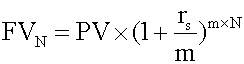Edited, memorised or added to reading queue
on 04-Sep-2017 (Mon)
Do you want BuboFlash to help you learning these things? Click here to log in or create user.
Flashcard 1435822591244
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
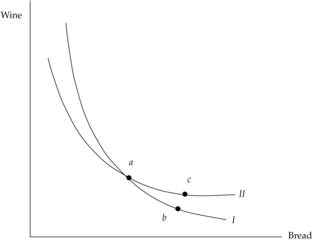
Open itindifference curves will generally be strictly convex and negatively sloped, and they cannot cross. These are the only restrictions we place on indifference curve maps.
Original toplevel document
Indifference curves cannot touchhe same indifference curve, she must be indifferent between these two bundles as well. But because bundle c contains more of both wine and bread than bundle b, she must prefer c to b, which violates transitivity of preferences. So we see that <span>indifference curves will generally be strictly convex and negatively sloped, and they cannot cross. These are the only restrictions we place on indifference curve maps.<span><body><html>
Flashcard 1613878922508
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 1. Classification of Cash Flows and Non-Cash Activities
amples are: Sale or purchase of property, plant and equipment. Investments in joint ventures and affiliates and long-term investments in securities. Loans to other entities or collection of loans from other entities. <span>Financing Activities These involve liability and owner's equity items, and include: Obtaining capital from owners and providing them with a return on (and a return of) their investments. Borrowing money from creditors and repaying the amounts
Flashcard 1625083481356
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
subject 3. The Future Value and Present Value of a Single Cash Flow
. When you calculate these amounts, make sure that periodic interest rates correspond to the number of compounding periods in the year. For example, if time periods are quoted in quarters, quarterly interest rates should be used. <span>When compounding periods are other than annual r s = the quoted annual interest rate m = the number of compounding periods per year N = the number of years. Example 2 An analyst invests $5 million in a 5-year certificate of deposit (CD) at a local financial institution. The CD promises to pay 7% per year, compounded semi-a
Flashcard 1625129618700
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 4. The Future Value and Present Value of a Series of Equal Cash Flows (Ordinary Annuities, Annuity Dues, and Perpetuities)
e present value of a regular annuity of (N - 1) period. Use the above formula to calculate the second part and add the two parts together. This process can also be simplified to a formula: Note that, <span>all other factors being equal, the present value of an annuity due is equal to the present value of an ordinary annuity multiplied by (1 + r). Hint: Remember these formulas - you can use them to solve annuity-related questions directly, or to double-check the answers given by your calculator. A perpe
Flashcard 1678115736844
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itThe phrase pharmacokinetic analysis of drug absorption and distribution describes onset time and magnitude of drug response. Drug elimination kinetic analysis describes the dura- tion of the tissue response.</s
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1678116785420
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itThe phrase pharmacokinetic analysis of drug absorption and distribution describes onset time and magnitude of drug response. Drug elimination kinetic analysis describes the dura- tion of the tissue response.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1678117833996
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itThe phrase pharmacokinetic analysis of drug absorption and distribution describes onset time and magnitude of drug response. Drug elimination kinetic analysis describes the dura- tion of the tissue response.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1678118882572
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itThe phrase pharmacokinetic analysis of drug absorption and distribution describes onset time and magnitude of drug response. Drug elimination kinetic analysis describes the dura- tion of the tissue response.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1678119931148
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itAntagonists that possess the property of weak affinity for the same receptor protein (e.g., atropine, esmolol) are competitive and may be displaced by an agonist. Noncompetitive antagonists, such as phenoxybenzamine and aspirin, have a strong affinity for the receptor protein, usually via
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1678121766156
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itthe same receptor protein (e.g., atropine, esmolol) are competitive and may be displaced by an agonist. Noncompetitive antagonists, such as phenoxybenzamine and aspirin, have a strong affinity for the receptor protein, usually via <span>covalent bonds, and cannot be displaced by the agonist<span><body><html>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1678123863308
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itagonists that possess the property of weak affinity for the same receptor protein (e.g., atropine, esmolol) are competitive and may be displaced by an agonist. Noncompetitive antagonists, such as phenoxybenzamine and aspirin, have a <span>strong affinity for the receptor protein, usually via covalent bonds, and cannot be displaced by the agonist<span><body><html>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1678125698316
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open it(e.g., atropine, esmolol) are competitive and may be displaced by an agonist. Noncompetitive antagonists, such as phenoxybenzamine and aspirin, have a strong affinity for the receptor protein, usually via covalent bonds, and cannot be <span>displaced by the agonist<span><body><html>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1678127533324
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itNew receptor protein must be synthe- sized if agonist receptor complexing is to occur. As with ago- nist drugs, not all receptors are bound by antagonists. Antagonists cause a rightward shift in the drug dose-response curve. The extent of rightward shift reflects the number of available receptors occu- pied by the antagonist drug (Figure 5-9). Comparison of the ED 50 i
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1678130416908
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itis to occur. As with ago- nist drugs, not all receptors are bound by antagonists. Antagonists cause a rightward shift in the drug dose-response curve. The extent of rightward shift reflects the number of available receptors occu- pied by the <span>antagonist drug (Figure 5-9). Comparison of the ED 50 in Figure 5-9 shows a reduced affinity of the agonist for its receptor when the antagonist is present.<span><body><html>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1678132251916
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itWith drug- receptor-response triad, when a drug combines with its receptor, a conformational change occurs in the receptor protein itself. No tissue response can occur without the structural shift. Evidence does suggest that events within the biosphere after drug associa- tion
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1678134086924
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itWith drug- receptor-response triad, when a drug combines with its receptor, a conformational change occurs in the receptor protein itself. No tissue response can occur without the structural shift. Evidence does suggest that events within the biosphere after drug associa- tion with the receptor are the principal regulatory variables of the response onset-offset time course<
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1678136446220
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itConstitutively active receptors can exist and are shifted toward the activated state, even though no agonist or ligand is present. Receptors for benzodiazepines, cannabinoids, and serotonin are examples. Agonists shift the equilibrium toward activation. Antagonist
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1678138281228
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itConstitutively active receptors can exist and are shifted toward the activated state, even though no agonist or ligand is present. Receptors for benzodiazepines, cannabinoids, and serotonin are examples. Agonists shift the equilibrium toward activation. Antagonists freeze the equilibrium, and inverse ago- nists sh
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1678140116236
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open it>Constitutively active receptors can exist and are shifted toward the activated state, even though no agonist or ligand is present. Receptors for benzodiazepines, cannabinoids, and serotonin are examples. Agonists shift the equilibrium toward <span>activation. Antagonists freeze the equilibrium, and inverse ago- nists shift the equilibrium toward inactivation. The two-state model<span><body><html>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1678141951244
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open iteceptors can exist and are shifted toward the activated state, even though no agonist or ligand is present. Receptors for benzodiazepines, cannabinoids, and serotonin are examples. Agonists shift the equilibrium toward activation. Antagonists <span>freeze the equilibrium, and inverse ago- nists shift the equilibrium toward inactivation. The two-state model<span><body><html>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1678143786252
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itoward the activated state, even though no agonist or ligand is present. Receptors for benzodiazepines, cannabinoids, and serotonin are examples. Agonists shift the equilibrium toward activation. Antagonists freeze the equilibrium, and inverse <span>ago- nists shift the equilibrium toward inactivation. The two-state model<span><body><html>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1678146407692
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itagonist-antagonist drugs have recep- tor protein affinity and intrinsic activity, but often only a fraction of the potency of the pure agonist
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1678147456268
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itagonist-antagonist drugs have recep- tor protein affinity and intrinsic activity, but often only a fraction of the potency of the pure agonist
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1678148504844
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itagonist-antagonist drugs have recep- tor protein affinity and intrinsic activity, but often only a fraction of the potency of the pure agonist
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1678149553420
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itChronic administration of an antagonist results in up- regulation as the number and sensitivity of the receptors increase as a response to chronic blockade.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1678150601996
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itChronic administration of an antagonist results in up- regulation as the number and sensitivity of the receptors increase as a response to chronic blockade.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1678151650572
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itWith up-regulation, the patient develops tol- erance, requiring higher doses of the antagonist to counteract the increasing receptor number
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1678152699148
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itWith up-regulation, the patient develops tol- erance, requiring higher doses of the antagonist to counteract the increasing receptor number
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1678153747724
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itAddition The combined effect of two drugs acting via the same mechanism is equal to that expected by simple addition of their individual actions. 1 + 1 = 2 Synergism The combined effect of two drugs is greater than the algebraic sum of their individual effects. 1 + 1 = 3 Potentiation The enhancement of the action of one drug by a second drug th
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1678156369164
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itthe same mechanism is equal to that expected by simple addition of their individual actions. 1 + 1 = 2 Synergism The combined effect of two drugs is greater than the algebraic sum of their individual effects. 1 + 1 = 3 Potentiation <span>The enhancement of the action of one drug by a second drug that has no detectable action of its own. 1 + 0 = 3 Antagonism The action of one drug opposes the action of another. 1 + 1 = 0<span><body><html>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1678157417740
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itsm The combined effect of two drugs is greater than the algebraic sum of their individual effects. 1 + 1 = 3 Potentiation The enhancement of the action of one drug by a second drug that has no detectable action of its own. 1 + 0 = 3 <span>Antagonism The action of one drug opposes the action of another. 1 + 1 = 0<span><body><html>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1678159252748
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itAddition The combined effect of two drugs acting via the same mechanism is equal to that expected by simple addition of their individual actions. 1 + 1 = 2 Synergism The combined effect of
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1678161087756
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itA drug interaction is an alteration in the therapeutic action of a drug by concurrent administration of other drugs or exogenous substances.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1678162136332
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itA drug interaction is an alteration in the therapeutic action of a drug by concurrent administration of other drugs or exogenous substances.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1678163184908
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itA drug interaction is an alteration in the therapeutic action of a drug by concurrent administration of other drugs or exogenous substances.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1678164233484
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itThe drug receptor sub- unit site is the primary regulator of onset-offset drug response
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1678165282060
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itMore and more evidence suggests that individual genetic variation in receptor proteins accounts for drug-response variation within seem- ingly normal populations. In clinical anesthesia, the range of patient responses to a given drug dose reflects this variation
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1678167117068
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itThe age-related decline in anesthetic drug dose needed to achieve a desired anesthetic end-point is related to a change in both pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1678168165644
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itThe age-related decline in anesthetic drug dose needed to achieve a desired anesthetic end-point is related to a change in both pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1678169214220
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itPhysiologic antagonism, another form of antagonism, involves two agonist drugs that bind to different receptors. At the physiological antagonism, drugs bind to specific unrelated receptor proteins, initiate a protein conformational shift, and el
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1678171049228
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itPhysiologic antagonism, another form of antagonism, involves two agonist drugs that bind to different receptors. At the physiological antagonism, drugs bind to specific unrelated receptor proteins, initiate a protein conformational shift, and elicit individual tissue responses. The
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1678172884236
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itPhysiologic antagonism, another form of antagonism, involves two agonist drugs that bind to different receptors. At the physiological antagonism, drugs bind to specific unrelated receptor proteins, initiate a protein conformational shift, and elicit individual tissue responses. The responses, however, generate opposing forces such as are observed with isoprotere
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1678174719244
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itPhysiologic antagonism, another form of antagonism, involves two agonist drugs that bind to different receptors. At the physiological antagonism, drugs bind to specific unrelated receptor proteins, initiate a protein conformational shift, and elicit individual tissue responses. The responses, however, generate opposing forces such as are observed with isoproterenol-induced vasodi
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1678176554252
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itPhysiologic antagonism, another form of antagonism, involves two agonist drugs that bind to different receptors. At the physiological antagonism, drugs bind to specific unrelated receptor proteins, initiate a protein conformational shift, and elicit individual tissue responses. The responses, however, generate opposing forces such as are observed with isoproterenol-induced vasodilation and norepinephrine- induced vasoco
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1678178389260
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itrugs that bind to different receptors. At the physiological antagonism, drugs bind to specific unrelated receptor proteins, initiate a protein conformational shift, and elicit individual tissue responses. The responses, however, generate <span>opposing forces such as are observed with isoproterenol-induced vasodilation and norepinephrine- induced vasoconstriction.<span><body><html>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1678180224268
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itThe anesthetist uses pharmacologic intervention to elicit a desired patient response. The site of the intervention is the bio- sphere, or the protein drug receptor, which is the primary regulator of the therapeutic response. Observed variation in patient drug response reflects the functionality of the biospher
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1678182845708
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itse. The site of the intervention is the bio- sphere, or the protein drug receptor, which is the primary regulator of the therapeutic response. Observed variation in patient drug response reflects the functionality of the biosphere and <span>genetics, as well as physiologic variability<span><body><html>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1678184680716
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itFor competitive antagonism, the agonist and antagonist have affinity for the same receptor protein;
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1678185729292
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itThe mean, median, and mode typically describe the dose- response relationship of a “normally distributed” population.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1678186777868
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itThe SD, SEM, and median effective dose provide a description of a population’s response to a drug. Such descriptors provide only an approximate dosage; the anesthetist must adjust this dosage for each patient to achieve the desired physiologic response</
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1678187826444
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itan>The SD, SEM, and median effective dose provide a description of a population’s response to a drug. Such descriptors provide only an approximate dosage; the anesthetist must adjust this dosage for each patient to achieve the desired <span>physiologic response<span><body><html>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1678188875020
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itChemical antagonism occurs when a drug’s action is blocked and no receptor activity is involved. For example, protamine is a positively charged protein that forms an ionic bond with he
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1678189923596
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itChemical antagonism occurs when a drug’s action is blocked and no receptor activity is involved. For example, protamine is a positively charged protein that forms an ionic bond with heparin, thus rendering it inactive. Sugammadex, mentioned previously, is another example
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1678192545036
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itChemical antagonism occurs when a drug’s action is blocked and no receptor activity is involved. For example, protamine is a positively charged protein that forms an ionic bond with heparin, thus rendering it inactive. Sugammadex, mentioned previously, is another example
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1678193593612
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itspan>Viewed at the molecular level, the observed response to a drug represents countless individual drug responses at the biosphere. Each drug-receptor interaction at the protein receptor elicits a fractional tissue response, and the sum of the fractional responses provides the observed response.<span><body><html>
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1678195428620
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itIn accor- dance with the law of mass action, when free drug binds to a recep- tor, a conformational shift occurs in the receptor protein. This shift causes a central space or channel to open, allowing specific ions to enter or leave the cell or a G protein to be activated, resulting in a biochemical cascade yielding pharmacologic effects. The resultant tissue res
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1678196477196
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itIn accor- dance with the law of mass action, when free drug binds to a recep- tor, a conformational shift occurs in the receptor protein. This shift causes a central space or channel to open, allowing specific ions to enter or leave the cell or a G protein to be activated, resulting
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1678200147212
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itAntagonist drugs also bind to the receptor but lack the ability to initiate the required protein conformational shift. The sum of fractional tissue responses elicited when an antagonist is prese
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1678201982220
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itContinued stimulation of cells with agonists generally results in a state of desensitization, also referred to as refractoriness or down-regulation, such that the effect that follows continued or sub- sequent exposure to the same concentration of drug is diminished.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1678203030796
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itMolecular pharmacology is identifying site-specific and age- related causes for the observed variation in patient drug response.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1678204865804
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itrefractoriness or down-regulation is very important in therapeutic situations; an example is attenuated response to the repeated use of β-adrenergic agonists as bronchodilators for the treatment of asthma
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Flashcard 1678761659660
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itA Lawyer focused on nerve injuries
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfs| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |