degree of Product Differentiation Barriers to Entry Pricing Power of Firm Non-price Competition Perfect competition Many Homogeneous/ Standardized Very Low None None Monopolistic competition Many Differentiated Low Some Advertising and Product Differentiation Oligopoly Few Homogeneous/ Standardized High Some or Considerable Advertising and Product Differentiation Monopoly One Unique Product Very High Considerable Advertising From the perspective of the owners of the firm, the most desirable market structure is that with the most control over price, because this control can lead to large profits. Monopoly and oligopoly markets offer the greatest potential control over price; monopolistic competition offers less control. Firms operating under perfectly competitive market conditions have no control over price. From the consumers’ perspective, the most desirable market structure is that with the greatest degree of competition, because prices are generally lower. Thus, consumers would prefer as many goods and services as possible to be offered in competitive markets. As often happens in economics, there is a trade-off. While perfect competition gives the largest quantity of a good at the lowest price, other market forms may spur more innovation. Specifically, there may be high costs in researching a new product, and firms will incur such costs only if they expect to earn an attractive return on their research investment. This is the case often made for medical innovations, for example—the cost of clinical trials and experiments to create new medicines would bankrupt perfectly competitive firms but may be acceptable in an oligopoly market structure. Therefore, consumers can benefit from less-than-perfectly-competitive markets. PORTER’S FIVE FORCES AND MARKET STRUCTURE A financial analyst aiming to establish market conditions and consequent profitability of incumbent firms should start with the questions framed by Exhibit 1: How many sellers are there? Is the product differentiated? and so on. Moreover, in the case of monopolies and quasi monopolies, the analyst should evaluate the legislative and regulatory framework: Can the company set prices freely, or are there governmental controls? Finally, the analyst should consider the threat of competition from potential entrants. This analysis is often summarized by students of corporate strategy as “Porter’s five forces,” named after Harvard Business School professor Michael E. Porter. His book, Competitive Strategy, presented a systematic analysis of the practice of market strategy. Porter (2008) identified the five forces as: Threat of entry; Power of suppliers; Power of buyers (customers); Threat of substitutes; and Rivalry among existing competitors. It is easy to note the parallels between four of these five forces and the columns in Exhibit 1. The only “orphan” is the power of suppliers, which is not at the core of the theoretical economic analysis of competition, but which has substantial weight in the practical analysis of competition and profitability. Some stock analysts (e.g., Dorsey 2004) use the term “economic moat” to suggest that there are factors protecting the profitability of a firm that are similar to the moats (ditches full of water) that used to protect some medieval castles. A deep moat means that there is little or no threat of entry by invaders, i.e. competitors. It also means that customers are locked in because of high switching costs. <span><body><html>
Flashcard 1479821102348
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itIn the % of completion method What happens to costs? Contract costs for the period are expensed against the revenue.
Original toplevel document
3.2.1. Long-Term Contractsts. Under the percentage-of-completion method, in each accounting period, the company estimates what percentage of the contract is complete and then reports that percentage of the total contract revenue in its income statement. <span>Contract costs for the period are expensed against the revenue. Therefore, net income or profit is reported each year as work is performed. Under IFRS, if the outcome of the contract cannot be measured reliably, then revenue may be reco
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1622919744780
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1622938619148
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1624283155724
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1624301767948
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1632800214284
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 4. Different Yield Measures of a U.S. Treasury Bill
bills). Pure discount instruments such as T-bills are quoted differently than U.S. government bonds. They are quoted on a bank discount basis rather than on a price basis: <span>r BD = the annualized yield on a bank discount basis D = the dollar discount, which is equal to the difference between the face value of the bill, F, and its purchase price, P t = the number of days remaining to maturity 360 = the bank convention of the number of days in a year. Bank discount yield is not a meaningful measure of the return on investment because: It is based on the face value, not on the purchase price. Instead, return on inves
Flashcard 1635170258188
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 1. The Nature of Statistics
mple are called statistics. A parameter is a numerical quantity measuring some aspect of a population of scores. The mean, for example, is a measure of central tendency. Greek letters are used to designate parameters. <span>Parameters are rarely known and are usually estimated by statistics computed in samples. Populations can have many parameters, but investment analysts are usually only concerned with a few, such as the mean return or the standard deviation of returns.
Flashcard 1641053293836
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1641160772876
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itrs x i (where i = 1, 2, ..., n) is: The special cases of n = 2 and n = 3 are given by: and so on. <span>For n = 2, the harmonic mean is related to arithmetic mean A and geometric mean G by: <span><body><html>
Original toplevel document
Subject 4. Measures of Center Tendency, therefore, is not recommended for use as the only measure of central tendency. A further disadvantage of the mode is that many distributions have more than one mode. These distributions are called "multimodal." <span>Harmonic Mean The harmonic mean of n numbers x i (where i = 1, 2, ..., n) is: The special cases of n = 2 and n = 3 are given by: and so on. For n = 2, the harmonic mean is related to arithmetic mean A and geometric mean G by: The mean, median, and mode are equal in symmetric distributions. The mean is higher than the median in positively skewed distributions and lower than the median in negatively skewed dist
Flashcard 1644926733580
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1646697778444
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Open it
A semilogarithmic scale describes a scale constructed so that equal intervals on the vertical scale represent equal rates of change, and equal intervals on the horizontal scale represent equal amounts o
Flashcard 1647717780748
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1647761820940
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1647763918092
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649061530892
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itthis risk of graft loss and overall mortality increase with the length of dialysis prior to transplant
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649184214284
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itstudy did not detect a significant protective effect of protein-restricted diets in preventing progression of kidney disease. However, low protein diets may delay onset of symptomatic uremia in patients with late-stage CKD (stage G4/G5).
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649203088652
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itdosis occurs in patients with chronic ethanol abuse and liver disease and develops following an episode of acute intoxication, at which time the ingested ethanol may have already been extensively metabolized, leading to <span>low or normal serum ethanol levels. Ethanol is oxidized to acetaldehyde and then to acetic acid,<span><body><html>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1649204661516
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itnd liver disease and develops following an episode of acute intoxication, at which time the ingested ethanol may have already been extensively metabolized, leading to low or normal serum ethanol levels. Ethanol is oxidized to <span>acetaldehyde and then to acetic acid,<span><body><html>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1649206234380
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itvelops following an episode of acute intoxication, at which time the ingested ethanol may have already been extensively metabolized, leading to low or normal serum ethanol levels. Ethanol is oxidized to acetaldehyde and then to <span>acetic acid,<span><body><html>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649210166540
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itD-Lactic acidosis is an uncommon cause of increased anion gap metabolic acidosis that is typically identified in patients with small-bowel bacterial overgrowth.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649213312268
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itRhabdomyolysis is a diagnostic consideration in a patient with a history of alcohol abuse and an anion gap metabolic acidosis, but this condition is frequently associated with hyperkalemia, hyperphosphatemia, hypocalcemia, and a urinalysis positive for blood with no erythrocytes visible on urine microscopy.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1649214885132
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itRhabdomyolysis is a diagnostic consideration in a patient with a history of alcohol abuse and an anion gap metabolic acidosis, but this condition is frequently associated with hyperkalemia, hyperphosphatemia, hypocalcemia, and a urinalysis positive for blood with no erythrocytes visible on urine microscopy.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1649216457996
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itd><head>Rhabdomyolysis is a diagnostic consideration in a patient with a history of alcohol abuse and an anion gap metabolic acidosis, but this condition is frequently associated with hyperkalemia, hyperphosphatemia, hypocalcemia, and a urinalysis positive for blood with no erythrocytes visible on urine microscopy.<html>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649220652300
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itIgA vasculitis is associated with abdominal pain, palpable purpura, arthralgia, and glomerulonephritis, with normal complement levels.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649224060172
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itInfection-related glomerulonephritis such as endocarditis activates the alternative pathway of complement with low C3 and normal C4 levels. The classical pathway of complement is activated with cryoglobulinemic vasculitis (C4, and sometimes C3, is depressed) and systemic lupus ery
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1649225895180
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itInfection-related glomerulonephritis such as endocarditis activates the alternative pathway of complement with low C3 and normal C4 levels. The classical pathway of complement is activated with cryoglobulinemic vasculitis (C4, and sometimes C3, is depressed) and systemic lupus erythematosus (bo
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1649227468044
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itonephritis such as endocarditis activates the alternative pathway of complement with low C3 and normal C4 levels. The classical pathway of complement is activated with cryoglobulinemic vasculitis (C4, and sometimes C3, is <span>depressed) and systemic lupus erythematosus (both C3 and C4 are low).<span><body><html>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1649229040908
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itway of complement with low C3 and normal C4 levels. The classical pathway of complement is activated with cryoglobulinemic vasculitis (C4, and sometimes C3, is depressed) and systemic lupus erythematosus (both C3 and C4 are <span>low).<span><body><html>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649232186636
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itcryoglobulinemic vasculitis is associated with hepatitis C virus infection,
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649235332364
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itHypokalemia due to vomiting is associated with metabolic alkalosis, increased urine potassium excretion, and decreased urine chloride excretion.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1649236905228
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itHypokalemia due to vomiting is associated with metabolic alkalosis, increased urine potassium excretion, and decreased urine chloride excretion.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1649238478092
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itHypokalemia due to vomiting is associated with metabolic alkalosis, increased urine potassium excretion, and decreased urine chloride excretion.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649241623820
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itHypovolemia activates the renin-angiotensin system with an increase in sodium-hydrogen exchange and increased bicarbonate reabsorption in the proximal tubule due to increased luminal hydrogen ion, and exacerbated by decreased chloride available for reabsorption
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1649243196684
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itHypovolemia activates the renin-angiotensin system with an increase in sodium-hydrogen exchange and increased bicarbonate reabsorption in the proximal tubule due to increased luminal hydrogen ion, and exacerbated by decreased chloride available for reabsorption with sodium.<
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1649244769548
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itpan>Hypovolemia activates the renin-angiotensin system with an increase in sodium-hydrogen exchange and increased bicarbonate reabsorption in the proximal tubule due to increased luminal hydrogen ion, and exacerbated by decreased chloride available for reabsorption with sodium.<span><body><html>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649248177420
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itThe urine chloride concentration is low (<20 mEq/L [20 mmol/L]), reflecting gastrointestinal losses and prolonged volume contraction that leads to avid reabsorption of chloride with sodium.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1649250012428
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itThe urine chloride concentration is low (<20 mEq/L [20 mmol/L]), reflecting gastrointestinal losses and prolonged volume contraction that leads to avid reabsorption of chloride with sodium.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649253158156
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itBartter syndrome mimics the effect of a loop diuretic and is accompanied by increased urine sodium (>40 mEq/L [40 mmol/L]), urine potassium (>40 mEq/L [40 mmol/L]), and chloride excretion (>40 mEq/L [40 mmol
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1649254731020
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itl>Bartter syndrome mimics the effect of a loop diuretic and is accompanied by increased urine sodium (>40 mEq/L [40 mmol/L]), urine potassium (>40 mEq/L [40 mmol/L]), and chloride excretion (>40 mEq/L [40 mmol/L]).<html>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649257876748
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itHypokalemic periodic paralysis is due to a shift of potassium into cells and is not associated with a metabolic alkalosis; furthermore, urine potassium would be low (<20 mEq/L [20 mmol/L]) and not increased.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649262071052
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itShiga toxin–associated hemolytic uremic syndrome is a diarrhea- associated syndrome of microangiopathic hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenia, and kidney failure caused by Shiga toxin– producing Escherichia coli.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1649263643916
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itShiga toxin–associated hemolytic uremic syndrome is a diarrhea- associated syndrome of microangiopathic hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenia, and kidney failure caused by Shiga toxin– producing Escherichia coli.<
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649267576076
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itUltrasonography is the preferred diagnostic imaging modality for pregnant patients with suspected nephrolithiasis because it does not expose patients to radiation.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649270721804
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itTransvaginal ultrasonography may be used to detect distal ureteral stones in pregnant women with suspected nephrolithiasis and an unrevealing kidney ultrasound.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649274129676
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itPatients with enteric hyperoxaluria and calcium oxalate nephrolithiasis may benefit from treatment with bile salt binders to decrease intestinal oxalate absorption.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649277537548
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itTreatment with cholestyramine is an appropriate additional therapy for this patient with enteric hyperoxaluria.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649280945420
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itThiazide diuretics, such as hydrochlorothiazide, are used in patients with idiopathic hypercalciuria to reduce calcium excretion in the urine by inducing mild hypovolemia that results in increased sodium reabsorption and passive calcium reabsorption in the proximal tubule.</s
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1649282780428
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open ittml>Thiazide diuretics, such as hydrochlorothiazide, are used in patients with idiopathic hypercalciuria to reduce calcium excretion in the urine by inducing mild hypovolemia that results in increased sodium reabsorption and passive calcium reabsorption in the proximal tubule.<html>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1649284353292
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itn>Thiazide diuretics, such as hydrochlorothiazide, are used in patients with idiopathic hypercalciuria to reduce calcium excretion in the urine by inducing mild hypovolemia that results in increased sodium reabsorption and passive <span>calcium reabsorption in the proximal tubule.<span><body><html>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649289071884
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itUrine citrate inhibits stone formation by binding calcium in the tubular lumen, preventing it from precipitating with oxalate. Citrate excretion can be enhanced in patients with low urine citrate levels by alkalinizing the serum with potass
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1649290644748
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itUrine citrate inhibits stone formation by binding calcium in the tubular lumen, preventing it from precipitating with oxalate. Citrate excretion can be enhanced in patients with low urine citrate levels by alkalinizing the serum with potassium citrate, which decreases uptake of filtered citrate from the tub
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1649292217612
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itUrine citrate inhibits stone formation by binding calcium in the tubular lumen, preventing it from precipitating with oxalate. Citrate excretion can be enhanced in patients with low urine citrate levels by alkalinizing the serum with potassium citrate, which decreases uptake of filtered citrate from the tubular lumen.<span><body><html>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649295887628
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itThe expected compensation for chronic respiratory alkalosis is a decrease in the serum bicarbonate of 4 to 5 mEq/L (4-5 mmol/L) for each 10 mm Hg (1.3 kPa) decrease in the PCO2. The expected serum bicarbonate concentration in this patient is calculated to be 14 to 16 mEq/L (14-16 mmol/L), and the measu
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649299295500
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itan>Calculating the ratio of the change in the anion gap (Δ anion gap) to the change in bicarbonate level (Δ bicarbonate), or the “Δ-Δ ratio,” can help confirm if there is a coexisting acid-base disturbance. A ratio of <1 may reflect the presence of concurrent normal anion gap metabolic acidosis, whereas a ratio of >2 may indicate the presence of metabolic alkalosis<span><body><html>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1649300868364
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itbicarbonate level (Δ bicarbonate), or the “Δ-Δ ratio,” can help confirm if there is a coexisting acid-base disturbance. A ratio of <1 may reflect the presence of concurrent normal anion gap metabolic acidosis, whereas a ratio of ><span>2 may indicate the presence of metabolic alkalosis<span><body><html>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649304276236
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itEvidence for a tubulointerstitial process includes a slowly progressive course without a clear inciting event, subnephrotic proteinuria, bland urine sediment, and a kidney ultrasound showing atrophic kidneys
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1649305849100
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itl>Evidence for a tubulointerstitial process includes a slowly progressive course without a clear inciting event, subnephrotic proteinuria, bland urine sediment, and a kidney ultrasound showing atrophic kidneys<html>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649309256972
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itAn associated characteristic that may be present with tubulointerstitial disease is abnormal tubular handling of glucose, amino acids, uric acid, phosphate, and bicarbonate (termed Fanconi syndrome);
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1649310829836
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itAn associated characteristic that may be present with tubulointerstitial disease is abnormal tubular handling of glucose, amino acids, uric acid, phosphate, and bicarbonate (termed Fanconi syndrome);
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649314237708
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itHypertensive nephropathy involves damage to the vascular structures, glomeruli, and tubulointerstitial regions of the kidney. It may cause progressive kidney failure, often with elevated protein excretion (less than 1000 mg/24 h).
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1649315810572
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itn>Hypertensive nephropathy involves damage to the vascular structures, glomeruli, and tubulointerstitial regions of the kidney. It may cause progressive kidney failure, often with elevated protein excretion (less than 1000 mg/24 h).<span><body><html>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649320004876
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itMembranoproliferative glomerulonephritis may also be associated with chronic hepatitis B infection and involves immune complex deposition in the glomeruli. It typically presents with hematuria (often with dysmorphic erythrocytes and/or erythrocyte casts), variable degrees
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1649321577740
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itMembranoproliferative glomerulonephritis may also be associated with chronic hepatitis B infection and involves immune complex deposition in the glomeruli. It typically presents with hematuria (often with dysmorphic erythrocytes and/or erythrocyte casts), variable degrees of proteinuria, and a reduced glomer
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1649323150604
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itMembranoproliferative glomerulonephritis may also be associated with chronic hepatitis B infection and involves immune complex deposition in the glomeruli. It typically presents with hematuria (often with dysmorphic erythrocytes and/or erythrocyte casts), variable degrees of proteinuria, and a reduced glomerular filtration rate.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1649324723468
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open iterative glomerulonephritis may also be associated with chronic hepatitis B infection and involves immune complex deposition in the glomeruli. It typically presents with hematuria (often with dysmorphic erythrocytes and/or erythrocyte <span>casts), variable degrees of proteinuria, and a reduced glomerular filtration rate.<span><body><html>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1649326296332
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itciated with chronic hepatitis B infection and involves immune complex deposition in the glomeruli. It typically presents with hematuria (often with dysmorphic erythrocytes and/or erythrocyte casts), variable degrees of proteinuria, and a <span>reduced glomerular filtration rate.<span><body><html>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649329442060
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itMembranous glomerulopathy is common in patients with chronic hepatitis B infection and appears to be related to subendothelial and mesangial immune deposits in the glomeruli. Because it primarily affects the glomeruli, it is associated w
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1649331014924
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itin patients with chronic hepatitis B infection and appears to be related to subendothelial and mesangial immune deposits in the glomeruli. Because it primarily affects the glomeruli, it is associated with high levels of <span>proteinuria, usually in the nephrotic range,<span><body><html>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649335209228
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itIntravenous dextrose-containing fluids can exacerbate hypophosphatemia by stimulating insulin release, which promotes phosphate uptake by the cells and worsening hypophosphatemia.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649339141388
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itely cause of this patient's respiratory failure is hypophosphatemia, which occurs in patients with chronic alcohol use, malnutrition, or critical illness. Symptoms rarely occur unless the serum phosphate concentration is <<span>2.0 mg/dL (0.65 mmol/L); severe symptoms occur with a serum phosphate concentration <1.0 mg/dL (0.32 mmol/L). Symptoms include weakness, myalgia, rhabdomyolysis, arrhythmias, heart failure,
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1649340714252
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itrs in patients with chronic alcohol use, malnutrition, or critical illness. Symptoms rarely occur unless the serum phosphate concentration is <2.0 mg/dL (0.65 mmol/L); severe symptoms occur with a serum phosphate concentration <<span>1.0 mg/dL (0.32 mmol/L). Symptoms include weakness, myalgia, rhabdomyolysis, arrhythmias, heart failure, respiratory failure, seizures, coma, and hemolysis.<span><body><html>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1649342287116
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open it, malnutrition, or critical illness. Symptoms rarely occur unless the serum phosphate concentration is <2.0 mg/dL (0.65 mmol/L); severe symptoms occur with a serum phosphate concentration <1.0 mg/dL (0.32 mmol/L). Symptoms include <span>weakness, myalgia, rhabdomyolysis, arrhythmias, heart failure, respiratory failure, seizures, coma, and hemolysis.<span><body><html>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649345694988
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itSevere hypophosphatemia can cause respiratory failure from impaired diaphragmatic contractility
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649348840716
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itAll NSAIDs contribute to hypertension by inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2 in the kidneys, promoting sodium retention and increased intravascular volume.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649352248588
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itAdditional effects of NSAIDs include hyperkalemia
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649356967180
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itManifestations of D-lactic acidosis include intermittent confusion, slurred speech, ataxia, and an increased anion gap metabolic acidosis with a normal plasma lactate level.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1649358540044
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itManifestations of D-lactic acidosis include intermittent confusion, slurred speech, ataxia, and an increased anion gap metabolic acidosis with a normal plasma lactate level.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1649360112908
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itManifestations of D-lactic acidosis include intermittent confusion, slurred speech, ataxia, and an increased anion gap metabolic acidosis with a normal plasma lactate level.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649363258636
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itThis patient has an increased anion gap metabolic acidosis, and the most likely cause is D-lactic acidosis. Accumulation of the D-isomer of lactate can occur in patients with short-bowel syndrome following jejunoileal bypass or small-bowel resection
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649366404364
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itEthylene glycol or methanol intoxication should be suspected in patients with an increased anion gap metabolic acidosis associated with a serum bicarbonate level <10 mEq/L (10 mmol/L) and a plasma osmolal gap >10 mOsm/kg H 2 O.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1649367977228
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open it<head>Ethylene glycol or methanol intoxication should be suspected in patients with an increased anion gap metabolic acidosis associated with a serum bicarbonate level <10 mEq/L (10 mmol/L) and a plasma osmolal gap >10 mOsm/kg H 2 O.<html>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649371385100
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itPyroglutamic acidosis is a cause of increased anion gap metabolic acidosis in patients receiving therapeutic doses of acetaminophen on a chronic basis. Clinical manifestations are limited to mental status changes and increased a
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1649372957964
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itPyroglutamic acidosis is a cause of increased anion gap metabolic acidosis in patients receiving therapeutic doses of acetaminophen on a chronic basis. Clinical manifestations are limited to mental status changes and increased anion gap metabolic acidosis. The syndrome most commonly occurs in patients with critic
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1649374530828
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open ittions are limited to mental status changes and increased anion gap metabolic acidosis. The syndrome most commonly occurs in patients with critical illness, poor nutrition, liver disease, or chronic kidney disease as well as in persons on a <span>vegetarian diet. Diagnosis can be confirmed by measuring urine levels of pyroglutamic acid.<span><body><html>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1649376103692
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itic acidosis. The syndrome most commonly occurs in patients with critical illness, poor nutrition, liver disease, or chronic kidney disease as well as in persons on a vegetarian diet. Diagnosis can be confirmed by measuring urine levels of <span>pyroglutamic acid.<span><body><html>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649379773708
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itMeasurement of urine chloride levels can be useful to determine volume status and saline responsiveness in patients with metabolic alkalosis.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649383443724
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itUrine chloride measurement can help determine the cause of metabolic alkalosis, particularly if it is difficult to clinically assess volume status. In such patients, a low (<15 mEq/L [15 mmol/L]) urine chloride suggests reduction in extracellular volume and the presence of saline-responsive metabolic alkalosis.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1649385278732
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itbody>Urine chloride measurement can help determine the cause of metabolic alkalosis, particularly if it is difficult to clinically assess volume status. In such patients, a low (<15 mEq/L [15 mmol/L]) urine chloride suggests reduction in extracellular volume and the presence of saline-responsive metabolic alkalosis.<body><html>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1649386851596
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itthe cause of metabolic alkalosis, particularly if it is difficult to clinically assess volume status. In such patients, a low (<15 mEq/L [15 mmol/L]) urine chloride suggests reduction in extracellular volume and the presence of saline-<span>responsive metabolic alkalosis.<span><body><html>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649390259468
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itConditions that are associated with saline-responsive metabolic alkalosis include vomiting, remote use of diuretics, and post-hypercapnic metabolic alkalosis.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649393667340
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itIf the urine chloride is high (>15 mEq/L [15 mmol/L]), the metabolic alkalosis is saline resistant and can be caused by active diuretic use, stimulant laxative abuse, and rare renal tubular disorders such as Gitelman and Bartte
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1649395240204
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itIf the urine chloride is high (>15 mEq/L [15 mmol/L]), the metabolic alkalosis is saline resistant and can be caused by active diuretic use, stimulant laxative abuse, and rare renal tubular disorders such as Gitelman and Bartter syndromes.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1649397075212
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itIf the urine chloride is high (>15 mEq/L [15 mmol/L]), the metabolic alkalosis is saline resistant and can be caused by active diuretic use, stimulant laxative abuse, and rare renal tubular disorders such as Gitelman and Bartter syndromes.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1649398648076
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itead><head>If the urine chloride is high (>15 mEq/L [15 mmol/L]), the metabolic alkalosis is saline resistant and can be caused by active diuretic use, stimulant laxative abuse, and rare renal tubular disorders such as Gitelman and Bartter syndromes.<html>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649404153100
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itIn patients with metabolic alkalosis, measurement of urine chloride rather than urine sodium is used to determine volume status and saline responsiveness
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649407560972
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itA negative family history does not exclude autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD)—approximately 15% of patients with ADPKD have spontaneous mutations that result in the disease.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649412803852
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itPatients with tumor lysis syndrome and evidence of uric acid nephropathy require treatment with rasburicase to reduce serum urate levels.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649415949580
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itRasburicase is appropriate to treat hyperuricemia in this patient with tumor lysis syndrome (TLS). TLS is characterized by the massive release of uric acid, potassium, and phosphate into the blood from rapid lysis of malignant cells. It typically occurs after initiation of cytotoxic therapy for hematologic malignancies with large tumor burden (such as h
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1649417784588
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open ituricemia in this patient with tumor lysis syndrome (TLS). TLS is characterized by the massive release of uric acid, potassium, and phosphate into the blood from rapid lysis of malignant cells. It typically occurs after initiation of <span>cytotoxic therapy for hematologic malignancies with large tumor burden (such as high-grade lymphomas) or high cell counts (such as acute lymphoblastic leukemia),<span><body><html>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649420930316
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itRasburicase rapidly converts uric acid to allantoin, which is 5 to 10 times more soluble than uric acid and readily excreted through the kidney. Rasburicase has a much faster action than allopurinol and can decrease serum urate levels
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1649422503180
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itRasburicase rapidly converts uric acid to allantoin, which is 5 to 10 times more soluble than uric acid and readily excreted through the kidney. Rasburicase has a much faster action than allopurinol and can decrease serum urate levels within 4 hours of
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1649424076044
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itsburicase rapidly converts uric acid to allantoin, which is 5 to 10 times more soluble than uric acid and readily excreted through the kidney. Rasburicase has a much faster action than allopurinol and can decrease serum urate levels within <span>4 hours of administration.<span><body><html>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649427483916
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itUrine alkalinization increases the excretion of uric acid by increasing its solubility. However, in the setting of hyperphosphatemia, it can cause precipitation of calcium phosphate crystals in the kidney. Urine alkalinization is not necessary when rasburicase is used, and it role in TLS is controversial
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649431153932
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itAllopurinol competitively inhibits xanthine oxidase, blocking the metabolism of hypoxanthine and xanthine to uric acid. Allopurinol effectively decreases the formation of new uric acid and therefore does not affect circulati
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1649432726796
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itAllopurinol competitively inhibits xanthine oxidase, blocking the metabolism of hypoxanthine and xanthine to uric acid. Allopurinol effectively decreases the formation of new uric acid and therefore does not affect circulating uric acid
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1649434299660
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itspan>Allopurinol competitively inhibits xanthine oxidase, blocking the metabolism of hypoxanthine and xanthine to uric acid. Allopurinol effectively decreases the formation of new uric acid and therefore does not affect circulating uric acid<span><body><html>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649437969676
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itObservation with serial blood pressure measurements, urine studies, and serum creatinine levels is appropriate for patients with IgA nephropathy with low-risk features for progression
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649443212556
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itPreeclampsia is classically defined as new-onset hypertension after 20 weeks of pregnancy with proteinuria (≥300 mg/24 h or a urine protein- creatinine ratio ≥300 mg/g). Delivery of the baby is the definitive treatment for preeclampsia
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1649444785420
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itPreeclampsia is classically defined as new-onset hypertension after 20 weeks of pregnancy with proteinuria (≥300 mg/24 h or a urine protein- creatinine ratio ≥300 mg/g). Delivery of the baby is the definitive treatment for preeclampsia
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1649446358284
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itPreeclampsia is classically defined as new-onset hypertension after 20 weeks of pregnancy with proteinuria (≥300 mg/24 h or a urine protein- creatinine ratio ≥300 mg/g). Delivery of the baby is the definitive treatment for preeclampsia
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649450028300
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itIn patients with preeclampsia and severe disease, generally defined as severe hypertension (systolic blood pressure ≥160 mm Hg or diastolic blood pressure ≥110 mm Hg), thrombocytopenia (platelet count <100,000/µL [100 × 109/L]), kidney dysfunction (serum creatinine concentration >1.1 mg/dL [
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1649451601164
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itIn patients with preeclampsia and severe disease, generally defined as severe hypertension (systolic blood pressure ≥160 mm Hg or diastolic blood pressure ≥110 mm Hg), thrombocytopenia (platelet count <100,000/µL [100 × 109/L]), kidney dysfunction (serum creatinine concentration >1.1 mg/dL [97.2 µmol/L] or doubling of the s
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1649453174028
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open ithead><head>In patients with preeclampsia and severe disease, generally defined as severe hypertension (systolic blood pressure ≥160 mm Hg or diastolic blood pressure ≥110 mm Hg), thrombocytopenia (platelet count <100,000/µL [100 × 109/L]), kidney dysfunction (serum creatinine concentration >1.1 mg/dL [97.2 µmol/L] or doubling of the serum creatinine concentration in the absence of other kidney d
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1649454746892
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itine concentration >1.1 mg/dL [97.2 µmol/L] or doubling of the serum creatinine concentration in the absence of other kidney disease), impaired liver function (elevated blood concentrations of liver aminotransferases to <span>twice the normal concentration), pulmonary edema, or cerebral or visual symptoms, management decisions are usually made based on the balance of fetal and maternal risk with the
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649457892620
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itantihypertensive treatment is generally reserved for patients with preeclampsia with severe hypertension
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649462086924
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itIn obese patients with likely secondary focal segmental glomerulosclerosis, weight loss is sometimes associated with a drop in proteinuria, as is the use of ACE inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers, and is the preferred initial therapy.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649466019084
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itPrimary FSGS involves glomerular injury due to an unclear insult; features suggesting primary FSGS include a low serum albumin level and extensive foot process effacement on kidney biopsy. Patients usually present with hypertension, hypoalbuminemia, and some degree of kidney failure in ad
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1649467591948
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itPrimary FSGS involves glomerular injury due to an unclear insult; features suggesting primary FSGS include a low serum albumin level and extensive foot process effacement on kidney biopsy. Patients usually present with hypertension, hypoalbuminemia, and some degree of kidney failure in addition to nephrotic-range proteinu
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1649469164812
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itive foot process effacement on kidney biopsy. Patients usually present with hypertension, hypoalbuminemia, and some degree of kidney failure in addition to nephrotic-range proteinuria. Some patients with primary FSGS respond well to <span>immunosuppressive therapy, and this is typically offered to patients with this diagnosis.<span><body><html>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649472572684
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itSecondary FSGS is believed to result from an adaptive response to glomerular hypertrophy or hyperfiltration associated with a number of conditions (including obesity) in which the glomerular filtration rate may be markedly increased; glomeruli on biopsy are often enlarged, reflecting hyper
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1649474145548
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itSecondary FSGS is believed to result from an adaptive response to glomerular hypertrophy or hyperfiltration associated with a number of conditions (including obesity) in which the glomerular filtration rate may be markedly increased; glomeruli on biopsy are often enlarged, reflecting hyperfiltration with only mild foot process effacement. These p
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1649475718412
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itar hypertrophy or hyperfiltration associated with a number of conditions (including obesity) in which the glomerular filtration rate may be markedly increased; glomeruli on biopsy are often enlarged, reflecting hyperfiltration with only <span>mild foot process effacement. These patients have minimal edema and rarely have the full spectrum of the nephrotic syndrome.<span><body><html>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649479388428
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itAcute kidney injury is a common result of cholesterol embolization, which causes peripheral eosinophilia and hypocomplementemia and shows evidence of inflammation on urinalysis, frequently with eosinophiluria present.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1649480961292
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itAcute kidney injury is a common result of cholesterol embolization, which causes peripheral eosinophilia and hypocomplementemia and shows evidence of inflammation on urinalysis, frequently with eosinophiluria present.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1649482534156
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itAcute kidney injury is a common result of cholesterol embolization, which causes peripheral eosinophilia and hypocomplementemia and shows evidence of inflammation on urinalysis, frequently with eosinophiluria present.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649485679884
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itEmbolization may also lead to digital ischemia or infarction (“blue toe” syndrome) due to digital arterial occlusion or central scotoma due to central retinal artery occlusion. Although not specific for cholesterol atheroembolism, live
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1649487252748
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itEmbolization may also lead to digital ischemia or infarction (“blue toe” syndrome) due to digital arterial occlusion or central scotoma due to central retinal artery occlusion. Although not specific for cholesterol atheroembolism, livedo reticularis (areas of lace-like mottled and purplish skin over the legs and
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1649488825612
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itlization may also lead to digital ischemia or infarction (“blue toe” syndrome) due to digital arterial occlusion or central scotoma due to central retinal artery occlusion. Although not specific for cholesterol atheroembolism, <span>livedo reticularis (areas of lace-like mottled and purplish skin over the legs and thighs) is commonly associated with this disorder.<span><body><html>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649491971340
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itEosinophiluria was previously believed to diagnose AIN, but urine eosinophil determination has been shown to be neither sensitive nor specific in the diagnostic evaluation of AIN.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649498000652
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itthiazide diuretic or a calcium channel blocker alone or in combination as initial therapy for black patients with hypertension.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649501146380
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itsimvastatin) that undergoes significant metabolism via the cytochrome P450 3A4 (CYP3A4) pathway; lovastatin and, to a lesser extent, amlodipine are also metabolized through this pathway. Several calcium channel blockers inhibit or are metabolized through the CYP3A4 pathway and can increase the risk of statin myopathy
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649505340684
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itEmpiric therapy with sodium bicarbonate, fomepizole, and hemodialysis is indicated for patients with suspected ethylene glycol intoxication.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649509272844
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open it>Intravenous ethanol was traditionally used as a competitive inhibitor of alcohol dehydrogenase; it is effective because this enzyme has greater affinity for ethanol than for ethylene glycol or methanol. However, fomepizole has been found to be a superior therapy to ethanol, is easier to administer, and has fewer side effects. Although ethanol is a reasonable second-line therapy, there is no be
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1649510845708
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itan for ethylene glycol or methanol. However, fomepizole has been found to be a superior therapy to ethanol, is easier to administer, and has fewer side effects. Although ethanol is a reasonable second-line therapy, there is <span>no benefit to coadministration of fomepizole and ethanol. <span><body><html>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649514515724
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itPatients with chronic kidney disease and normal calcium and phosphorus levels should be treated with active vitamin D analogues to reduce elevated parathyroid hormone levels and prevent renal osteodystrophy
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649517923596
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itVitamin D analogues should be discontinued in the setting of hypercalcemia or hyperphosphatemia.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1649519496460
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itVitamin D analogues should be discontinued in the setting of hypercalcemia or hyperphosphatemia.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649523166476
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itCurrent Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) guidelines do not recommend the routine use of dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DEXA) scans in patients with CKD because DEXA has poor predictive value for distinguishing histologic subtypes of bone d
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1649524739340
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itspan>Current Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) guidelines do not recommend the routine use of dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DEXA) scans in patients with CKD because DEXA has poor predictive value for distinguishing histologic subtypes of bone disease in patients with CKD.<span><body><html>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649528409356
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itrum sodium due to the presence in the serum of elevated serum lipid levels or abnormal paraproteins such as myeloma proteins. The most likely diagnosis is pseudohyponatremia. Plasma osmolality can be measured using the following equation: <span>Plasma Osmolality (mOsm/kg H 2 O) = 2 × Serum Sodium (mEq/L) + Plasma Glucose (mg/dL)/18 + Blood Urea Nitrogen (mg/dL)/2.8 <span><body><html>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649536273676
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itead>Patients with adrenal insufficiency may also have hyponatremia, caused by increased antidiuretic hormone (ADH) secretion in response to hypovolemia from urine salt wasting. However, these patients demonstrate a decrease in plasma osmolality rather than a normal plasma osmolality<html>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649539419404
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itPsychogenic polydipsia, in which patients ingest massive amounts of water, is characterized by hyponatremia with decreased plasma osmolality and decreased urine osmolality to less than the plasma osmolality, indicating maximum suppression of ADH with maximal urine dilution.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649542827276
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itPatients with the syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion have hyponatremia with decreased plasma osmolality
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649546235148
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itGlucocorticoids are recommended as first-line therapy in the treatment of minimal change glomerulopathy unless there are contraindications.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649549643020
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itThe abrupt onset of the full nephrotic syndrome, a history of kidney disease in childhood that remitted, negative serologic tests, and a kidney biopsy showing normal light microscopic findings and negative immunofluorescence are diagnostic of MCG. Electron microscopy is confirmatory and usually demonstrates the extensive effacement of the podocyte foot processes
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649554885900
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itGlucocorticoids such as prednisone are recommended as first-line therapy unless there are contraindications. More than 80% of patients respond within 16 weeks of treatment. Alternative first-line therapy for minimal change glomerulopathy patients with contraindications to glucocorticoids (for example, obesity, impaired glucose toleranc
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1649556458764
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itirst-line therapy for minimal change glomerulopathy patients with contraindications to glucocorticoids (for example, obesity, impaired glucose tolerance or diabetes mellitus, or psychiatric conditions) includes calcineurin inhibitors such as <span>cyclosporine.<span><body><html>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649559604492
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itAlkylating agents such as cyclophosphamide are reserved for frequently relapsing or glucocorticoid-dependent patients with MCG.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649563012364
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itACE inhibitors such as lisinopril or angiotensin receptor blockers (typically used to inhibit the progression of chronic kidney disease) are typically not indicated to treat MCG because the duration of disease is short with glucocorticoid therapy, and patients are not hypertensive.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649566944524
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itHypokalemic periodic paralysis secondary to thyrotoxicosis is characterized by generalized flaccid muscle weakness from a sudden intracellular potassium shift precipitated by strenuous exercise or a high carbohydrate meal.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1649568517388
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open ithtml>Hypokalemic periodic paralysis secondary to thyrotoxicosis is characterized by generalized flaccid muscle weakness from a sudden intracellular potassium shift precipitated by strenuous exercise or a high carbohydrate meal. <html>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649572449548
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itBartter syndrome represents a group of autosomal recessive renal tubular disorders characterized by metabolic alkalosis, hypokalemia, and normal to low blood pressure with mild volume depletion.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1649574022412
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itBartter syndrome represents a group of autosomal recessive renal tubular disorders characterized by metabolic alkalosis, hypokalemia, and normal to low blood pressure with mild volume depletion.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1649575595276
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itBartter syndrome represents a group of autosomal recessive renal tubular disorders characterized by metabolic alkalosis, hypokalemia, and normal to low blood pressure with mild volume depletion.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649579265292
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itAn inadequate response to water restriction (urine osmolality does not rise despite rising plasma osmolality) suggests either central or nephrogenic diabetes insipidus.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649582411020
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itDI is caused by either an absence of antidiuretic hormone (ADH) secretion (central DI) or renal resistance to ADH (nephrogenic DI), which results in an inability to appropriately concentrate the urine in response to an increase in plasma osmolali
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1649583983884
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itDI is caused by either an absence of antidiuretic hormone (ADH) secretion (central DI) or renal resistance to ADH (nephrogenic DI), which results in an inability to appropriately concentrate the urine in response to an increase in plasma osmolality.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649587391756
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itThe most appropriate diagnostic test to perform next is a water restriction test to evaluate for diabetes insipidus (DI)
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649590537484
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itLithium is one of the most common causes of nephrogenic DI in adults.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649593945356
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itbecause increased thirst stimulates oral consumption of fluids, which maintains the serum sodium near the upper normal range as long as access to fluids is not impaired. In a water restriction (or deprivation) test, urine volume, urine osmolality, and plasma sodium concentration are measured hourly after complete water restriction. A normal urine osmolality response (usually defined as an increase in urine osmolality above 600 mOsm/kg H 2 O) indicates that ADH release and corresponding renal response to ADH are intact. A failure of the urine osmolality to rise despite rising plasma osmolality suggests either central or nephrogenic DI. Desmopressin is then administered. Patients with central DI will respond with increased urine osmolality, whereas in patients with nephrogenic DI (as is likely in this patient), desmopressin will not result in increased urine osmolality after water restriction, confirming the diagnosis.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649597877516
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itThe cosyntropin stimulation test is used to diagnose adrenal insufficiency, which is manifested by hyponatremia, decreased plasma osmolality, and increased urine osmolality
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649601023244
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itA urine sodium measurement is useful in the evaluation of patients with suspected urinary salt wasting, such as those with adrenal insufficiency.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649621732620
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itOral alkali therapy ( NaHCO3 ) to maintain serum bicarbonate levels between 23 and 29 mEq/L (23-29 mmol/L) reduces the risk of progression of chronic kidney disease.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649625926924
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itMesalamine-induced interstitial nephritis is a well-described
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649629072652
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itSterile pyuria and leukocyte casts are hallmarks of interstitial nephritis, which can present acutely or may progress indolently and present as chronic kidney disease of unclear duration. Mild subnephrotic proteinuria also can be seen with interstitial nephr
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1649630645516
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itSterile pyuria and leukocyte casts are hallmarks of interstitial nephritis, which can present acutely or may progress indolently and present as chronic kidney disease of unclear duration. Mild subnephrotic proteinuria also can be seen with interstitial nephritis
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649633791244
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itRapidly progressive glomerulonephritis is associated with hematuria and erythrocyte casts and variable proteinuria, usually with other clinical manifestations such as hypertension. In some cases, other systemic symptoms or clinical findings associate
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1649635364108
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itRapidly progressive glomerulonephritis is associated with hematuria and erythrocyte casts and variable proteinuria, usually with other clinical manifestations such as hypertension. In some cases, other systemic symptoms or clinical findings associated with an underlying et
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1649636936972
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itia and erythrocyte casts and variable proteinuria, usually with other clinical manifestations such as hypertension. In some cases, other systemic symptoms or clinical findings associated with an underlying etiology may be present, such as <span>pulmonary hemorrhage or upper and lower respiratory tract involvement<span><body><html>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649641393420
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itChronic hypertension is defined as systolic pressure ≥140 mm Hg and/or diastolic pressure ≥90 mm Hg that existed before pregnancy, is present before the 20th week of gestation, or persists longer than 12 weeks POST DELIVERY
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1649642966284
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itChronic hypertension is defined as systolic pressure ≥140 mm Hg and/or diastolic pressure ≥90 mm Hg that existed before pregnancy, is present before the 20th week of gestation, or persists longer than 12 weeks POST DELIVERY
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649646374156
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itThe diagnosis of HELLP (hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, and low platelets) syndrome requires evidence of hemolysis and abnormal liver chemistry tests in addition to thrombocytopenia.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649649782028
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itElevated serum phosphorus levels, particularly exceeding 6.5 mg/dL (2.09 mmol/L), are closely associated with increased mortality.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649652927756
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itFerric citrate, another non-calcium– containing phosphorus binder, was recently approved for use in patients receiving dialysis but is not yet approved for patients with non-dialysis CKD. </s
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649657646348
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itIron deficiency is the most common cause of hyporesponsiveness to erythropoietin, and guidelines recommend intravenous rather than oral iron replacement among hemodialysis patients who require iron.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649660792076
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open it(KDIGO) recommendations suggest maintaining transferrin saturation levels of >30% and serum ferritin levels of >500 ng/mL (500 µg/L). In hemodialysis patients,
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1649662364940
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open it(KDIGO) recommendations suggest maintaining transferrin saturation levels of >30% and serum ferritin levels of >500 ng/mL (500 µg/L). In hemodialysis patients,
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649666034956
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itKDIGO guidelines suggest avoiding dosing erythropoietin to achieve a hemoglobin level >11.5 g/dL (115 g/L)
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649671277836
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itPrimary membranous glomerulopathy MG is associated with the antibody to the phospholipase A2 receptor (PLA2R) on the podocyte surface in up to 80% of patients, and the presence of the antibody supports this diagnosis.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1649672850700
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itPrimary membranous glomerulopathy MG is associated with the antibody to the phospholipase A2 receptor (PLA2R) on the podocyte surface in up to 80% of patients, and the presence of the antibody supports this diagnosis.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1649677307148
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itSecondary causes of membranous glomerulopathy MG include malignancies (solid organ cancers, especially lung, colon, and breast), autoimmune diseases (such as lupus or mixed connective tissue disease), infections (hepatitis B and C), and medications (penicillamine, gold, and NSAIDs). Evaluation for potential secondary causes should always be undertaken in patients with MG, especially those who are negative for PLA2R antibodies.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
A JACE Can Increase Efficiency (and save money) | eSPACE
r not your system includes this device or one very similar (as there are various names by different suppliers for this component) To get started, let’s look at some terminology related to the building automation industry to set the table: <span>Niagara AX/4 – The Niagara Framework is a universal software infrastructure that allows organizations to easily build custom, Web-enabled applications for accessing, automating and controlling “smart” devices in real-time over the Internet. BACnet (Building Automation and Control networks) – A Data Communication Protocol for Building Automation and Control Networks. A data communication protocol is a set of rules govern
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
A JACE Can Increase Efficiency (and save money) | eSPACE
rol Networks. A data communication protocol is a set of rules governing the exchange of data over a computer network. The rules take the form of a written specification that spells out what is required to conform to the protocol.[imagelink] <span>JACE (Java Application Control Engine) – In order to integrate diverse systems, a physical connection to a device’s network is required. A JACE is a mechanism/device that provides connectivity to systems (HVAC, electrical…even security in some instances) within a building via the Niagara framework. By connecting common network protocols such as LonWorks, BACnet, and Modbus, along with many proprietary networks a unified system without seams emerges. Enough technical terms. Here is the long and short of the above. The building automation industry…including HVAC, electrical, IT, security, etc… has developed several means, method
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
What is Tridium Part 1 - Building Automation Monthly
is and what Tridium isn’t. At the end of this article I will provide you some related articles and a chance to learn more about building automation. So what is Tridium? Tridium is the latest buzz word in the Building Automation Industry. <span>There are three driving factors behind the adoption of Tridium: A large amount of third-party integration drivers A distributor model that provides open availability of the product A SDK that allows developers to customize their own integrations Tridium is built on Niagara AX (or N4 as Tridium is calling the new platform) which is a proprietary framework. Tridium itself is the brand name for the product built upon the AX framework. A typical Tridium device is comprised of several open and proprietary protocols provided on a scalable pl
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |