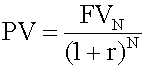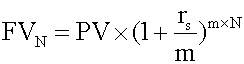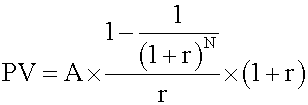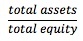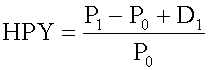Edited, memorised or added to reading queue
on 16-Dec-2017 (Sat)
Do you want BuboFlash to help you learning these things? Click here to log in or create user.
Flashcard 1428259474700
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itLos signos empleados en Algebra son de tres clases: Signos de Ope ración, Signos de Relación y Signos de Agrupación.
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1450267249932
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itNormal profit is considered to be a fixed cost because it is a return required by investors on their equity capital regardless of output level. At zero output, total costs are always equal to the amount of total fixed cost that is i
Original toplevel document
Costsrate of change in total variable cost. In Exhibit 13, TC at 5 units is 400—of which 300 is variable cost and 100 is fixed cost. At 10 units, total costs are 1,650, which is the sum of 1,550 in variable cost and 100 in fixed cost. <span>Total fixed cost (TFC) is the summation of all expenses that do not change when production varies. It can be a sunk or unavoidable cost that a firm has to cover whether it produces anything or not, or it can be a cost that stays the same over a range of production but can change to another constant level when production moves outside of that range. The latter is referred to as a quasi-fixed cost , although it remains categorized as part of TFC. Examples of fixed costs are debt service, real estate lease agreements, and rental contracts. Quasi-fixed cost examples would be certain utilities and administrative salaries that could be avoided or be lower when output is zero but would assume higher constant values over different production ranges. Normal profit is considered to be a fixed cost because it is a return required by investors on their equity capital regardless of output level. At zero output, total costs are always equal to the amount of total fixed cost that is incurred at this production point. In Exhibit 13, total fixed cost remains at 100 throughout the entire production range. Other fixed costs evolve primarily from investments in such fixed assets as real estate, production facilities, and equipment. As a firm grows in size, fixed asset expansion occurs along with a related increase in fixed cost. However, fixed cost cannot be arbitrarily cut when production declines. Regardless of the volume of output, an investment in a given level of fixed assets locks the firm into a certain amount of fixed cost that is used to finance the physical capital base, technology, and other capital assets. When a firm downsizes, the last expense to be cut is usually fixed cost. Total variable cost (TVC), which is the summation of all variable expenses, has a direct relationship with quantity. When quantity increases, total variable cost increases
Flashcard 1453621906700
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itEven if you are listening intently, it’s still easy for others to feel like you are not. Namely, when you jump in immediately after they have finished speaking. Why is this negative? The other person who just stopped speaking will likely come to the conclusion that you did not really listen to him or her. You appeared to b
Original toplevel document (pdf)
cannot see any pdfsFlashcard 1473837665548
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itFor paid-in capital, an example of an increase is a new issuance of equity and an example of a decrease is a repurchase of previously issued stock.
Original toplevel document
3.1.3. Statement of Changes in Equityents of retained earnings. The statement of changes in equity is organized to present, for each component of equity, the beginning balance, any increases during the period, any decreases during the period, and the ending balance. <span>For paid-in capital, an example of an increase is a new issuance of equity and an example of a decrease is a repurchase of previously issued stock. For retained earnings, income (both net income as reported on the income statement and other comprehensive income) is the most common increase and a dividend payment is the most common
Flashcard 1474146995468
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open ita disclaimer of opinion occurs when, for some reason, such as a scope limitation, the auditors are unable to issue an opinion.
Original toplevel document
3.1.7. Auditor’s Reportsart from accounting standards and are not fairly presented. An adverse opinion makes analysis of the financial statements easy: Do not bother analyzing these statements, because the company’s financial statements cannot be relied on. Finally, <span>a disclaimer of opinion occurs when, for some reason, such as a scope limitation, the auditors are unable to issue an opinion. Exhibit 10 presents the independent auditor’s report for Volkswagen. Note that Volkswagen received an unqualified or clean audit opinion from PricewaterhouseCoopers for the company’s fi
Flashcard 1474400750860
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itBusiness activities may be classified into three groups for financial reporting purposes: operating, investing, and financing activities.
Original toplevel document
2. THE CLASSIFICATION OF BUSINESS ACTIVITIESilar accounting treatment to similar types of business transactions. Therefore, a first step in understanding financial reporting mechanics is to understand how business activities are classified for financial reporting purposes. <span>Business activities may be classified into three groups for financial reporting purposes: operating, investing, and financing activities. Operating activities are those activities that are part of the day-to-day business functioning of an entity. Examples include the sale of meals by a restaurant, th
Flashcard 1474582940940
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itf merchandise). Other receivables represent amounts owed to the company from parties other than customers. Cash refers to cash on hand (e.g., petty cash and cash not yet deposited to the bank) and in the bank. <span>Cash equivalents are very liquid short-term investments, usually maturing in 90 days or less. The presentation of assets as current or non-current will vary from industry to industry and from
Original toplevel document
3.1. Financial Statement Elements and Accountsldings); other property held for investment, and investments in the securities of other companies. Current assets are those that are expected to be consumed or converted into cash in the near future, typically one year or less. <span>Inventory is the unsold units of product on hand (sometimes referred to as inventory stock). Trade receivables (also referred to as commercial receivables , or simply accounts receivable ) are amounts customers owe the company for products that have been sold as well as amounts that may be due from suppliers (such as for returns of merchandise). Other receivables represent amounts owed to the company from parties other than customers. Cash refers to cash on hand (e.g., petty cash and cash not yet deposited to the bank) and in the bank. Cash equivalents are very liquid short-term investments, usually maturing in 90 days or less. The presentation of assets as current or non-current will vary from industry to industry and from country to country. Some industries present current assets first, whereas others list non-current assets first. This is discussed further in later readings. <span><body><html>
Flashcard 1477983472908
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itThe format for the operating cash section which begins with net income and shows adjustments to derive operating cash flow, is known as the indirect format .
Original toplevel document
Open itIn the cashflow statement direct format , which refers to the operating cash section appearing simply as operating cash receipts less operating cash disbursements. An alternative format for the operating cash section, which begins with net income and shows adjustments to derive operating cash flow, is known as the indirect format . The alternative formats and detailed rules are discussed in the reading on understanding the statement of cash flows.
Flashcard 1478051368204
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itlustration, the company had incurred wage expenses at month end, but the payment would not be made until after the end of the month (Transaction 11). To reflect the company’s position at the end of the month, the accounting treatment involved <span>an originating entry to record wage expense and the corresponding liability for wages payable, and a future adjusting entry to eliminate the liability when cash is paid (not shown because wages will be paid only in February). Similarly, the IAL illustration included interest accrual on the company’s bank borrowing. (See the boxes showing the accounting treatment of Transaction 8, where Transaction 8 refers
Original toplevel document
Open itved and the corresponding liability to deliver newsletters) and, subsequently, 12 future adjusting entries, the first one of which was illustrated as Transaction 12. Each adjusting entry reduces the liability and records revenue. <span>In practice, a large amount of unearned revenue may cause some concern about a company’s ability to deliver on this future commitment. Conversely, a positive aspect is that increases in unearned revenue are an indicator of future revenues. For example, a large liability on the balance sheet of an airline relates to cash received for future airline travel. Revenue will be recognized as the travel occurs, so an increase in this liability is an indicator of future increases in revenue. <span><body><html>
Flashcard 1478133681420
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1478487313676
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itOperating profit results from deducting operating expenses such as selling, general, administrative, and research and development expenses from gross profit.
Original toplevel document
2. COMPONENTS AND FORMAT OF THE INCOME STATEMENToods or services. Other expenses related to running the business are subtracted after gross profit. Another important subtotal which may be shown on the income statement is operating profit (or, synonymously, operating income). <span>Operating profit results from deducting operating expenses such as selling, general, administrative, and research and development expenses from gross profit. Operating profit reflects a company’s profits on its usual business activities before deducting taxes, and for non-financial companies, before deducting interest expense. For financial
Flashcard 1481584807180
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
4.1. General Principles
ade from inventory purchased in a previous period or previous periods. It is also likely that some of the inventory purchased in the current period will remain unsold at the end of the current period and so will be sold in a following period. <span>Matching requires that a company recognizes cost of goods sold in the same period as revenues from the sale of the goods. Period costs , expenditures that less directly match revenues, are reflected in the period when a company makes the expenditure or incurs the liability to pay. Administrati
ade from inventory purchased in a previous period or previous periods. It is also likely that some of the inventory purchased in the current period will remain unsold at the end of the current period and so will be sold in a following period. <span>Matching requires that a company recognizes cost of goods sold in the same period as revenues from the sale of the goods. Period costs , expenditures that less directly match revenues, are reflected in the period when a company makes the expenditure or incurs the liability to pay. Administrati
Flashcard 1497102683404
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Capital Structure Definition | Investopedia
What is a 'Capital Structure' <span>The capital structure is how a firm finances its overall operations and growth by using different sources of funds. Debt comes in the form of bond issues or long-term notes payable, while equity is classified as common stock, preferred stock or retained earnings. Short-term debt such as working capit
What is a 'Capital Structure' <span>The capital structure is how a firm finances its overall operations and growth by using different sources of funds. Debt comes in the form of bond issues or long-term notes payable, while equity is classified as common stock, preferred stock or retained earnings. Short-term debt such as working capit
Flashcard 1497406508300
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itFair value is defined as a sale price agreed to by a willing buyer and seller, assuming both parties enter the transaction freely. Many investments have a fair value determined by a market where t
Original toplevel document
Fair Value Definition | InvestopediaWhat is 'Fair Value' <span>Fair value is defined as a sale price agreed to by a willing buyer and seller, assuming both parties enter the transaction freely. Many investments have a fair value determined by a market where the security is traded. Fair value also represents the value of a company’s assets and liabilities when a subsidiary company’s financial statements are consolidated with a parent company. BREAKING DOWN 'Fair Value' The most reliable way to determine an investment’s fair value is to list the security on an exchange. If XYZ stock trad
Flashcard 1598502604044
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itdinary items Extraordinary items are BOTH unusual in nature AND infrequent in occurrence, and material in amount. They must be reported separately (below the line) net of income tax. Common examples are: <span>Expropriations by foreign governments. Uninsured losses from earthquakes, eruptions, and tornadoes. Note that gains and losses from the early retirement of debt used to be treated as extraordinary items; SFAS No
Original toplevel document
Subject 6. Non-Recurring Items and Non-Operating Items. Subsidiaries and investees also qualify as separate components. Disposal of a portion of a business component does not qualify as discontinued operations. Instead, this is recorded as an unusual or infrequent item. <span>2. Extraordinary items Extraordinary items are BOTH unusual in nature AND infrequent in occurrence, and material in amount. They must be reported separately (below the line) net of income tax. Common examples are: Expropriations by foreign governments. Uninsured losses from earthquakes, eruptions, and tornadoes. Note that gains and losses from the early retirement of debt used to be treated as extraordinary items; SFAS No. 145 now requires them to be treated as part of continuing operations. 3. Unusual or infrequent items These are either unusual in nature OR infrequent in occurrence but not both. They may be disclosed separately (as a single-line
Flashcard 1602913176844
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Comprehensive income
Comprehensive income includes both net income and other revenue and expense items that are excluded from the net income calculation. Comprehensive income is the sum of net income and other items that must bypass the income statement because they have not been realized, including items like an unrealized holding gain or loss from available-for-sale securities and foreign currency translation gains or losses. These items are not part of net income, yet are important enough to be included in comprehensive income, giving the user a bigger, more comprehensive picture of the organization as a wh
Comprehensive income includes both net income and other revenue and expense items that are excluded from the net income calculation. Comprehensive income is the sum of net income and other items that must bypass the income statement because they have not been realized, including items like an unrealized holding gain or loss from available-for-sale securities and foreign currency translation gains or losses. These items are not part of net income, yet are important enough to be included in comprehensive income, giving the user a bigger, more comprehensive picture of the organization as a wh
Flashcard 1602915011852
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Comprehensive income
sition of comprehensive income. It begins with net income and then includes those items affecting stockholders' equity that do not flow through the income statement. For 3M, these items include: Cumulative translation adjustment. <span>Minimum pension liability adjustment. Unrealized gains (losses) on available-for-sale investments. Unrealized gains (losses) on derivative investments. FASB has taken the position that income for a period shoul
sition of comprehensive income. It begins with net income and then includes those items affecting stockholders' equity that do not flow through the income statement. For 3M, these items include: Cumulative translation adjustment. <span>Minimum pension liability adjustment. Unrealized gains (losses) on available-for-sale investments. Unrealized gains (losses) on derivative investments. FASB has taken the position that income for a period shoul
Flashcard 1602974780684
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 1. Components and Format of the Balance Sheet
he left and liabilities and equity at the right of a central dividing line. A report format balance sheet lists assets, liabilities, and equity in a single column. Balance Sheet Components Current Assets <span>These are cash and other assets expected to be converted into cash, sold, or consumed either in one year or in the operating cycle, whichever is longer. The operating cycle is the average time between the acquisition of materials and supplies and the realization of cash through sales of the product for which the materials and supplies w
he left and liabilities and equity at the right of a central dividing line. A report format balance sheet lists assets, liabilities, and equity in a single column. Balance Sheet Components Current Assets <span>These are cash and other assets expected to be converted into cash, sold, or consumed either in one year or in the operating cycle, whichever is longer. The operating cycle is the average time between the acquisition of materials and supplies and the realization of cash through sales of the product for which the materials and supplies w
Flashcard 1602996014348
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 1. Components and Format of the Balance Sheet
stments set aside in special funds, such as a sinking fund, pension fund, or plant expansion fund. The cash surrender value of life insurance is included here. Investments in non-consolidated subsidiaries or affiliated companies. <span>Property, Plant, and Equipment These are properties of a durable nature used in the regular operations of the business. With the exception of land, most assets are either depreciable (such as a building) or consumable. Intangible Assets These lack physical substance and usually have a high degree of uncertainty concerning their future benefits. They include patents, copyright
stments set aside in special funds, such as a sinking fund, pension fund, or plant expansion fund. The cash surrender value of life insurance is included here. Investments in non-consolidated subsidiaries or affiliated companies. <span>Property, Plant, and Equipment These are properties of a durable nature used in the regular operations of the business. With the exception of land, most assets are either depreciable (such as a building) or consumable. Intangible Assets These lack physical substance and usually have a high degree of uncertainty concerning their future benefits. They include patents, copyright
Flashcard 1603172175116
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 2. Measurement Bases of Assets and Liabilities
feasibility) are met. A company should assess whether the useful life of an intangible asset is finite or infinite and, if finite, the length of its life. The straight-line method is typically used for amortization. <span>Goodwill is an example of an unidentifiable intangible asset which cannot be acquired singly and typically possesses an indefinite benefit period. It stems from such factors as a good reputation, loyal customers, and superior management. Any business that earns significantly more than a normal rate of return actually has goodwill.
feasibility) are met. A company should assess whether the useful life of an intangible asset is finite or infinite and, if finite, the length of its life. The straight-line method is typically used for amortization. <span>Goodwill is an example of an unidentifiable intangible asset which cannot be acquired singly and typically possesses an indefinite benefit period. It stems from such factors as a good reputation, loyal customers, and superior management. Any business that earns significantly more than a normal rate of return actually has goodwill.
Flashcard 1603218050316
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 3. Financial Instruments: Financial Assets and Financial Liabilities
me statement. Realized gains and losses are not affected by any unrealized gains or losses recognized before. Available-for-sale securities. Debt and equity securities not classified as held-to-maturity or trading securities. <span>Unrealized gains and losses are reported as part of other comprehensive income (in contrast, the unrealized gains or losses of trading securities are reported in the income statement as part of net income). Other than that, they are accounted for in the same way as trading securities. <span><body><html>
me statement. Realized gains and losses are not affected by any unrealized gains or losses recognized before. Available-for-sale securities. Debt and equity securities not classified as held-to-maturity or trading securities. <span>Unrealized gains and losses are reported as part of other comprehensive income (in contrast, the unrealized gains or losses of trading securities are reported in the income statement as part of net income). Other than that, they are accounted for in the same way as trading securities. <span><body><html>
Flashcard 1611303095564
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 5. Uses and Analysis of the Balance Sheet
less than 1 indicates the company has negative working capital. Quick Ratio (Acid-Test Ratio) eliminates less liquid assets, such as inventory and pre-paid expenses, from the current ratio. <span>If inventory is not moving, the quick ratio is a better indicator of cash and near-cash items that will be available to meet current obligations. Cash Ratio is the most conservative liquidity ratio, determined by eliminating receivables from the quick ratio. As with the elimination of
less than 1 indicates the company has negative working capital. Quick Ratio (Acid-Test Ratio) eliminates less liquid assets, such as inventory and pre-paid expenses, from the current ratio. <span>If inventory is not moving, the quick ratio is a better indicator of cash and near-cash items that will be available to meet current obligations. Cash Ratio is the most conservative liquidity ratio, determined by eliminating receivables from the quick ratio. As with the elimination of
Flashcard 1614198738188
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 1. Components and Format of the Balance Sheet
dent upon the occurrence or non-occurrence of one or more future events to confirm the amount payable, or the payee, or the date payable, such as services or product warranties and other contingencies. Owner's Equity <span>The complexity of capital stock agreements and the various restrictions on residual equity imposed by state corporation laws, liability agreements, and boards of directors make the owner's equity section one of the most difficult sections to prepare and understand. This section is usually divided into three parts: Capital stock: the par or stated value of the shares issued. Additional paid-in capital: the excess of amounts paid in ove
dent upon the occurrence or non-occurrence of one or more future events to confirm the amount payable, or the payee, or the date payable, such as services or product warranties and other contingencies. Owner's Equity <span>The complexity of capital stock agreements and the various restrictions on residual equity imposed by state corporation laws, liability agreements, and boards of directors make the owner's equity section one of the most difficult sections to prepare and understand. This section is usually divided into three parts: Capital stock: the par or stated value of the shares issued. Additional paid-in capital: the excess of amounts paid in ove
Flashcard 1615947500812
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 2. Preparing the Cash Flow Statement
ccurrence of the underlying cash flows. Finally, non-operating gains and losses enter into the determination of net income, but the related cash flows are classified as investing or financing activities, not operating activities. <span>There are two methods of converting the income statement from an accrual basis to a cash basis. Companies can use either the direct or the indirect method for reporting their operating cash flow. The direct method discloses operating cash inflows by source (e.g., cash
ccurrence of the underlying cash flows. Finally, non-operating gains and losses enter into the determination of net income, but the related cash flows are classified as investing or financing activities, not operating activities. <span>There are two methods of converting the income statement from an accrual basis to a cash basis. Companies can use either the direct or the indirect method for reporting their operating cash flow. The direct method discloses operating cash inflows by source (e.g., cash
Flashcard 1615964802316
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 2. Preparing the Cash Flow Statement
average reader. The indirect method reconciles net income to net cash flow from operating activities by adjusting net income for all non-cash items and the net changes in the operating working capital accounts. <span>It shows why net income and operating cash flows differ. It is used by most companies. The direct and indirect methods are alternative formats for reporting net cash flows from operating activities. Both methods produc
average reader. The indirect method reconciles net income to net cash flow from operating activities by adjusting net income for all non-cash items and the net changes in the operating working capital accounts. <span>It shows why net income and operating cash flows differ. It is used by most companies. The direct and indirect methods are alternative formats for reporting net cash flows from operating activities. Both methods produc
Flashcard 1619910855948
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
In calculating the cash payments for other operating expenses, which of the following items must a company add to the other operating expenses reported on the income statement?
An increase in prepaid expenses must be added to the other operating expenses reported on the income statement to calculate the cash payments for other operating expenses. An increase in prepaid expenses represents an outflow of cash that is not yet reported on the income statement as an expense.
Flashcard 1620805553420
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itExhibit 2. Common Accounts Assets Cash and cash equivalents Accounts receivable, trade receivables Prepaid expenses Inventory Property, plant, and equipment Investment propert
Original toplevel document
3.1. Financial Statement Elements and Accountsounting periods), and sales returns and allowances (an offset to revenue reflecting any cash refunds, credits on account, and discounts from sales prices given to customers who purchased defective or unsatisfactory items). <span>Exhibit 2. Common Accounts Assets Cash and cash equivalents Accounts receivable, trade receivables Prepaid expenses Inventory Property, plant, and equipment Investment property Intangible assets (patents, trademarks, licenses, copyright, goodwill) Financial assets, trading securities, investment securities Investments accounted for by the equity method Current and deferred tax assets [for banks, Loans (receivable)] Liabilities Accounts payable, trade payables Provisions or accrued liabilities Financial liabilities Current and deferred tax liabilities Reserves Unearned revenue Debt payable Bonds (payable) [for banks, Deposits] Owners’ Equity Capital, such as common stock par value Additional paid-in capital Retained earnings Other comprehensive income Minority interest Revenue Revenue, sales Gains Investment income (e.g., interest and dividends) Expense Cost of goods sold Selling, general, and administrative expenses “SG&A” (e.g., rent, utilities, salaries, advertising) Depreciation and amortization Interest expense Tax expense Losses For presentation purposes, assets are sometimes categorized as “current” or “non-current.” For example, Tesco (a large European retailer) prese
Flashcard 1620834651404
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itExhibit 2. Common Accounts Assets Cash and cash equivalents Accounts receivable, trade receivables Prepaid expenses Inventory Property, plant, and equipment Investment propert
Original toplevel document
3.1. Financial Statement Elements and Accountsounting periods), and sales returns and allowances (an offset to revenue reflecting any cash refunds, credits on account, and discounts from sales prices given to customers who purchased defective or unsatisfactory items). <span>Exhibit 2. Common Accounts Assets Cash and cash equivalents Accounts receivable, trade receivables Prepaid expenses Inventory Property, plant, and equipment Investment property Intangible assets (patents, trademarks, licenses, copyright, goodwill) Financial assets, trading securities, investment securities Investments accounted for by the equity method Current and deferred tax assets [for banks, Loans (receivable)] Liabilities Accounts payable, trade payables Provisions or accrued liabilities Financial liabilities Current and deferred tax liabilities Reserves Unearned revenue Debt payable Bonds (payable) [for banks, Deposits] Owners’ Equity Capital, such as common stock par value Additional paid-in capital Retained earnings Other comprehensive income Minority interest Revenue Revenue, sales Gains Investment income (e.g., interest and dividends) Expense Cost of goods sold Selling, general, and administrative expenses “SG&A” (e.g., rent, utilities, salaries, advertising) Depreciation and amortization Interest expense Tax expense Losses For presentation purposes, assets are sometimes categorized as “current” or “non-current.” For example, Tesco (a large European retailer) prese
Flashcard 1620861390092
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itExhibit 2. Common Accounts Assets Cash and cash equivalents Accounts receivable, trade receivables Prepaid expenses Inventory Property, plant, and equipment Investment propert
Original toplevel document
3.1. Financial Statement Elements and Accountsounting periods), and sales returns and allowances (an offset to revenue reflecting any cash refunds, credits on account, and discounts from sales prices given to customers who purchased defective or unsatisfactory items). <span>Exhibit 2. Common Accounts Assets Cash and cash equivalents Accounts receivable, trade receivables Prepaid expenses Inventory Property, plant, and equipment Investment property Intangible assets (patents, trademarks, licenses, copyright, goodwill) Financial assets, trading securities, investment securities Investments accounted for by the equity method Current and deferred tax assets [for banks, Loans (receivable)] Liabilities Accounts payable, trade payables Provisions or accrued liabilities Financial liabilities Current and deferred tax liabilities Reserves Unearned revenue Debt payable Bonds (payable) [for banks, Deposits] Owners’ Equity Capital, such as common stock par value Additional paid-in capital Retained earnings Other comprehensive income Minority interest Revenue Revenue, sales Gains Investment income (e.g., interest and dividends) Expense Cost of goods sold Selling, general, and administrative expenses “SG&A” (e.g., rent, utilities, salaries, advertising) Depreciation and amortization Interest expense Tax expense Losses For presentation purposes, assets are sometimes categorized as “current” or “non-current.” For example, Tesco (a large European retailer) prese
Flashcard 1621185400076
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 3. Cash Flow Statement Analysis
3; The add-back is after-tax, because the discount rate in the FCFF model (WACC) is also calculated on an after-tax basis. FCInv: Investment in fixed capital. It equals capital expenditures for PP&E minus sales of fixed assets. <span>WCInv: Investment in working capital. It equals the increase in short-term operating assets net of operating liabilities. Example Quinton is evaluating Proust Company for 2014. Quinton has gathered the following information (in millions):
Flashcard 1622008794380
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1622737554700
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1622883306764
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1622886976780
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Open it
An interest rate can be viewed as the sum of the real risk-free interest rate and a set of premiums that compensate lenders for risk: an inflation premium, a default risk premium, a liquidity premium, and a maturity premium. <span>The future value, FV, is the present value, PV, times the future value factor, (1 + r) N . The interest rate, r, makes current and future currency amounts equivalent based on their time value. The stated annual interest rate is a quoted interes
Flashcard 1623805005068
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1623820995852
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1625076403468
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
subject 3. The Future Value and Present Value of a Single Cash Flow
e n PV = present value r = interest rate per period N = number of years A key assumption of the future value formula is that interim interest earned is reinvested at the given interest rate (r). This is known as compounding. <span>In order to receive a single future cash flow N years from now, you must make an investment today in the following amount: Notice that the future cash flow is discounted back to the present. Therefore, the interest rate is called the discount rate. You sh
Flashcard 1625081122060
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
subject 3. The Future Value and Present Value of a Single Cash Flow
. When you calculate these amounts, make sure that periodic interest rates correspond to the number of compounding periods in the year. For example, if time periods are quoted in quarters, quarterly interest rates should be used. <span>When compounding periods are other than annual r s = the quoted annual interest rate m = the number of compounding periods per year N = the number of years. Example 2 An analyst invests $5 million in a 5-year certificate of deposit (CD) at a local financial institution. The CD promises to pay 7% per year, compounded semi-a
Flashcard 1625113627916
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 4. The Future Value and Present Value of a Series of Equal Cash Flows (Ordinary Annuities, Annuity Dues, and Perpetuities)
Annuity is a finite set of sequential cash flows, all with the same value. Ordinary annuity has a first cash flow that occurs one period from now (indexed at t = 1). In other words, the payments occur at the end of each period. Future value
Flashcard 1625124900108
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 4. The Future Value and Present Value of a Series of Equal Cash Flows (Ordinary Annuities, Annuity Dues, and Perpetuities)
future value of one annuity payment now, and the future value of a regular annuity of (N -1) period. Calculate the two parts and add them together. Alternatively, you can use this formula: Note that, <span>all other factors being equal, the future value of an annuity due is equal to the future value of an ordinary annuity multiplied by (1 + r). Present value of an annuity due This consists of two parts: an annuity payment now and the present value of a regular annuity of (N - 1) period. Use the a
Flashcard 1625127259404
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 4. The Future Value and Present Value of a Series of Equal Cash Flows (Ordinary Annuities, Annuity Dues, and Perpetuities)
u can use this formula: Note that, all other factors being equal, the future value of an annuity due is equal to the future value of an ordinary annuity multiplied by (1 + r). <span>Present value of an annuity due This consists of two parts: an annuity payment now and the present value of a regular annuity of (N - 1) period. Use the above formula to calculate the second part and add the two parts together. This process can also be simplified to a formula: Note that, all other factors being equal, the present value of an annuity due is equal to the present value of an ordinary annuity multiplied
Flashcard 1626081463564
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 5. Uses and Analysis of the Balance Sheet
ing debt such as accounts payables, accrued expenses, and deferred taxes. This ratio is especially useful in analyzing a company with substantial financing from short-term borrowing. Total Debt Ratio = <span>Financial Leverage Ratio = Financial statement analysis aims to investigate a company's financial condition and operating performance. Using financial ratios helps to examine relationships among indi
ing debt such as accounts payables, accrued expenses, and deferred taxes. This ratio is especially useful in analyzing a company with substantial financing from short-term borrowing. Total Debt Ratio = <span>Financial Leverage Ratio = Financial statement analysis aims to investigate a company's financial condition and operating performance. Using financial ratios helps to examine relationships among indi
Flashcard 1626630917388
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 1. NPV and IRR
A company should choose those capital investment processes that maximize shareholder wealth. The net present value (NPV) of an investment is the present value of its cash inflows minus the present value of its cash outflows. The internal rate of return (IRR) is the discou
Flashcard 1626634849548
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 1. NPV and IRR
ater than the discount rate used (WACC) and reject those in which the IRR is less than the discount rate. An IRR greater than the WACC suggests that the project will more than repay the capital costs (opportunity costs) incurred. <span>There are three problems associated with IRR as a decision rule. Reinvestment The IRR is intended to provide a single number that represents the rate of return generated by a capital investment. As such, it is an easy number
Flashcard 1632905858316
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 4. Different Yield Measures of a U.S. Treasury Bill
tead, return on investment should be measured based on cost of investment. It is annualized using a 360-day year, not a 365-day year. It annualizes with simple interest and ignores the effect of interest on interest (compound interest). <span>Holding period yield (HPY) is the return earned by an investor if the money market instrument is held until maturity: P 0 = the initial price of the instrument P 1 = the price received for the instrument at its maturity D 1 = the cash distributio
Flashcard 1633194216716
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 4. Different Yield Measures of a U.S. Treasury Bill
#13; Since a pure discount instrument (e.g., a T-bill) makes no interest payment, its HPY is (P 1 - P 0 )/P 0 . Note that HPY is computed on the basis of purchase price, not face value. It is not an annualized yield. <span>The effective annual yield is the annualized HPY on the basis of a 365-day year. It incorporates the effect of compounding interest. Money market yield (also known as CD equivalent yield) is the annualized HPY on the basis of
Flashcard 1633252412684
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 4. Different Yield Measures of a U.S. Treasury Bill
se price, not face value. It is not an annualized yield. The effective annual yield is the annualized HPY on the basis of a 365-day year. It incorporates the effect of compounding interest. <span>Money market yield (also known as CD equivalent yield) is the annualized HPY on the basis of a 360-day year using simple interest. Example An investor buys a $1,000 face-value T-bill due in 60 days at a price of $990. Bank discount yield: (1000 - 990
Flashcard 1633413631244
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 4. Different Yield Measures of a U.S. Treasury Bill
ld: (360 x 6%)/(360 - 60 x 6%) = 6.0606% If we know HPY, then: EAY = (1 + HPY) 365/t - 1 r MM = HPY x 360/t If we know EAY, then: HPY = ( 1 + EAY) t/365 - 1 r MM = [(1 + EAY) t/365 - 1] x (360/t) <span>If we know r MM , then: HPY = r MM x (t/360) EAY = (1 + r MM x t/360) 365/t - 1 <span><body><html>
Flashcard 1633971997964
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 5. Bond Equivalent Yield
The convention is to double it and call the result the bond's yield to maturity. This method ignores the effect of compounding semi-annual YTM, and the YTM calculated in this way is called a bond-equivalent yield (BEY). However, <span>yields of a semi-annual-pay and an annual-pay bond cannot be compared directly without conversion. This conversion can be done in one of the two ways: Convert the bond-equivalent yield of a semi-annual-pay bond to an annual-pay bond.
Flashcard 1633989037324
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 5. Bond Equivalent Yield
ted in this way is called a bond-equivalent yield (BEY). However, yields of a semi-annual-pay and an annual-pay bond cannot be compared directly without conversion. This conversion can be done in one of the two ways: <span>Convert the bond-equivalent yield of a semi-annual-pay bond to an annual-pay bond. Convert the equivalent annual yield of an annual-pay bond to a bond-equivalent yield. Example 
Flashcard 1635130412300
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1635132509452
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1635160296716
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1635393080588
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 2. Measurement Scales
uish between different measurement scales or levels of measurement. Nominal Scale Nominal measurement represents the weakest level of measurement. It consists of assigning items to groups or categories. <span>No quantitative information is conveyed and no ordering (ranking) of the items is implied. Nominal scales are qualitative rather than quantitative. Religious preference, race, and sex are all examples of nominal scales. Another example is portfolio managers cate
Flashcard 1636534193420
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 4. Measures of Center Tendency
ulation, the arithmetic mean is called a population mean. If the data set includes a sample of values taken from a population, the arithmetic mean is called a sample mean. This is the most widely used measure of central tendency. <span>When the word "mean" is used without a modifier, it can be assumed to refer to the arithmetic mean. The mean is the sum of all scores divided by the number of scores. It is used to measure the prospective (expected future) performance (return) of an investment over a number of periods
Flashcard 1637159144716
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1637216292108
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1641119616268
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1644303093004
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1644338744588
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1644406639884
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1644434427148
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1644482399500
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1644486069516
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1644555799820
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1644705484044
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 4. Different Yield Measures of a U.S. Treasury Bill
ld: (360 x 6%)/(360 - 60 x 6%) = 6.0606% If we know HPY, then: EAY = (1 + HPY) 365/t - 1 r MM = HPY x 360/t If we know EAY, then: HPY = ( 1 + EAY) t/365 - 1 r MM = [(1 + EAY) t/365 - 1] x (360/t) <span>If we know r MM , then: HPY = r MM x (t/360) EAY = (1 + r MM x t/360) 365/t - 1 <span><body><html>
Flashcard 1644775476492
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1644809555212
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1644811914508
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1644903140620
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1644981259532
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1644983880972
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1644996726028
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Stem-and-leaf graph
2|0158 3|233 4|45 5|8 The shape of the resulting display looks something like a bar graph oriented vertically. By examining the stemplot, you can determine certain properties of the data. <span>You can find the median by counting from either end of the stemplot until you find its center. Here, since there are 12 numbers, the center lies between 28 and 32. The median is the average of the two data points: (28+32)/2 = 30.) You can also determine if
2|0158 3|233 4|45 5|8 The shape of the resulting display looks something like a bar graph oriented vertically. By examining the stemplot, you can determine certain properties of the data. <span>You can find the median by counting from either end of the stemplot until you find its center. Here, since there are 12 numbers, the center lies between 28 and 32. The median is the average of the two data points: (28+32)/2 = 30.) You can also determine if
Flashcard 1645014551820
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itHarmonic Mean The harmonic mean of n numbers x i (where i = 1, 2, ..., n) is: The special cases of n = 2 and n = 3 are given by: and so on.
Original toplevel document
Subject 4. Measures of Center Tendency, therefore, is not recommended for use as the only measure of central tendency. A further disadvantage of the mode is that many distributions have more than one mode. These distributions are called "multimodal." <span>Harmonic Mean The harmonic mean of n numbers x i (where i = 1, 2, ..., n) is: The special cases of n = 2 and n = 3 are given by: and so on. For n = 2, the harmonic mean is related to arithmetic mean A and geometric mean G by: The mean, median, and mode are equal in symmetric distributions. The mean is higher than the median in positively skewed distributions and lower than the median in negatively skewed dist
Flashcard 1645233966348
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1645250743564
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Lesson 1. Sample space
e first step, namely, the description of the possible outcomes of the experiment. So we carry out an experiment. For example, we flip a coin. Or maybe we flip five coins simultaneously. Or maybe we roll a die. <span>Whatever that experiment is, it has a number of possible outcomes, and we start by making a list of the possible outcomes-- or, a better word, instead of the word "list", is to use the word "set", which has a more formal mathematical meaning. So we create a set that we usually denote by capital omega. That set is called the sample
e first step, namely, the description of the possible outcomes of the experiment. So we carry out an experiment. For example, we flip a coin. Or maybe we flip five coins simultaneously. Or maybe we roll a die. <span>Whatever that experiment is, it has a number of possible outcomes, and we start by making a list of the possible outcomes-- or, a better word, instead of the word "list", is to use the word "set", which has a more formal mathematical meaning. So we create a set that we usually denote by capital omega. That set is called the sample
Flashcard 1645253102860
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Lesson 1. Sample space
ng a list of the possible outcomes-- or, a better word, instead of the word "list", is to use the word "set", which has a more formal mathematical meaning. So we create <span>a set that we usually denote by capital omega. That set is called the sample space and is the set of all possible outcomes of our experiment. The elements of that set should have certa
ng a list of the possible outcomes-- or, a better word, instead of the word "list", is to use the word "set", which has a more formal mathematical meaning. So we create <span>a set that we usually denote by capital omega. That set is called the sample space and is the set of all possible outcomes of our experiment. The elements of that set should have certa
Flashcard 1645296094476
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 2. Unconditional, Conditional, and Joint Probabilities
total more than 8 (6,3; 6,4; 6,5; 6,6). The probability of a total greater than 8, given that the first dice is 6, is therefore 4/6 = 2/3. More formally, this probability can be written as: P(total>8 | Dice 1 = 6) = 2/3. In this equation, <span>the expression to the left of the vertical bar represents the event and the expression to the right of the vertical bar represents the condition. Thus, it would be read as "The probability that the total is greater than 8, given that Dice 1 is 6, is 2/3." In more abstract form, P(A|B) is the probability of event A given
total more than 8 (6,3; 6,4; 6,5; 6,6). The probability of a total greater than 8, given that the first dice is 6, is therefore 4/6 = 2/3. More formally, this probability can be written as: P(total>8 | Dice 1 = 6) = 2/3. In this equation, <span>the expression to the left of the vertical bar represents the event and the expression to the right of the vertical bar represents the condition. Thus, it would be read as "The probability that the total is greater than 8, given that Dice 1 is 6, is 2/3." In more abstract form, P(A|B) is the probability of event A given
Flashcard 1645424020748
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 2. Unconditional, Conditional, and Joint Probabilities
nction of two random variables, X and Y, gives the probability of joint occurrences of the values of X and Y. If we know the conditional probability P(A|B) and we want to know the joint probability P(AB), we can use the following <span>multiplication rule for probabilities: P(AB) = P(A|B) x P(B) Example 1 If someone draws a card at random from a deck and then, without replacing the first card, draws a second card, what is the probability that both card
nction of two random variables, X and Y, gives the probability of joint occurrences of the values of X and Y. If we know the conditional probability P(A|B) and we want to know the joint probability P(AB), we can use the following <span>multiplication rule for probabilities: P(AB) = P(A|B) x P(B) Example 1 If someone draws a card at random from a deck and then, without replacing the first card, draws a second card, what is the probability that both card
Flashcard 1645888277772
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 3. Addition Rule for Probabilities: the Probability that at Least One of Two Events Will Occur
use of the word "or," the key to this rule. The "or" is what we call an "inclusive or." In other words, either one event can occur or both events can occur. Such probabilities are calculated using the <span>addition rule for probabilities. P(A or B) = P(A) + P(B) - P(AB) The logic behind this formula is that when P(A) and P(B) are added, the occasions on which A and B both occur are counted twice. To adjust for this, P(AB) is subtracted. &#
use of the word "or," the key to this rule. The "or" is what we call an "inclusive or." In other words, either one event can occur or both events can occur. Such probabilities are calculated using the <span>addition rule for probabilities. P(A or B) = P(A) + P(B) - P(AB) The logic behind this formula is that when P(A) and P(B) are added, the occasions on which A and B both occur are counted twice. To adjust for this, P(AB) is subtracted. &#
Flashcard 1645908725004
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 4. Multiplication Rule for Independent Events
ffect the probability of getting heads on the second flip. Therefore, the event of getting heads on the second flip is independent of the event of getting heads on the first flip. When two events are not independent, they must be <span>dependent: the occurrence of one is related to the probability of the occurrence of the other. If we are trying to forecast one event, information about a dependent event will be useful but information about an independent event will not be useful. Examp
ffect the probability of getting heads on the second flip. Therefore, the event of getting heads on the second flip is independent of the event of getting heads on the first flip. When two events are not independent, they must be <span>dependent: the occurrence of one is related to the probability of the occurrence of the other. If we are trying to forecast one event, information about a dependent event will be useful but information about an independent event will not be useful. Examp
Flashcard 1646937115916
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itFactor, in mathematics, a number or algebraic expression that divides another number or expression evenly—i.e., with no remainder.
Original toplevel document
https://www.google.com.mx/search?q=factor%2Bmeaning%2Bmathematics&rlz=1C5CHFA_enMX588MX588&oq=factor%2Bmeaning%2Bmathematics&aqs=chrome..69i57j0.5916j0j1&sourceid=chrome&ie=UTF-8istorySearch help Tools Any time Any time Past hour Past 24 hours Past week Past month Past year Custom range... Customised date range From To All results All results Verbatim About 24,400,000 results (0.52 seconds) Search Results <span>Factor, in mathematics, a number or algebraic expression that divides another number or expression evenly—i.e., with no remainder. For example, 3 and 6 are factors of 12 because 12 ÷ 3 = 4 exactly and 12 ÷ 6 = 2 exactly. factor | mathematics | Britannica.com https://www.britannica.com/topic/factor-mathematics
Flashcard 1647755267340
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1648902409484
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1648908176652
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1648998092044
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1652306873612
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Expected value
Variance is a number greater than or equal to 0 because it is the sum of squared terms. If variance is 0, there is no dispersion or risk. The outcome is certain, and the quantity X is not random at all. Variance greater than 0 indicates dispersion of outcomes. Increasing variance indicates increasing dispersion, all else
Flashcard 1652322077964
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itRegarding counting, there can never be more combinations than permutations for the same problem, because permutations take into account all possible orderings of items, whereas combinations do not.
Original toplevel document
Subject 10. Principles of Countinghe ten stocks you are analyzing and invest $10,000 in one stock and $20,000 in another stock, how many ways can you select the stocks? Note that the order of your selection is important in this case. 10 P 2 = 10!/(10 - 2)! = 90 <span>Note that there can never be more combinations than permutations for the same problem, because permutations take into account all possible orderings of items, whereas combinations do not. <span><body><html>
Flashcard 1652342263052
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open it>A combination is a listing in which the order of listing does not matter. This describes the number of ways that we can choose r objects from a total of n objects, where the order in which the r objects is listed does not matter (The combination formula, or the binomial formula): <body><html>
Original toplevel document
Subject 10. Principles of Countingnlike the multiplication rule, factorial involves only a single group. It involves arranging items within a group, and the order of the arrangement does matter. The arrangement of ABCDE is different from the arrangement of ACBDE. <span>A combination is a listing in which the order of listing does not matter. This describes the number of ways that we can choose r objects from a total of n objects, where the order in which the r objects is listed does not matter (The combination formula, or the binomial formula): For example, if you select two of the ten stocks you are analyzing, how many ways can you select the stocks? 10! / [(10 - 2)! x 2!] = 45. &
Flashcard 1652353535244
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Open it
To analyze a portfolio’s expected return and variance of return, we must understand these quantities are a function of characteristics of the individual securities’ returns. Looking at the dispersion or variance of portfolio return, we see that the way individual security returns move together or covary is important. To understand the significance of these movements, we need to explore some new concepts, covariance and correlation.
Flashcard 1652396002572
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Counting
question. Do I want to count the number of ways to apply one of three or more labels to each member of a group? If the answer is yes, use the multinomial formula. If the answer is no, go to the fourth question. <span>Do I want to count the number of ways that I can choose r objects from a total of n, when the order in which I list the r objects does not matter (can I give the r objects a label)? If the answer to these questions is yes, the combination formula applies. If the answer is no, go to the fifth question. Do I want to count the number of ways I can choose r objects from a total of n, when the order in which I list the r objec
Flashcard 1655394143500
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 1. Basic Definitions
rn depends on the desired number of decimal spaces. Statistics computed from discrete variables are continuous. The mean on a five-point scale could be 3.117 even though 3.117 is not possible for an individual score. <span>For any random variable, it is necessary to know two things: the list of all possible values that the random variable can take on. the probability of each value occurring. These give a probability distribution. The first item on the list is called the range. With regard to the range of possible outcomes of a specified random variable: &#
rn depends on the desired number of decimal spaces. Statistics computed from discrete variables are continuous. The mean on a five-point scale could be 3.117 even though 3.117 is not possible for an individual score. <span>For any random variable, it is necessary to know two things: the list of all possible values that the random variable can take on. the probability of each value occurring. These give a probability distribution. The first item on the list is called the range. With regard to the range of possible outcomes of a specified random variable: &#
Flashcard 1656383212812
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Subject 4. Measures of Center Tendency
thmetic mean computation. A data set has only one arithmetic mean. This indicates that the mean is unique. The arithmetic mean is the only measure of central tendency where the sum of the deviations of each value from the mean is always zero. <span>Deviation from the arithmetic mean is the distance between the mean and an observation in the data set. The arithmetic mean has the following disadvantages: The mean can be affected by extremes, that is, unusually large or small values. The mean cannot be determi
Flashcard 1706274983180
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itThe role of financial reporting is to provide information about a company's financial position and performance for use by parties both internal and external to the company.
Original toplevel document
Subject 1. The Roles of Financial Reporting and Financial Statement AnalysisThe role of financial reporting is to provide information about a company's financial position and performance for use by parties both internal and external to the company. Financial statements are issued by management, who is responsible for their form and content. The role of financial statement analysis, on the other hand, is to take these
Flashcard 1706416540940
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itIf the company can invest elsewhere and earn a return of r, or if the company can repay its sources of capital and save a cost of r, then r is the company’s opportunity cost of funds.
Original toplevel document
3. BASIC PRINCIPLES OF CAPITAL BUDGETINGhe “required rate of return.” The required rate of return is the discount rate that investors should require given the riskiness of the project. This discount rate is frequently called the “opportunity cost of funds” or the “cost of capital.” <span>If the company can invest elsewhere and earn a return of r, or if the company can repay its sources of capital and save a cost of r, then r is the company’s opportunity cost of funds. If the company cannot earn more than its opportunity cost of funds on an investment, it should not undertake that investment. Unless an investment earns more than the cost of funds from
Flashcard 1706419424524
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itFinancial statements are issued by management, who is responsible for their form and content.
Original toplevel document
Subject 1. The Roles of Financial Reporting and Financial Statement AnalysisThe role of financial reporting is to provide information about a company's financial position and performance for use by parties both internal and external to the company. Financial statements are issued by management, who is responsible for their form and content. The role of financial statement analysis, on the other hand, is to take these financial statements and other information to evaluate the company's past, current, and prosp
Flashcard 1706423094540
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itLiquidity refers to the "nearness to cash" of assets and liabilities, or having enough cash available to pay debts when they are due.
Original toplevel document
Subject 2. Major Financial Statementscreditors. Equity ownership is the owner's investments and the total earnings retained from the commencement of the company. Equity represents the source of financing provided to the company by the owners. <span>Cash Flow Statement The primary purpose of the cash flow statement is to provide information about a company's cash receipts and cash payments during a period. It reports the cash receipts and cash outflows classified according to operating, investment, and financing activities. The cash flow statement is useful because it provides answers to the following simple yet important questions: Where did the cash come from during the period? What was the cash used for during the period? What was the change in the cash balance during the period? The statement's value is that it helps users evaluate liquidity, solvency, and financial flexibility. Liquidity refers to the "nearness to cash" of assets and liabilities, or having enough cash available to pay debts when they are due. Solvency refers to the company's ability to pay its debts as they mature. Cash flows reflect the company's liquidity and long-term solvency. Financial flexibility refers to a company's ability to respond and adapt to financial adversity and unexpected needs and opportunities. For example, cash flow information can be used to evaluate the effects of major investment and financing decisions. The details of income statements, balance sheets and cash flow statements will be covered in Study Session 8. Statement of Changes in Owners' Equity This statement reports the amounts and sources of changes in equity from capital transactions with owners.
Flashcard 1708344872204
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1708347755788
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1708349590796
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1708445273356
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1708447370508
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1708457594124
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1708460739852
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1708467293452
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1708469128460
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1708523916556
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1708526537996
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1708780555532
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Introduction
Weak CG is a common thread found in many company failures. A lack of proper oversight by the board of directors, inadequate protection for minority shareholders, and incentives at companies that promote excessive risk taking are a few examples
Weak CG is a common thread found in many company failures. A lack of proper oversight by the board of directors, inadequate protection for minority shareholders, and incentives at companies that promote excessive risk taking are a few examples
Flashcard 1708782914828
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Introduction
Weak CG is a common thread found in many company failures. A lack of proper oversight by the board of directors, inadequate protection for minority shareholders, and incentives at companies that promote excessive risk taking are a few examples of problems. Poor corporate governance practices have been cited as significantly contributing to the 2008–2009 global financial crisis. In response to these company failures, regulations
Weak CG is a common thread found in many company failures. A lack of proper oversight by the board of directors, inadequate protection for minority shareholders, and incentives at companies that promote excessive risk taking are a few examples of problems. Poor corporate governance practices have been cited as significantly contributing to the 2008–2009 global financial crisis. In response to these company failures, regulations
Flashcard 1708785274124
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Introduction
ommon thread found in many company failures. A lack of proper oversight by the board of directors, inadequate protection for minority shareholders, and incentives at companies that promote excessive risk taking are a few examples of problems. <span>Poor corporate governance practices have been cited as significantly contributing to the 2008–2009 global financial crisis. In response to these company failures, regulations have been introduced to promote stronger governance practices and protect financial markets and investors. Academics, polic
ommon thread found in many company failures. A lack of proper oversight by the board of directors, inadequate protection for minority shareholders, and incentives at companies that promote excessive risk taking are a few examples of problems. <span>Poor corporate governance practices have been cited as significantly contributing to the 2008–2009 global financial crisis. In response to these company failures, regulations have been introduced to promote stronger governance practices and protect financial markets and investors. Academics, polic
Flashcard 1710316981516
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1710318816524
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1710320651532
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1710323272972
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1710325107980
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1710335593740
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itAlthough retrievals are the key to moving conceptual learning into memory, repetition is the key for habit design.
Original toplevel document
Unknown titleas links to TED Talks, articles, and assignments to further hone their skills. This blended approach allows me to create three retrievals spaced with sleep, and it also starts to build the habits of the behaviors I am trying to cultivate. <span>Tip #6: Be a habit designer Ultimately, the goal of most learning activities is behavior change. No matter the topic, we are trying to elicit new and better behaviors in the learner. Charles Duhigg's The Power of Habit changed the way I see my work. He shares the science of how the basal ganglia in the brain builds habit loops that include a cue or trigger, the routine of behavior, and the reward for completing that routine. Over time, habits become well-grooved neural pathways that almost happen on autopilot, for example how you currently log in to your computer or how you get to work. When we are trying to create behavior change, we need to think about the habits that are currently in place and how to design new, better habits that will be more compelling than the comfort of the current ones. I now think of myself as a habit designer. All of my learning design starts with identifying the habit loop I hope to instill, and I work backward from there. Although retrievals are the key to moving conceptual learning into memory, repetition is the key for habit design. The more we fire neurons together, the stronger that neural pathway becomes, to the point that researchers can measure the neurons growing thicker. As talent development professionals, we are in the business of cultivating potential. Your organization as a whole—as well as every person in it—have unrealized ability, and your job is to cultivate that potential through the learning experiences you create. Work with the natural processes of the brain and nervous system to maximize the impact of your great work. Brain Science Resources Brain science is a burgeoning field and, within it, you will find a wide range of defined specialties from neurology to psychology to biology. This is a lis
Flashcard 1713011821836
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1713608985868
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itHTML consists of a series of elements, which you use to enclose, wrap, or mark up different parts of the content to make it appear or act a certain way.
Original toplevel document
Getting started with HTML - Learn web development | MDNis HTML? HTML (Hypertext Markup Language) is not a programming language; it is a markup language used to tell your browser how to structure the webpages you visit. It can be as complicated or as simple as the web developer wishes it to be. <span>HTML consists of a series of elements, which you use to enclose, wrap, or mark up different parts of the content to make it appear or act a certain way. The enclosing tags can make a bit of content into a hyperlink to link to another page on the web, italicize words, and so on. For example, take the following line of content: My cat
Flashcard 1713611345164
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itThe main parts of our element are: The opening tag: This consists of the name of the element (in this case, p), wrapped in opening and closing angle brackets . This states where the element begins, or starts to take effect — in this case where the start of the paragraph is. The closing tag: This is the same as the opening tag, except that it includes a forward slash before the element name. This states where the element ends — in this case where the end of the paragraph is. Failing to include a closing tag is a common beginner error and can lead to strange results. The content: This is the content of the element, which in this case is just text. The element: The opening tag plus the closing tag plus the content equals the element.
Original toplevel document
Getting started with HTML - Learn web development | MDNd by itself, we could specify that it is a paragraph by enclosing it in a paragraph tag (
) element:
My cat is very grumpy
Anatomy of an HTML element Let's explore our paragraph element a bit further: The main parts of our element are: The opening tag: This consists of the name of the element (in this case, p), wrapped in opening and closing angle brackets . This states where the element begins, or starts to take effect — in this case where the start of the paragraph is. The closing tag: This is the same as the opening tag, except that it includes a forward slash before the element name. This states where the element ends — in this case where the end of the paragraph is. Failing to include a closing tag is a common beginner error and can lead to strange results. The content: This is the content of the element, which in this case is just text. The element: The opening tag plus the closing tag plus the content equals the element. Active learning: creating your first HTML element Edit the line below in the Input area by wrapping it with the tags and (put before it to openFlashcard 1713613704460
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itThe main parts of our element are: The opening tag: This consists of the name of the element (in this case, p), wrapped in opening and closing angle brackets . This states where the element begins, or starts to take effect — in this case where the start of the paragraph is. The closing tag: This is the same as the opening tag, except that it includes a forward slash before the element name. This states where the element ends — in this case where the end o
Original toplevel document
Getting started with HTML - Learn web development | MDNd by itself, we could specify that it is a paragraph by enclosing it in a paragraph tag (
) element:
My cat is very grumpy
Anatomy of an HTML element Let's explore our paragraph element a bit further: The main parts of our element are: The opening tag: This consists of the name of the element (in this case, p), wrapped in opening and closing angle brackets . This states where the element begins, or starts to take effect — in this case where the start of the paragraph is. The closing tag: This is the same as the opening tag, except that it includes a forward slash before the element name. This states where the element ends — in this case where the end of the paragraph is. Failing to include a closing tag is a common beginner error and can lead to strange results. The content: This is the content of the element, which in this case is just text. The element: The opening tag plus the closing tag plus the content equals the element. Active learning: creating your first HTML element Edit the line below in the Input area by wrapping it with the tags and (put before it to openFlashcard 1713616063756
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itThe opening tag: This consists of the name of the element (in this case, p), wrapped in opening and closing angle brackets . This states where the element begins, or starts to take effect — in this case where the start of the paragraph is. <span>The closing tag: This is the same as the opening tag, except that it includes a forward slash before the element name. This states where the element ends — in this case where the end of the paragraph is. Failing to include a closing tag is a common beginner error and can lead to strange results. The content: This is the content of the element, which in this case is just text. The element: The opening tag plus the closing tag plus the content equals the element.<span><
Original toplevel document
Getting started with HTML - Learn web development | MDNd by itself, we could specify that it is a paragraph by enclosing it in a paragraph tag (
) element:
My cat is very grumpy
Anatomy of an HTML element Let's explore our paragraph element a bit further: The main parts of our element are: The opening tag: This consists of the name of the element (in this case, p), wrapped in opening and closing angle brackets . This states where the element begins, or starts to take effect — in this case where the start of the paragraph is. The closing tag: This is the same as the opening tag, except that it includes a forward slash before the element name. This states where the element ends — in this case where the end of the paragraph is. Failing to include a closing tag is a common beginner error and can lead to strange results. The content: This is the content of the element, which in this case is just text. The element: The opening tag plus the closing tag plus the content equals the element. Active learning: creating your first HTML element Edit the line below in the Input area by wrapping it with the tags and (put before it to openFlashcard 1713618423052
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itexcept that it includes a forward slash before the element name. This states where the element ends — in this case where the end of the paragraph is. Failing to include a closing tag is a common beginner error and can lead to strange results. <span>The content: This is the content of the element, which in this case is just text. The element: The opening tag plus the closing tag plus the content equals the element.<span><body><html>
Original toplevel document
Getting started with HTML - Learn web development | MDNd by itself, we could specify that it is a paragraph by enclosing it in a paragraph tag (
) element:
My cat is very grumpy
Anatomy of an HTML element Let's explore our paragraph element a bit further: The main parts of our element are: The opening tag: This consists of the name of the element (in this case, p), wrapped in opening and closing angle brackets . This states where the element begins, or starts to take effect — in this case where the start of the paragraph is. The closing tag: This is the same as the opening tag, except that it includes a forward slash before the element name. This states where the element ends — in this case where the end of the paragraph is. Failing to include a closing tag is a common beginner error and can lead to strange results. The content: This is the content of the element, which in this case is just text. The element: The opening tag plus the closing tag plus the content equals the element. Active learning: creating your first HTML element Edit the line below in the Input area by wrapping it with the tags and (put before it to openFlashcard 1713702571276
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Parent (intermediate) annotation
Open itthe element ends — in this case where the end of the paragraph is. Failing to include a closing tag is a common beginner error and can lead to strange results. The content: This is the content of the element, which in this case is just text. <span>The element: The opening tag plus the closing tag plus the content equals the element.<span><body><html>
Original toplevel document
Getting started with HTML - Learn web development | MDNd by itself, we could specify that it is a paragraph by enclosing it in a paragraph tag (
) element:
My cat is very grumpy
Anatomy of an HTML element Let's explore our paragraph element a bit further: The main parts of our element are: The opening tag: This consists of the name of the element (in this case, p), wrapped in opening and closing angle brackets . This states where the element begins, or starts to take effect — in this case where the start of the paragraph is. The closing tag: This is the same as the opening tag, except that it includes a forward slash before the element name. This states where the element ends — in this case where the end of the paragraph is. Failing to include a closing tag is a common beginner error and can lead to strange results. The content: This is the content of the element, which in this case is just text. The element: The opening tag plus the closing tag plus the content equals the element. Active learning: creating your first HTML element Edit the line below in the Input area by wrapping it with the tags and (put before it to openFlashcard 1716397935884
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1716399508748
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1716404751628
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1716408159500
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1716410518796
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1716413140236
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1716415761676
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1716420480268
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1716425461004
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1716430703884
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1716433587468
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1716435946764
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1716438306060
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1716440665356
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1716443548940
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1716445908236
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1716448791820
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1716451151116
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |
Flashcard 1716454034700
| status | not learned | measured difficulty | 37% [default] | last interval [days] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| repetition number in this series | 0 | memorised on | scheduled repetition | ||||
| scheduled repetition interval | last repetition or drill |